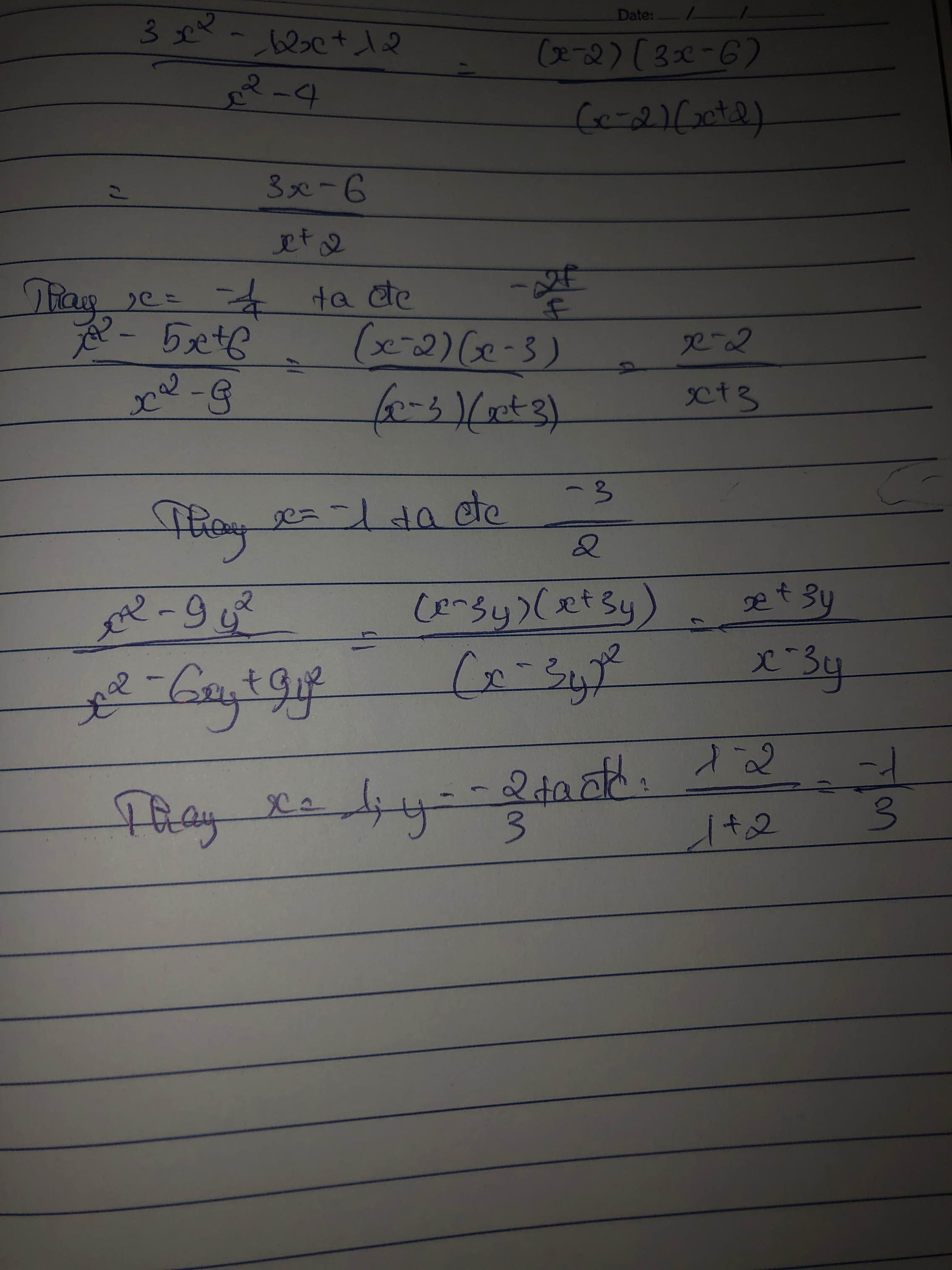Rút gọn: \(\dfrac{2}{x^2-y^2}\cdot\sqrt{\dfrac{3x^2+6xy+3y^2}{4}}\)

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Rút gọn biểu thức sau: \(B=\dfrac{2}{x^2-y^2}.\sqrt{\dfrac{3x^2+6xy+3y^2}{4}}\)
\(\dfrac{2}{x^2-y^2}.\sqrt{\dfrac{3x^2+6xy+3y^2}{4}}\)
\(ĐK:x\ne\pm y\)
\(=\dfrac{2\left|x+y\right|}{2\left(x+y\right)\left(x-y\right)}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}\left|x+y\right|}{\left(x+y\right)\left(x-y\right)}\)
Nếu x > -y thì x + y > 0 , ta có :\(\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{x-y}\)
Nếu x < -y thì x + y < 0 , ta có :\(\dfrac{-\sqrt{3}}{x-y}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Rút gọn
a)\(A=\dfrac{2}{x^2-y^2}.\sqrt{\dfrac{3x^2+6xy+3y^2}{4}}\)
b)\(B=\dfrac{1}{2a-1}.\sqrt{5a^4\left(1-4a+4a^2\right)}\)
\(a.A=\dfrac{2}{x^2-y^2}.\sqrt{\dfrac{3x^2+6xy+3y^2}{4}}=\dfrac{2}{\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)}.\dfrac{\left(x+y\right)\sqrt{3}}{2}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{x-y}\) ( x # y )
\(b.\dfrac{1}{2x-1}.\sqrt{5a^4\left(1-4x+4a^2\right)}=\dfrac{1}{2a-1}.\left(2a-1\right)a^2\sqrt{5}=a^2\sqrt{5}\) ( a # \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) )
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
1) rút gọn
a) \(\dfrac{x^2+3x-y^2-3y}{x^2-y^2}=\)
b) \(\dfrac{x^3+3x^2-2}{x^3+3x+4}=\)
\(b,\dfrac{x^3+3x^2-2}{x^3+3x+4}=\dfrac{x^3+x^2+2x^2+2x-2x-2}{x^3+x^2-x^2-x+4x+4}\\ =\dfrac{x^2\left(x+1\right)+2x\left(x+1\right)-2\left(x+1\right)}{x^2\left(x+1\right)-x\left(x+1\right)+4\left(x+1\right)}\\ =\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+2x-2\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+4\right)}=\dfrac{x^2+2x-2}{x^2-x+4}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(a,\dfrac{x^2+3x-y^2-3y}{x^2-y^2}=\dfrac{\left(x^2-y^2\right)+\left(3x-3y\right)}{x^2-y^2}\\ =\dfrac{\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)+3\left(x-y\right)}{\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)}\\ =\dfrac{\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y+3\right)}{\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)}=\dfrac{x+y+3}{x+y}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Rút gọn:
\(A=\dfrac{3x+\sqrt{9x}-3}{x+\sqrt{x}-2}-\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}+2}+\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-2}{\sqrt{x}}\cdot\left(\dfrac{1}{1-\sqrt{x}}-1\right)\)
rút gọn rồi tính giá trị biểu thức
\(\dfrac{3x^2-12x+12}{x^2-4}\) tại x=\(-\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(\dfrac{x^2-5x-6}{x^2-9}\) tại x=-1
\(\dfrac{x^2-9y^2}{x^2-6xy+9y^2}\) tại x=1, y=-\(\dfrac{2}{3}\)
a) Ta có: \(\dfrac{3x^2-12x+12}{x^2-4}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\left(x^2-4x+4\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\left(x-2\right)^2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\left(x-2\right)}{x+2}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\cdot\left(\dfrac{-1}{4}-2\right)}{\dfrac{-1}{4}+2}=-\dfrac{27}{7}\)
b) Ta có: \(\dfrac{x^2-5x-6}{x^2-9}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x-6\right)\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(-1-6\right)\left(-1+1\right)}{\left(-1-3\right)\left(-1+3\right)}\)
=0
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
rút gọn rồi tính giá trị biểu thức
\(\dfrac{3x^2-12x+12}{x^2-4}\) tại x= -\(\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(\dfrac{x^2-5x+6}{x^2-9}\) tại x= -1
\(\dfrac{x^2-9y^2}{x^2-6xy+9y^2}\) tại x=1, y =-\(\dfrac{2}{3}\)
rút gọn biểu thức
\(A=\frac{2}{x^2-y^2}.\sqrt{\frac{3x^2+6xy+3y^2}{4}}\)
Điều kiện \(x\ne y\)
\(A=\frac{2}{x^2-y^2}\sqrt{\frac{3\left(x+y\right)^2}{4}}=\frac{2}{\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)}.\frac{\sqrt{3}.\left|x+y\right|}{2}=\frac{\sqrt{3}\left|x+y\right|}{\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)}\)
Nếu \(x+y>0\) thì \(A=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{x-y}\)
Nếu \(x+y< 0\) thì \(A=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{y-x}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
rút gọn biểu thức
\(A=\frac{2}{x^2-y^2}.\sqrt{\frac{3x^2+6xy+3y^2}{4}}\)
1. Rút gọn
\(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}-1}-\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{5}+1}\)
2. Giải hpt :
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+3y=5\\3x+y=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
1)
\(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}-1}-\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{5}+1}=\dfrac{1+\sqrt{5}}{4}-\dfrac{4\sqrt{5}-4}{4}\) \(=\dfrac{5-3\sqrt{5}}{4}\)
2)
HPT \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+3y=5\\9x+3y=12\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}7x=7\\y=4-3x\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(1;1\right)\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
1: Rút gọn
Ta có: \(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}-1}-\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{5}+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{5}+1}{\left(\sqrt{5}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{5}+1\right)}-\dfrac{4\left(\sqrt{5}-1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{5}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{5}+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{5}+1-4\sqrt{5}+4}{\left(\sqrt{5}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{5}+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{5-3\sqrt{5}}{4}\)
2)
Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+3y=5\\3x+y=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}6x+9y=15\\6x+2y=8\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}7y=7\\3x+y=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=1\\3x=4-y=4-1=3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất là \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)