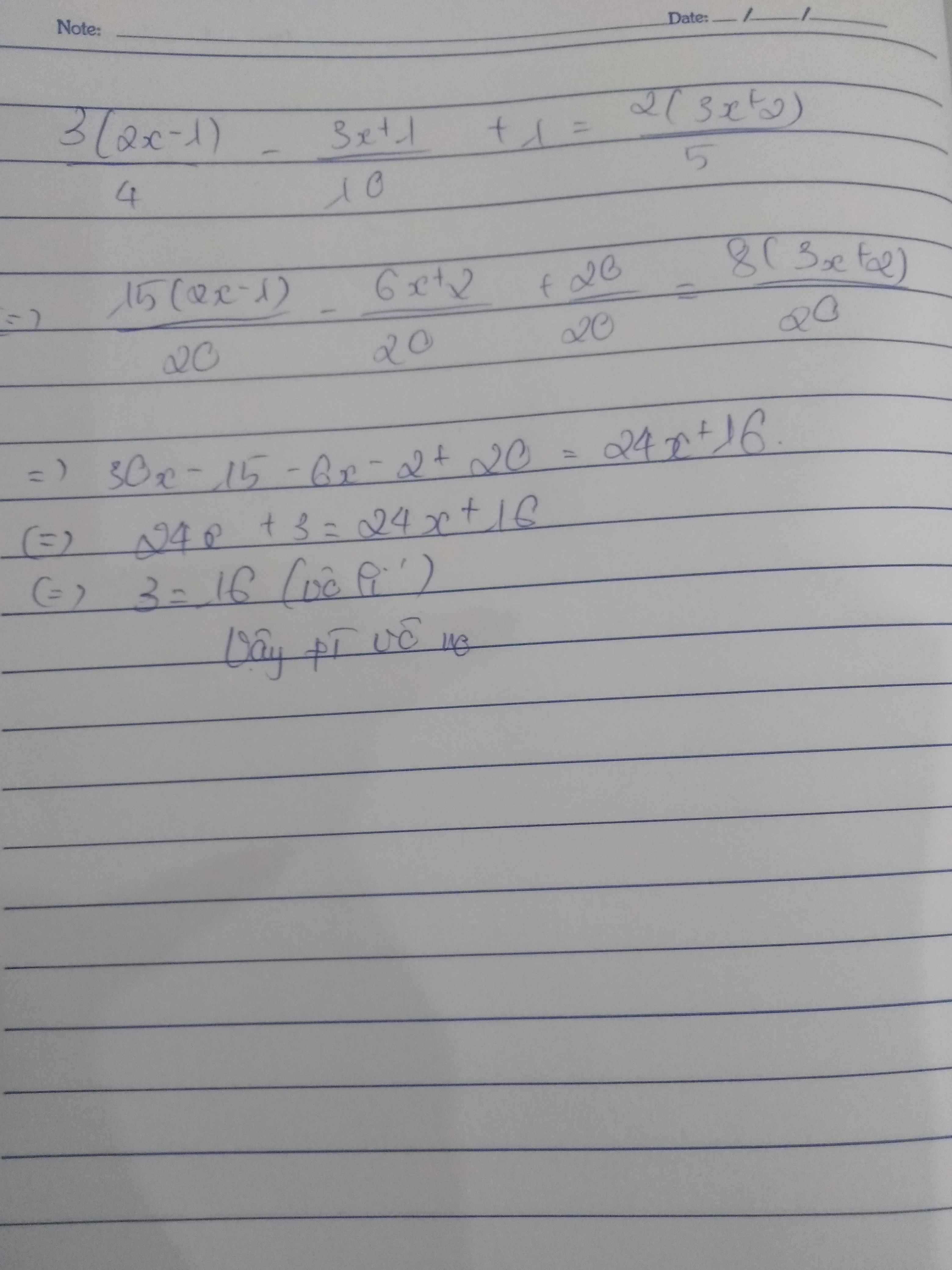giải pt \(\left|3x-1\right|+\left|2x+5\right|=4\)

Những câu hỏi liên quan
giải pt:
\(\dfrac{3\left(2x-1\right)}{4}-\dfrac{3x+1}{10}+1=\dfrac{2\left(3x+2\right)}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{15\left(2x-1\right)-2\left(3x+1\right)+20}{20}=\dfrac{8\left(3x+2\right)}{20}\)
\(\Rightarrow30x-15-6x-2+20=24x+16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0x=13\) (Vô lí)
Vậy phương trình vô nghiệm
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
1,Giải PT sau
a,\(\frac{4}{5}x-3=\frac{1}{5}x\left(4x-15\right)\)
b,(x-3)-\(\frac{\left(x-3\right)\left(2x-5\right)}{6}=\frac{\left(x-3\right)\left(3-x\right)}{4}\)
c,\(\frac{\left(3x+1\right)\left(3x-2\right)}{3}+5\left(3x+1\right)=\) \(\frac{2\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x+1\right)}{3}+2x\left(3x+1\right)\)
Bài 1:
a) Ta có: \(\frac{4}{5}x-3=\frac{1}{5}x\left(4x-15\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{4x}{5}-3=\frac{4x^2}{5}-3x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{12x}{15}-\frac{45}{15}-\frac{12x^2}{15}+\frac{45x}{15}=0\)
Suy ra: \(12x-45-12x^2+45x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-12x^2+57x-45=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-12x^2+12x+45x-45=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-12x\left(x-1\right)+45\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(-12x+45\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3\left(x-1\right)\left(4x-15\right)=0\)
mà \(-3\ne0\)
nên \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\4x-15=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\4x=15\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=\frac{15}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Tập nghiệm \(S=\left\{1;\frac{15}{4}\right\}\)
b) Ta có: \(\left(x-3\right)-\frac{\left(x-3\right)\left(2x-5\right)}{6}=\frac{\left(x-3\right)\left(3-x\right)}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)-\frac{\left(x-3\right)\left(2x-5\right)}{6}+\frac{\left(x-3\right)^2}{4}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{12\left(x-3\right)}{12}-\frac{2\left(x-3\right)\left(2x-5\right)}{12}+\frac{3\left(x-3\right)^2}{12}=0\)
Suy ra: \(12\left(x-3\right)-2\left(2x^2-11x+15\right)+3\left(x^2-6x+9\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x-36-4x^2+22x-30+3x^2-18x+27=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x^2+16x-39=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(x^2-16x+39\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-13x-3x+39=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-13\right)-3\left(x-13\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-13\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-13=0\\x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=13\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Tập nghiệm S={3;13}
c) Ta có: \(\frac{\left(3x+1\right)\left(3x-2\right)}{3}+5\left(3x+1\right)=\frac{2\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x+1\right)}{3}+2x\left(3x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{9x^2-3x-2}{3}+5\left(3x+1\right)-\frac{12x^2+10x+2}{3}-2x\left(3x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{9x^2-3x-2-12x^2-10x-2}{3}-6x^2+13x+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{-3x^2-13x-4}{3}+\frac{3\left(-6x^2+13x+5\right)}{3}=0\)
Suy ra: \(-3x^2-13x-4-18x^2+39x+15=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-21x^2+26x+11=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-21x^2-7x+33x+11=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-7x\left(3x+1\right)+11\left(3x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+1\right)\left(-7x+11\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x+1=0\\-7x+11=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x=-1\\-7x=-11\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\frac{-1}{3}\\x=\frac{11}{7}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Tập nghiệm \(S=\left\{-\frac{1}{3};\frac{11}{7}\right\}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải pt :
\(\left(x+5\right)^4+\left(x-4\right)^4=\left(2x+1\right)^4\)
\(\left(x^2+3x-4\right)^3+\left(3x^2+7x+4\right)^3=\left(4x^2+10x\right)^3\)
giải pt :
a,\(\left(6x-5\right)\sqrt{x+1}-\left(6x+2\right)\sqrt{x-1}+4\sqrt{x^2-1}=4x-3\)
b, \(\left(9x-2\right)\sqrt{3x-1}+\left(10-9x\right)\sqrt{3-3x}-4\sqrt{-9x^2+12x-3}=4\)
c, \(\left(13-4x\right)\sqrt{2x-3}+\left(4x-3\right)\sqrt{5-2x}=2+8\sqrt{-4x^2+16x-15}\)
Bằng cách phân tích vế trái thành nhân tử, giải các PT sau:
a) \(2x.\left(x-3\right)+5\left(x-3\right)\)
b) \(\left(x^2-4\right)+\left(x-2\right).\left(3-2x\right)=0\)
c) \(x^3-3x^2+3x-1=0\)
a: =(x-3)(2x+5)
b: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2+3-2x\right)=0\)
=>(x-2)(5-x)=0
=>x=2 hoặc x=5
c: =>x-1=0
hay x=1
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
giải pt :
a, \(\left(2x-6\right)\sqrt{x+4}-\left(x-5\right)\sqrt{2x+3}=3\left(x-1\right)\)
b, \(\left(4x+1\right)\sqrt{x+2}-\left(4x-1\right)\sqrt{x-2}=21\)
c, \(\left(4x+2\right)\sqrt{x+1}-\left(4x-2\right)\sqrt{x-1}=9\)
d, \(\left(2x-4\right)\sqrt{3x-2}+\sqrt{x+3}=5x-7+\sqrt{3x^2+7x-6}\)
giải pt
\(\left(2x-5\right)^3-\left(3x-4\right)^3+\left(x+1\right)^3=0\)
Bài toán phụ:Với \(a-b+c=0\) thì \(a^3-b^3+c^3=-3abc\)
Chứng minh:\(a-b+c=0\Rightarrow a+c=b\Rightarrow\left(a+c\right)^3=b^3\)
\(\Rightarrow a^3+3ac\left(a+c\right)+c^3=b^3\)\(\Rightarrow a^3-b^3+c^3=-3ac\left(a+c\right)\Rightarrow a^3-b^3+c^3=-3abc\)(đpcm)
Áp dụng vào bài toán ta có:\(2x-5-\left(3x-4\right)+x+1=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(2x-5\right)^3-\left(3x-4\right)^3+\left(x+1\right)^3=-3\left(2x-5\right)\left(3x-4\right)\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow-3\left(2x-5\right)\left(3x-4\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\)\(2x-5=0\) hoặc \(3x-4=0\) hoặc \(x+1=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\frac{5}{2}\) hoặc \(x=\frac{4}{3}\) hoặc \(x=-1\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải PT: \(\sqrt{x-1}+\sqrt{x+3}+2\sqrt{\left(x-1\right).\left(x^2-3x+5\right)}=4-2x\)
Bài 1: giải hệ pt
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+2y=1\\2x^{2^{ }}-5xy=48\end{matrix}\right.\)
bài 2: giải các pt sau:
a/ \(\left(x^2-1\right)^2-4\left(x^2-1\right)=5\)
b/\(\left(x+2\right)^2-3x-5=\left(1-x\right)\left(1+x\right)\)
c/ \(\left(x^2-3x+4\right)\left(x^2-3x+2\right)=3\)
Bài 1:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+2y=1\\2x^2-5xy=48\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1-2y\left(1\right)\\2x^2-5xy=48\left(2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thay (1) vào (2)\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(1-2y\right)^2-5\left(1-2y\right)y=48\Leftrightarrow2\left(1-4y+4y^2\right)-5y+10y^2=48\Leftrightarrow2-8y+8y^2-5y+10y^2=48\Leftrightarrow18y^2-13y-46=0\Leftrightarrow\left(y-2\right)\left(18y+23\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}y=2\\y=-\frac{23}{18}\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=\frac{32}{9}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy (x;y)={(\(-3;2\));(\(\frac{32}{9};-\frac{23}{18}\))}
Bài 2:
a) Đặt a=x2-1(a\(\ge-1\))
Vậy pt\(\Leftrightarrow a^2-4a=5\Leftrightarrow a^2-4a-5=0\Leftrightarrow\left(a-5\right)\left(a+1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=5\\a=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)(tm)
TH1: a=5\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-1=5\Leftrightarrow x^2=6\Leftrightarrow x=\pm\sqrt{6}\)
TH2: a=-1\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-1=-1\Leftrightarrow x^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=0\)
Vậy S={\(-\sqrt{6};0;\sqrt{6}\)}
b) \(\left(x+2\right)^2-3x-5=\left(1-x\right)\left(1+x\right)\Leftrightarrow x^2+4x+4-3x-5=1-x^2\Leftrightarrow2x^2+x-2=0\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\frac{-1+\sqrt{17}}{4}\\x=\frac{-1-\sqrt{17}}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy S={\(\frac{-1+\sqrt{17}}{4};\frac{-1-\sqrt{17}}{4}\)}
c) Đặt a=\(x^2-3x+2\)
Vậy pt\(\Leftrightarrow\left(a+2\right)a=3\Leftrightarrow a^2+2a-3=0\Leftrightarrow\left(a-1\right)\left(a+3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=1\\a=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)(tm)
TH1:\(a=1\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x+2=1\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x+1=0\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\frac{3+\sqrt{5}}{2}\\x=\frac{3-\sqrt{5}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
TH2: a=-3\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x+2=-3\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x+5=0\)(vô nghiệm)
Vậy S=\(\left\{\frac{3+\sqrt{5}}{2};\frac{3-\sqrt{5}}{2}\right\}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)