Cho A = 2x2 - 4x + 3
CMR: A > 0 với mọi số thực x
CMR:
a) 4x^2-6x+9>0 với mọi số thực x
b) x^2+2y^2-2xy+y+1>0 với mọi số thực x,y
a. Ta có : \(4x^2-6x+9=4x^2-6x+\dfrac{9}{4}+\dfrac{27}{4}\)
\(=\left[\left(2x\right)^2-6x+\left(\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2\right]+\dfrac{27}{4}\)
\(=\left(2x-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{27}{4}\)
Vì \(\left(2x-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2\ge0\forall x\)
nên \(\left(2x-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{27}{4}\ge\dfrac{27}{4}>0\forall x\)
b.Ta có : \(x^2+2y^2-2xy+y+1=\left(x^2+y^2-2xy\right)+\left(y^2+y+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)+\dfrac{3}{4}\)
\(=\left(x-y\right)^2+\left(y+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\)
Vì \(\left(x-y\right)^2\ge0\forall x;y\)
\(\left(y+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2\ge0\forall y\)
nên \(\left(x-y\right)^2+\left(y+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{1}{2}\ge\dfrac{1}{2}>0\forall x;y\)
Chứng minh rằng:
a, x^2-4x>-5 với mọi số thực x
b, Chứng minh 2x^2+4y^2-4x-4xy+5>0 với mọi số thực x;y
a) Xét \(x^2-4x+4=\left(x-2\right)^2\ge0\)
<=> \(x^2-4x\ge-4>-5\)
b) \(2x^2+4y^2-4x-4xy+5\)
= \(\left(x^2-4x+4\right)+\left(x^2-4xy+4y^2\right)+1\)
= \(\left(x-2\right)^2+\left(x-2y\right)^2+1\ge1>0\)
Có bao nhiêu giá trị nguyên của tham số m để phương trình m x 2 + 2 x 3 − 2 x 2 − 4 x + 2 = 0 có nghiệm đúng với mọi x ≤ − 3 ?
A. 4
B. Không có giá trị nào của m
C. Vô số giá trị của m
D. 6
Đáp án C
Phương trình
⇔ m x 2 + 2 x 3 − 2 x 2 + 2 x + 2 = 0 → t = x 2 + 2 x m t 3 − 2 t + 2 = 0 1
Ta có f x = x 2 + 2 x , x ≤ − 3 ⇒ f x ≥ 3 ⇒ t ∈ 3 ; + ∞
Khi đó 1 ⇔ m = 2 t 2 − 2 t 3 = f t với t ∈ 3 ; + ∞
Có f ' t = − 4 t 3 + 6 t 4 ⇒ f t nghịch biến trên 3 ; + ∞ ⇒ max 3 ; + ∞ f x ≤ f 3 = 4 27
Suy ra m ≤ max 3 ; + ∞ f x = 4 27 ⇒ có vô số nghiệm giá trị của m
Cm rằng : A= x2 + y2 - 4x +2y +7 > 0 với mọi số thực x, y
\(A=x^2+y^2-4x+2y+7\)
\(=x^2+y^2-4x+2y+4+1+3\)
\(=\left(x^2-4x+4\right)+\left(y^2+2y+1\right)+3\)
\(=\left(x-2\right)^2+\left(y+1\right)^2+3\)
Ta thấy: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(x-2\right)^2\ge0\forall x\\\left(y+1\right)^2\ge0\forall y\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2+\left(y+1\right)^2\ge0\forall x,y\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2+\left(y+1\right)^2+3\ge3>0\forall x,y\)
A= x2+y2-4x+2y+7
= (x2-4x+4)+(y2+2y+1)+2
= (x-2)2+(y+1)2+2
Ta thấy: (x-2)2\(\ge0\)
(y+1)2\(\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow\)(x-2)2+(y+1)2+2\(\ge2\)
\(\Rightarrow\)A\(\ge2\)
Vậy A>0 \(\forall x,y\)
\(A=x^2+y^2-4x+2y+7\)
\(=x^2+y^2-4x+2y+4+1+2\)
\(=\left(x^2-4x+4\right)+\left(y^2+2y+1\right)+2\)
\(=\left(x-2\right)^2+\left(y+1\right)^2+2\)
Ta thấy: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(x-2\right)^2\ge0\forall x\\\left(y+1\right)^2\ge0\forall y\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2+\left(y+1\right)^2\ge0\forall x,y\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2+\left(y+1\right)^2+2\ge2>0\forall x,y\)
Mệnh đề phủ định của mệnh đề: "Với mọi số thực x, x² > 0" là
A. Với mọi số thực x, x² ≤ 0 B. Tồn tại số thực x, x² < 0
C. Tồn tại số thực x, x² ≤ 0 D. Với mọi số thực x, x² < 0
Cho biểu thức : P = x 2 - 2 x 2 x 2 + 8 - 2 x 2 8 - 4 x + 2 x 2 - x 3 1 - 1 x - 2 x 2 x ≠ 0 , x ≠ 2
a) Rút gọn biểu thức P
b) Tính giá trị biểu thức P với x = 1/2
a) Ta có: 2x2 + 8 = 2(x2 + 4).
8 – 4x + 2x2 – x3
= (8 – x3) - ( 4x - 2x2)
= (2 – x).(4 + 2x + x2) - 2x.(2 - x)
= (2 – x).(4 + 2x + x2 – 2x)
= (2 - x). (4 + x2 )
* Do đó:
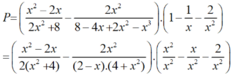
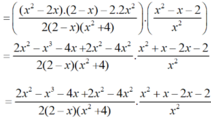
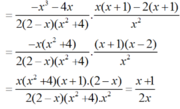
b) Tại x = 1 2 hàm số đã cho xác định nên thay x = 1 2 vào biểu thức rút gọn của P ta được:
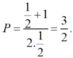
a) Tìm số a để đa thức x² + 5x + a chia hết cho đa thức x - 1
b) Chứng minh rằng: x² – x + 1 > 0 với mọi số thực x?
c) Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức A = x² – 6x + 11
d) Tìm giá trị lớn nhất của biểu thức B = – x² + 4x – 5
b: \(x^2-x+1=x^2-2\cdot x\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{3}{4}=\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}>0\forall x\)
c: \(A=x^2-6x+9+2=\left(x-3\right)^2+2\ge2\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x=3
d: \(B=-\left(x^2-4x+5\right)=-\left(x^2-4x+4+1\right)=-\left(x-2\right)^2-1\le-1\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x=2
a)chứng minh rằng x-x^2-1<0 với mọi số thực x
b)tìm gtnn của đa thức sau:f(x)=x^2-4x+9
\(-x^2+x-1=--\left(x^2-x+\frac{1}{4}\right)-\frac{3}{4}=-\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2-\frac{3}{4}< 0\)
\(f\left(x\right)=x^2-4x+4+5=\left(x-2\right)^2+5\ge5\)
\(f\left(x\right)_{min}=5\) khi \(x=2\)
CMR với mọi số thực x ta luôn có : x^2-6x+15>0
Làm phép tính
a,(5x-2y)(4x+3y)
Ta có:
x2-6x+15=(x2-6x+9)+6=(x-3)2+6 lớn hơn hoặc bằng 6
Vậy x2-6x+15 >0