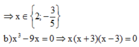Tìm x , biết :
a) x^3 - 9x = 0
b) x^2 - 5x - 6 = 0

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Tìm x biết:
a) 5x(x – 2) + 3x – 6 = 0
b) x 3 – 9 x = 0
tìm x, biết:
a)x^2+3x=0
b)x.(x-7).(x+7)=0
c)x^3-9x=0
d)x^2-5x-6=0
a) x^2+3x=0
<=> x(x+3)=0
<=> x+3=0
---> X=-3
b)x.(x-7).(x+7)=0
<=>x.(x^2-7^2)=0
<=> X^2-7^2=0
==>x= 7 và x=-7
c) x^3-9x=0
<=> x(x^2-3^2)=0
<=> x^2-3^2=0
~~> x = 3 và x=-3
d) x^2-5x-6=0
<=> x^2-5x-5-1=0
<=> (x^2-1)-(5x-5) =0
<=> x(x-1) - 5(x-1)=0
<=> (x-1)(x-5)=0
~~> x-1 = 0 ~> x=1
~~> x-5=0 ~~> x=5
Vậy x=1 và x=5
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm x biết
a.\(5x\left(x-2\right)+3x-6=0\)
b.\(x^3-9x=0\)
a)5x(x-2)+3x-6=0
5x(x-2)+3(x-2)=0
(5x+3)(x-2)=0
=> 5x+3=0 hoặc x-2=0
5x=-3 x=0+2
x=-3/5 x=2
Vậy x=-3/5 hoặc x=2
b)x3-9x=0
x(x2-9)=0
=>x=0 hoặc x2-9=0
x2=9
=>x=3 hoặc x=-3
Vậy x=0 hoặc x=3 hoặc x=-3
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a) 5x(x - 2) + 3x - 6 = 5x(x - 2) + 3(x - 2) = (5x + 3)(x - 2) = 0 =>\(\orbr{\begin{cases}5x+3=0\\x-2=0\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-0,6\\x=2\end{cases}}}\)
b) x3 - 9x = x(x2 - 9) = x(x - 3)(x + 3) => x = 0 hoặc x - 3 = 0 hay x + 3 = 0 =>\(x\in\left\{-3;0;3\right\}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a , 5 x ( x - 2 ) + 3 x - 6 = 0
5 x ( x - 2 ) + 3 ( x - 2 ) = 0
( 5 x + 3 ) ( x - 2 ) = 0
=> 5 x + 3 = 0 hoặc x - 2 = 0
5 x = -3 x = 0 + 2
x = \(\frac{-3}{5}\) x = 2
Vậy x = \(\frac{-3}{5}\)hoặc x = 2
b , x 3 - 9 x = 0
x ( x 2 - 9 ) = 0
x ( x 2 - 3 2 ) = 0
x ( x - 3 ) ( x + 3 ) = 0
=> x = 0 hoặc x - 3 = 0 hoặc x + 3 = 0
x = 3 x = -3
Vậy x = 0 hoặc x = 3 hoặc x = -3
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
b2 tìm x
a)x^2-4x-5=0
b)5x^2-9x-2=0
c)(x^2+1)-5(x^2+1)+6=0
d)(x^2+6x)-2(x+3)^2-17=0
Lời giải:
a. $x^2-4x-5=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x+1)(x-5)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x+1=0$ hoặc $x-5=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=-1$ hoặc $x=5$
b.
$5x^2-9x-2=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-2)(5x+1)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x-2=0$ hoặc $5x+1=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=2$ hoặc $x=\frac{-1}{5}$
c.
$(x^2+1)-5(x^2+1)+6=0$
$\Leftrightarrow a^2-5a+6=0$ (đặt $x^2+1=a$)
$\Leftrightarrow (a-2)(a-3)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow a-2=0$ hoặc $a-3=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x^2-1=0$ hoặc $x^2-2=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-1)(x+1)=0$ hoặc $(x-\sqrt{2})(x+\sqrt{2})=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{\pm 1; \pm \sqrt{2}\right\}$
d.
$(x^2+6x)-2(x+3)^2-17=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x^2+6x+9)-2(x+3)^2-26=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x+3)^2-2(x+3)^2-26=0$
$\Leftrightarrow -(x+3)^2-26=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x+3)^2=-26<0$ (vô lý)
Do đó không tồn tại $x$ thỏa mãn.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Câu 2.(1,5 điểm) Tìm x, biết:
a) 5x(x2 – 9) 0. b) 3(x+3) - x2 - 3x 0. c) x2 – 9x – 10 0
Đọc tiếp
Câu 2.(1,5 điểm) Tìm x, biết:
a) 5x(x2 – 9) = 0. b) 3(x+3) - x2 - 3x =0. c) x2 – 9x – 10 = 0
\(a,5x\left(x^2-9\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x^2=9\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=3\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\\ b,3\left(x+3\right)-x^2-3x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow3\left(x+3\right)-x\left(x+3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+3\right)\left(3-x\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\\ c,x^2-9x-10=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2+x-10x-10=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(x+1\right)-10\left(x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-10\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=10\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
a, 5\(x\)(\(x^2\) - 9) = 0
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x^2-9=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=3\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\) \(\in\) { -3; 0; 3}
b, 3.(\(x+3\)) - \(x^2\) - 3\(x\) = 0
3.(\(x+3\)) - \(x\).( \(x\) + 3) = 0
(\(x+3\))( 3 - \(x\)) = 0
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\) \(\in\){ -3; 3}
c, \(x^2\) - 9\(x\) - 10 = 0
\(x^2\) + \(x\) - 10\(x\) - 10 = 0
\(x.\left(x+1\right)\) - 10.( \(x-1\)) = 0
(\(x+1\))(\(x-10\)) = 0
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+1=0\\x-10=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=10\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\) \(\in\){ -1; 10}
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a) 5x(x2-9)=0
=> TH1 5x=0
<=> x= 0
TH2: 2x-9=0
<=> 2x=9
<=> x = \(\dfrac{9}{2}\)
b, 3(x+3) - x2- 3x = 0
<=> 3x + 9 - x2 -3x = 0
<=> - x2 +9 = 0
<=> - x2 = -9
<=> x = 3
c, x2 -9x -10 = 0
<=> x2 -x + 10x -10 = 0
<=> x(x-1)+10(x-1)=0
<=> (x-1)(x+10)=0
=> TH1: x-1=0
<=> x=1
TH2: x +10=0
<=> x=-10
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Tìm x , biết :
a. \(\left(x-2\right)^3-\left(x-3\right)\left(x^2+3x+9\right)+6\left(x+1\right)^2=15\)
b. \(2x^3-50x=0\)
c.\(5x^2-4\left(x^2-2x+1\right)-5=0\)
d. \(x^3-x=0\)
e. \(27x^3-27x^2+9x-1=1\)
a) Ta có: \(\left(x-2\right)^3-\left(x-3\right)\left(x^2+3x+9\right)+6\left(x+1\right)^2=15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-6x^2+12x-8-x^3+27+6\left(x^2+2x+1\right)=15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x^2+12x+19+6x^2+12x+6=15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow24x+25=15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow24x=-10\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{5}{12}\)
b) Ta có: \(2x^3-50x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=5\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) Ta có: \(5x^2-4\left(x^2-2x+1\right)-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x^2-4x^2+8x-4-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+8x-9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+9\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-9\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
d) Ta có: \(x^3-x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=1\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
e) Ta có: \(27x^3-27x^2+9x-1=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x\right)^3-3\cdot\left(3x\right)^2\cdot1+3\cdot3x\cdot1^2-1^3=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)^3=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-1=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=2\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)
Tìm x biết:
a) 5x (x - 2) + 3x - 6 = 0
b) x 3 - 9x = 0
a) 5x( x - 2) + 3x - 6 =0
(=) 5x( x - 2) + 3( x - 2) = 0
(=) ( x - 2)( 5x + 3) =0
Vậy , x = 2 ; x = \(-\dfrac{3}{5}\)
b) x3 - 9x = 0
(=) x( x2 - 32) = 0
(=) x( x - 3)( x + 3) =0
Vậy , x = 0 ; x = 3 ; x = -3
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a \(5x\left(x-2\right)+3x-6=0\)
\(\Rightarrow5x\left(x-2\right)+3\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(5x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\5x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{-3}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b, \(x^3-9x=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(x^2-9\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x-3=0\\x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=3\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(a,5x\left(x-2\right)+3x-6=0\)
\(\Rightarrow5x\left(x-2\right)+3\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(5x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\5x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{3}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(b,x^3-9x=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(x^2-9\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(x^2-3^2\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x-3=0\\x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=3\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a) 5x + 6 = 0
b) 9x - 3 = 6x + 21
c) x^3 - 9x = 0
d) 1/x-2 - x^2 -4 /4-x^2= 0
a) 5x + 6 = 0
<=> 5x = -6
<=> x = \(-\frac{6}{5}\)
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm là: S = {\(-\frac{6}{5}\)}
b) 9x - 3 = 6x + 21
<=> 3x = 24
<=> x = 8
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm là: S = {8}
c) x3 - 9x = 0
<=> x(x2 - 9) = 0
<=> x(x - 3)(x + 3) = 0
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x-3=0\\x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\) <=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=3\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm là: S = {0; 3; -3}
d) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne2;x\ne-2\)
\(\frac{1}{x-2}-\frac{x^2-4}{4-x^2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{1}{x-2}+\frac{x^2-4}{x^2-4}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x+2+x^2-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x-x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\left(loại\right)\\x=1\left(TM\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm là: S ={1}
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a) 5x + 6 = 0
b) 9x - 3 = 6x + 21
c) x^3 - 9x = 0
d) 1/x-2 - x^2 -4 /4-x^2= 0
a) Ta có: 5x+6=0
⇔5x=-6
hay \(x=-\frac{6}{5}\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-\frac{6}{5}\right\}\)
b) Ta có: 9x-3=6x+21
⇔9x-6x=21+3
⇔3x=24
hay x=8
Vậy: S={8}
c) Ta có: \(x^3-9x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x^2-9\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x-3=0\\x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=3\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={-3;0;3}
d) ĐKXĐ: x∉{2;-2}
Ta có: \(\frac{1}{x-2}-\frac{x^2-4}{4-x^2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{1}{x-2}+\frac{4-x^2}{4-x^2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{1}{x-2}+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{1}{x-2}+\frac{x-2}{x-2}=0\)
Suy ra: \(1+x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1=0\)
hay x=1(tm)
Vậy: S={1}
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)