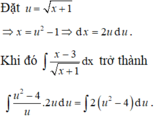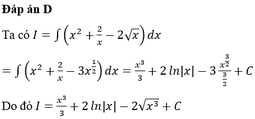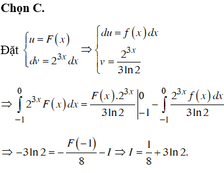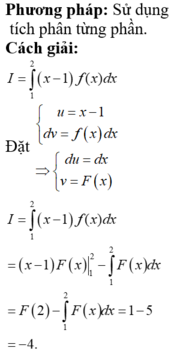Những câu hỏi liên quan
Khi tính nguyên hàm
∫
x
-
3
x
+
1
dx , bằng cách đặt
u
x
+
1
ta được nguyên hàm nào?
Đọc tiếp
Khi tính nguyên hàm ∫ x - 3 x + 1 dx , bằng cách đặt u = x + 1 ta được nguyên hàm nào?
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Tính nguyên hàm
I
∫
(
x
2
+
2
x
-
2
x
)
d
x
A.
I
x
3
3
-
2
l
n
|
x
|
+
2
x
3...
Đọc tiếp
Tính nguyên hàm I = ∫ ( x 2 + 2 x - 2 x ) d x
A. I = x 3 3 - 2 l n | x | + 2 x 3 + C
B. I = x 3 3 + 2 l n | x | + 2 x 3 + C
C. I = x 3 3 + 2 l n x - 2 x 3 + C
D. I = x 3 3 + 2 l n | x | - 2 x 3 + C
\(\int(x)ln(x+1)dx\)
Tính nguyên hàm
\(\int xln\left(x+1\right)dx\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}u=ln\left(x+1\right)\\dv=xdx\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}du=\dfrac{1}{x+1}dx\\v=\dfrac{x^2}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\int xln\left(x+1\right)dx=\dfrac{x^2}{2}.ln\left(x+1\right)-\int\dfrac{x^2}{2}.\dfrac{1}{x+1}dx=\dfrac{x^2}{2}.ln\left(x+1\right)-\dfrac{1}{2}\int\dfrac{x^2}{x+1}dx\)
Xet \(\int\dfrac{x^2}{x+1}dx=\int\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}{x+1}dx+\int\dfrac{1}{x+1}dx\)
\(=\int\left(x-1\right)dx+\int\dfrac{1}{x+1}dx\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2}{2}-x+ln\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\int xln\left(x+1\right)dx=\dfrac{x^2}{2}.ln\left(x+1\right)-\dfrac{1}{2}\left(\dfrac{x^2}{2}-x+ln\left(x+1\right)\right)\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)
Nguyên hàm sin ( bi chia 4 — x )dx
Nguyên hàm ( 7/cos^2(3—x) + 8 sin(9—3x) — 1/x + 6/3—2x + căn x )dx
Nguyên hàm (7/cos^2x — 8/ 2x+1 +9^2x+1 + e^5—2x +8) dx
Nguyên hàm ( 3—căn x + 5x^5—6x^7+1 tất cả / x )dx
Xem chi tiết
Biết F(x) là một số nguyên hàm của hàm số f(x) trên đoạn [-1;0],
F
-
1
-
1
;
F
0
0
và
∫
-
1...
Đọc tiếp
Biết F(x) là một số nguyên hàm của hàm số f(x) trên đoạn [-1;0], F - 1 = - 1 ; F 0 = 0 và ∫ - 1 0 2 3 x F ( x ) dx = - 1 . Tính I= ∫ - 1 0 2 3 x f ( x ) dx .
A. 1 8 - 3 ln 2
B. 1 8 + ln 2
C. 1 8 + 3 ln 2
D. - 1 8 + 3 ln 2
Cho hàm số f(x) có nguyên hàm là F(x) trên đoạn [1;2], biết F(2) 1 và
∫
1
2
F
(
x
)
d
x
5
. Tính I
∫
1
2
(
x
-
1
)
f
(
x
)
d
x
Đọc tiếp
Cho hàm số f(x) có nguyên hàm là F(x) trên đoạn [1;2], biết F(2) = 1 và ∫ 1 2 F ( x ) d x = 5 . Tính I= ∫ 1 2 ( x - 1 ) f ( x ) d x
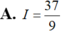
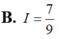
![]()
![]()
Cho hàm số f(x) có nguyên hàm là F(x) trên đoạn [1;2], biết F(2)1 và
∫
1
2
F
(
x
)
d
x
5
. Tính
I
∫
1
2
(
x
-
1
)
f
(
x
)
d
x
Đọc tiếp
Cho hàm số f(x) có nguyên hàm là F(x) trên đoạn [1;2], biết F(2)=1 và ∫ 1 2 F ( x ) d x = 5 . Tính I = ∫ 1 2 ( x - 1 ) f ( x ) d x
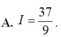
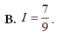
![]()
![]()
Tính nguyên hàm \(\int\dfrac{1}{x^3+x}dx\)
\(\int\dfrac{dx}{x^3+x}=\int\dfrac{dx}{x\left(x^2+1\right)}\)
\(t=x^2+1\Rightarrow dt=2xdx\Rightarrow\int\dfrac{dx}{x\left(x^2+1\right)}=\int\dfrac{dt}{2x^2t}=\dfrac{1}{2}\int\dfrac{dt}{\left(t-1\right).t}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{\left(t-1\right).t}=\dfrac{1}{t-1}-\dfrac{1}{t}\)
\(\Rightarrow\int\dfrac{dt}{\left(t-1\right)t}=\int\left(\dfrac{1}{t-1}-\dfrac{1}{t}\right)dt=\int\dfrac{dt}{t-1}-\int\dfrac{dt}{t}=ln\left|t-1\right|-ln\left|t\right|=ln\left|x^2\right|-ln\left|x^2+1\right|\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)
tính nguyên hàm sau:
\(\int\sqrt{4x-x^2}dx\)
\(\int\sqrt{4x-x^2}dx=\int\sqrt{4-\left(x-2\right)^2}dx=\int\sqrt{4-\left(x-2\right)^2}d\left(x-2\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\sqrt{4-\left(x-2\right)^2}}{2}+arcsin\left(\dfrac{x-2}{2}\right)+C\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)