giải phương trình \(\sqrt[n]{\left(x-2\right)^2}+4\sqrt[n]{x^2-4}=5\sqrt[n]{\left(x+2\right)^2}\)

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Giải các phương trình sau:
a) \(\sqrt[n]{\left(x-2\right)^2}+4.\sqrt[n]{x^2-4}=5\sqrt[n]{\left(x+2\right)^2}\)
b) \(x+y+z=\sqrt{xy}+3\sqrt{y}+2\sqrt{x}\)
Giải pt :\(\sqrt[n]{\left(x-2\right)^2}+4\sqrt[n]{x^2-4}=5\sqrt[n]{\left(x+2\right)^2}\)
x=2 không phải là nghiệm nên ta chia cả hai vế của phương trình cho (x-2)2
\(5\sqrt[n]{\left(\frac{x+2}{x-2}\right)^2}-4\sqrt[n]{\frac{x+2}{x-2}}-1=0\)(1)
Đặt\(\sqrt[n]{\frac{x+2}{x-2}}=y\)thì (1)trở thành
\(5y^2-4y-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(y-1\right)\left(5y+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}y_1=1\\y_2=-\frac{1}{5}\end{cases}}\)
Xét \(y=1\Leftrightarrow\sqrt[n]{\frac{x+2}{x-2}}=1\)phương trình vô nghiệm
Xét \(y=-\frac{1}{5}\Leftrightarrow\sqrt[n]{\frac{x+2}{x-2}}=-\frac{1}{5}\)(2)
Nếu n chẵn thì (2) vô nghiệm
Nếu n lẻ thì (2)\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x+2}{x-2}=-\frac{1}{5^n}\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{2\left(1-5^n\right)}{1+5^n}\)
Tóm lại : Nếu n chẵn thì phương trình đã cho vô nghiệm
Nếu n lẻ thì phương trình có nghiệm \(x=\frac{2\left(1-5^n\right)}{1+5^n}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau:a 2sqrt[3]{left(x+2right)^2}-sqrt[3]{left(x-2right)^2}sqrt[3]{x^2-4}b sqrt[3]{left(65+xright)^2}+4sqrt[3]{left(65-xright)^2}5sqrt[3]{65^2-x^2}c sqrt[3]{x+1}+sqrt[3]{x+2}1+sqrt[3]{x^2+3x+2}d sqrt[3]{x-2}+sqrt[3]{x+3}sqrt[3]{2x+1}e sqrt[3]{2x-1}+sqrt[3]{x-1}sqrt[3]{3x+1}
Đọc tiếp
Giải các phương trình sau:
a \(2\sqrt[3]{\left(x+2\right)^2}-\sqrt[3]{\left(x-2\right)^2}=\sqrt[3]{x^2-4}\)
b \(\sqrt[3]{\left(65+x\right)^2}+4\sqrt[3]{\left(65-x\right)^2}=5\sqrt[3]{65^2-x^2}\)
c \(\sqrt[3]{x+1}+\sqrt[3]{x+2}=1+\sqrt[3]{x^2+3x+2}\)
d \(\sqrt[3]{x-2}+\sqrt[3]{x+3}=\sqrt[3]{2x+1}\)
e \(\sqrt[3]{2x-1}+\sqrt[3]{x-1}=\sqrt[3]{3x+1}\)
a.
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt[3]{x+2}=a\\\sqrt[3]{x-2}=b\end{matrix}\right.\) ta được:
\(2a^2-b^2=ab\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(a-b\right)\left(2a+b\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=b\\2a=-b\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a^3=b^3\\8a^3=-b^3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+2=x-2\left(vô-nghiệm\right)\\8\left(x+2\right)=-\left(x-2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{14}{9}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
b.
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt[3]{65+x}=a\\\sqrt[3]{65-x}=b\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow a^2+4b^2=5ab\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(a-b\right)\left(a-4b\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=b\\a=4b\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a^3=b^3\\a^3=64b^3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}65+x=65-x\\65+x=64\left(65-x\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow...\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
c.
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt[3]{x+2}=a\\\sqrt[3]{x+1}=b\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow a+b=1+ab\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(a-1\right)\left(b-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=1\\b=1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a^3=1\\b^3=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+2=1\\x+1=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow...\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
1) Giải hệ phương trìnhleft{{}begin{matrix}3x^2+xy-4x+2y2xleft(x+1right)+yleft(y+1right)4end{matrix}right.2) Giải phương trìnhsqrt{x^2-5x+4}+2sqrt{x+5}2sqrt{x-4}+sqrt{x^2+4x-5}3) Tính giá trị của biểu thứcA2x^3+3x^2-4x+2Với xsqrt{2+sqrt{dfrac{5+sqrt{5}}{2}}}+sqrt{2-sqrt{dfrac{5+sqrt{5}}{2}}}-sqrt{3-sqrt{5}}-14) Cho x, y thỏa mãn:sqrt{x+2014}+sqrt{2015-x}-sqrt{2014-x}sqrt{y+2014}+sqrt{2015-y}-sqrt{2014-y}Chứng minh xy
Đọc tiếp
1) Giải hệ phương trình
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x^2+xy-4x+2y=2\\x\left(x+1\right)+y\left(y+1\right)=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
2) Giải phương trình
\(\sqrt{x^2-5x+4}+2\sqrt{x+5}=2\sqrt{x-4}+\sqrt{x^2+4x-5}\)
3) Tính giá trị của biểu thức
\(A=2x^3+3x^2-4x+2\)
Với \(x=\sqrt{2+\sqrt{\dfrac{5+\sqrt{5}}{2}}}+\sqrt{2-\sqrt{\dfrac{5+\sqrt{5}}{2}}}-\sqrt{3-\sqrt{5}}-1\)
4) Cho x, y thỏa mãn:
\(\sqrt{x+2014}+\sqrt{2015-x}-\sqrt{2014-x}=\sqrt{y+2014}+\sqrt{2015-y}-\sqrt{2014-y}\)
Chứng minh \(x=y\)
Câu 4:
Giả sử điều cần chứng minh là đúng
\(\Rightarrow x=y\), thay vào điều kiện ở đề bài, ta được:
\(\sqrt{x+2014}+\sqrt{2015-x}-\sqrt{2014-x}=\sqrt{x+2014}+\sqrt{2015-x}-\sqrt{2014-x}\) (luôn đúng)
Vậy điều cần chứng minh là đúng
Đúng 7
Bình luận (3)
2) \(\sqrt{x^2-5x+4}+2\sqrt{x+5}=2\sqrt{x-4}+\sqrt{x^2+4x-5}\)
⇔ \(\sqrt{\left(x-4\right)\left(x-1\right)}-2\sqrt{x-4}+2\sqrt{x+5}-\sqrt{\left(x+5\right)\left(x-1\right)}=0\)
⇔ \(\sqrt{x-4}.\left(\sqrt{x-1}-2\right)-\sqrt{x+5}\left(\sqrt{x-1}-2\right)=0\)
⇔ \(\left(\sqrt{x-4}-\sqrt{x+5}\right)\left(\sqrt{x-1}-2\right)=0\)
⇔ \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x-4}-\sqrt{x+5}=0\\\sqrt{x-1}-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔ \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x-4}=\sqrt{x+5}\\\sqrt{x-1}=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔ \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\in\varnothing\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔ x = 5
Vậy S = {5}
Đúng 4
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1:
ĐKĐB suy ra $x(x+1)+y(y+1)=3x^2+xy-4x+2y+2$
$\Leftrightarrow 2x^2+x(y-5)+(y-y^2+2)=0$
Coi đây là PT bậc 2 ẩn $x$
$\Delta=(y-5)^2-4(y-y^2+2)=(3y-3)^2$Do đó:
$x=\frac{y+1}{2}$ hoặc $x=2-y$. Thay vào một trong 2 phương trình ban đầu ta thu được:
$(x,y)=(\frac{-4}{5}, \frac{-13}{5}); (1,1)$
Đúng 4
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Giải các phương trình sau: \(\left(\sqrt{x+5}-\sqrt{x+2}\right).\left(4+\sqrt{x^2+7x+10}\right)=6\)
Giải Phương Trình
\(\sqrt{\left(2x+3\right)^2}=5\)
\(\sqrt{9\left(x-2\right)^2}=18\)
\(\sqrt{9x-18}-\sqrt{4x-8}+3\sqrt{x-2}=40\)
\(\sqrt{4.\left(x-3\right)^2}=8\)
\(\sqrt{5x-6}-3=0\)
giải phương trình :
\(9\left(\sqrt{x+1}+\sqrt{x-2}\right)+1=4\left(\sqrt{\left(x+1\right)^3}-\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)^3}\right)\)
Giải phương trình: \(\sqrt{\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x+3\right)\left(x^4+5\right)\left(x+7\right)}=\sqrt{\left(x+2\right)\left(x^4+4\right)\left(x+6\right)\left(x^2+8\right)}\)
Giải phương trình:
a)\(\left(x+2\right)\cdot\left(x+4\right)+5\cdot\left(x+2\right)\cdot\sqrt{\frac{x+4}{x+2}}=6\)
b)\(\sqrt{2x+4+6\sqrt{2x-5}}+\sqrt{2x-4-2\sqrt{2x-5}}=4\)
















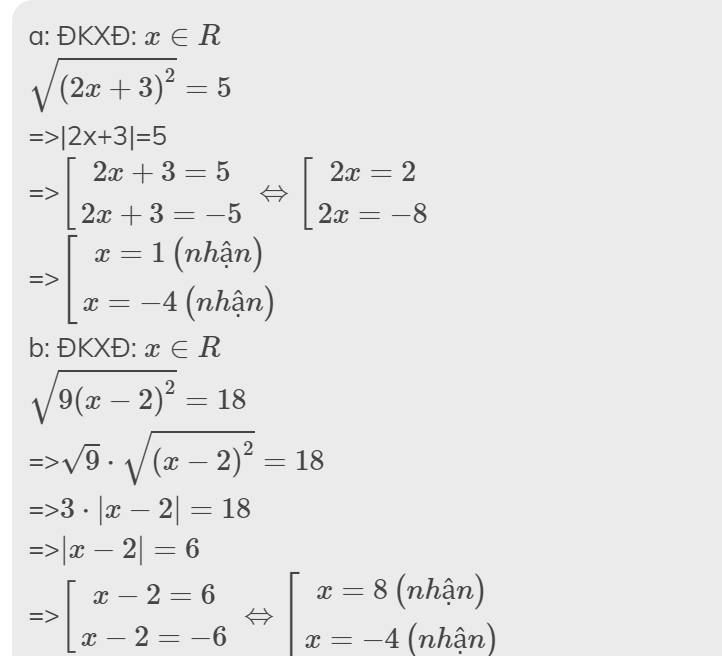
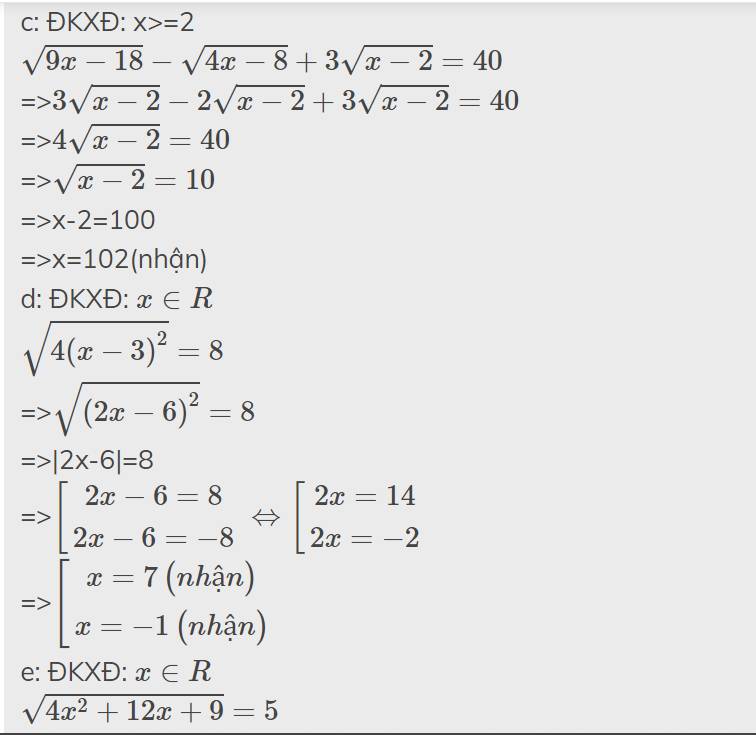
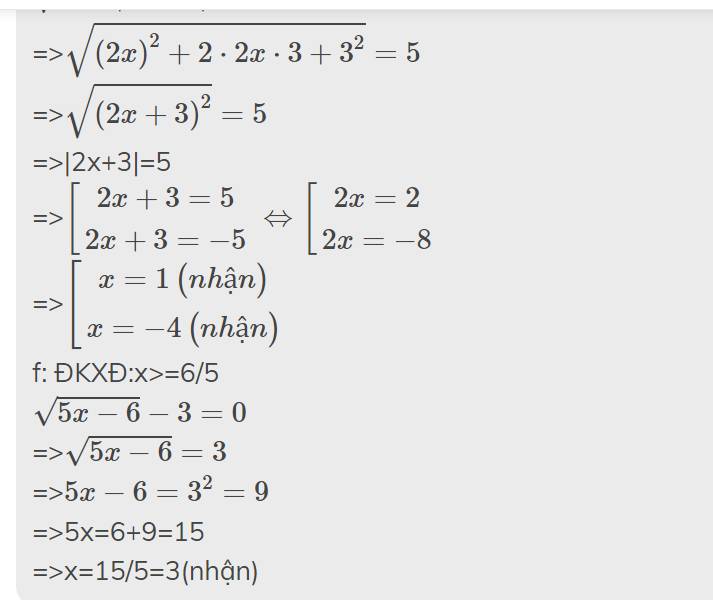
![[ ]](https://hoc24.vn/images/avt/avt78337201_256by256.jpg)

