tìm x
x4-2x3+10x2-20x =0
x3-3x2-16x + 48=0
tìm x
a 5x3-7x2-15x+21=0
b (x-3)2=4x2-20x+25
c x+x2-x3-x4=0
d 2x3+3x2+2x+3=0
b: 4x^2-20x+25=(x-3)^2
=>(2x-5)^2=(x-3)^2
=>(2x-5)^2-(x-3)^2=0
=>(2x-5-x+3)(2x-5+x-3)=0
=>(3x-8)(x-2)=0
=>x=8/3 hoặc x=2
c: x+x^2-x^3-x^4=0
=>x(x+1)-x^3(x+1)=0
=>(x+1)(x-x^3)=0
=>(x^3-x)(x+1)=0
=>x(x-1)(x+1)^2=0
=>\(x\in\left\{0;1;-1\right\}\)
d: 2x^3+3x^2+2x+3=0
=>x^2(2x+3)+(2x+3)=0
=>(2x+3)(x^2+1)=0
=>2x+3=0
=>x=-3/2
a: =>x^2(5x-7)-3(5x-7)=0
=>(5x-7)(x^2-3)=0
=>\(x\in\left\{\dfrac{7}{5};\sqrt{3};-\sqrt{3}\right\}\)
Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử:
a. x4 + 2x3 + 10x2 - 20x
b. x3 - x2y - xy2 + y3
c. x5 + x3 - x2 - 1
a/ 4x3 – xy2
b/ 5x3 – 10x2 + 5x
c/4x2 +24x+36-4y2
d/ 4x2y2 - 8xy2 + 4y2
e/ x3y + 10x2y + 35xy
f/2x3 –4x2y+2xy2–8x
g/3x2 –9xy–6x+18y
h/ x2y2 – 3xy2 + 2xy – 6y
a: \(4x^3-xy^2\)
\(=x\left(4x^2-y^2\right)\)
\(=x\left(2x-y\right)\left(2x+y\right)\)
b: \(5x^3-10x^2+5x\)
\(=5x\left(x^2-2x+1\right)\)
\(=5x\left(x-1\right)^2\)
c: \(4x^2+24x+36-4y^2\)
\(=4\left(x^2+6x+9-y^2\right)\)
\(=4\left(x+3-y\right)\left(x+3+y\right)\)
a) \(4x^3-xy^2=x\left(4x^2-y^2\right)=x\left(2x-y\right)\left(2x+y\right)\)
b) \(5x^3-10x^2+5x=5x\left(x^2-2x+1\right)=5x\left(x-1\right)^2\)
c) \(4x^2+24x+36-4y^2=\left(2x+6\right)^2-4y^2=\left(2x+6-2y\right)\left(2x+6+2y\right)\)
d) \(4x^2y^2-8xy^2+4y^2=4y^2\left(x^2-2x+1\right)=4y^2\left(x-1\right)^2\)
e) \(x^3y+10x^2y+35xy=xy\left(x^2+10x+35\right)\)
f) \(2x^3-4x^2y+2xy^2-8x=2x\left(x^2-2xy+y^2-4\right)=2x\left[\left(x-y\right)^2-4\right]=2x\left(x-y-2\right)\left(x-y+2\right)\)
g) \(3x^2-9xy-6x+18y=3x\left(x-2\right)-9y\left(x-2\right)=3\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3y\right)\)
h) \(x^2y^2-3xy^2+2xy-6y=xy\left(xy+2\right)-3y\left(xy+2\right)=\left(xy+2\right)\left(xy-3y\right)\)
g: \(3x^2-9xy-6x+18y\)
\(=3x\left(x-3y\right)-6\left(x-3y\right)\)
\(=3\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3y\right)\)
h: \(x^2y^2-3xy^2+2xy-6y\)
\(=xy^2\left(x-3\right)+2y\left(x-3\right)\)
\(=y\left(xy+2\right)\left(x-3\right)\)
Tìm x:
a) x(2-x)+(x2+x)=7
b) (2x+1)2-x(4-5x)=17
c) (4-x)2-(2x+1)2=0
d) (2x3-8x2+10x) : (2x)=0
e) (4x4-16x-48) : (-2x)2=0
a: Ta có: \(x\left(2-x\right)+\left(x^2+x\right)=7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-x^2+x^2+x=7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=7\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{7}{3}\)
b: Ta có: \(\left(2x+1\right)^2-x\left(4-5x\right)=17\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2+4x+1-4x+5x^2=17\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x^2=16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=\dfrac{16}{9}\)
hay \(x\in\left\{\dfrac{4}{3};-\dfrac{4}{3}\right\}\)
c: Ta có: \(\left(x-4\right)^2-\left(2x+1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-4-2x-1\right)\left(x-4+2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+5\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-5\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
d: ta có: \(\dfrac{2x^3-8x^2+10x}{2x}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2+1=0\)(vô lý)
a) \(4x^2+16x+3=0\)
\(\Delta'=84-12=72\Rightarrow\sqrt[]{\Delta'}=6\sqrt[]{2}\)
Phương trình có 2 nghiệm
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{-8+6\sqrt[]{2}}{4}\\x=\dfrac{-8-6\sqrt[]{2}}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{-2\left(4-3\sqrt[]{2}\right)}{4}\\x=\dfrac{-2\left(4+3\sqrt[]{2}\right)}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{-\left(4-3\sqrt[]{2}\right)}{2}\\x=\dfrac{-\left(4+3\sqrt[]{2}\right)}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3\sqrt[]{2}-4}{2}\\x=\dfrac{-3\sqrt[]{2}-4}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) \(7x^2+16x+2=1+3x^2\)
\(4x^2+16x+1=0\)
\(\Delta'=84-4=80\Rightarrow\sqrt[]{\Delta'}=4\sqrt[]{5}\)
Phương trình có 2 nghiệm
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{-8+4\sqrt[]{5}}{4}\\x=\dfrac{-8-4\sqrt[]{5}}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{-4\left(2-\sqrt[]{5}\right)}{4}\\x=\dfrac{-4\left(2+\sqrt[]{5}\right)}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\left(2-\sqrt[]{5}\right)\\x=-\left(2+\sqrt[]{5}\right)\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2+\sqrt[]{5}\\x=-2-\sqrt[]{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) \(4x^2+20x+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(x^2+5x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+5x+1=0\)
\(\Delta=25-4=21\Rightarrow\sqrt[]{\Delta}=\sqrt[]{21}\)
Phương trình có 2 nghiệm
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{-5+\sqrt[]{21}}{2}\\x=\dfrac{-5-\sqrt[]{21}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tập hợp nghiệm của hệ bất phương trình x 2 + 5 x + 4 ≤ 0 x 3 + 3 x 2 - 9 x - 10 > 0 là
A. - ∞ ; - 4
B. - 4 ; - 1
C. - 4 ; 1
D. [ - 1 ; + ∞ )
Tìm bậc của mỗi đa thức sau
a) f (x) = 3x2 + 2x3 - 6x - 2
b) g(x) = 5x2 + 9 - 2x3 - 3x2 - 4x + 2x3 - 2
f (x) = 3x2 + 2x3 - 6x - 2
bậc của đa thức là: 3
g(x) = 5x2 + 9 - 2x3 - 3x2 - 4x + 2x3 - 2
g(x) = ( 5x2 - 3x2 ) + ( 9 -2) + ( - 2x3 + 2x3 ) - 4x
g(x) = 2x2 + 7 - 4x
bậc của đa thức là : 2
Bài 2 ( 2đ): Tìm x, biết
a) x (x - 4 ) + 7 = 3x −5
b) 2x3 -3x2 - 2x + 3=0
Giải các phương trình trùng phương:
a ) x 4 − 5 x 2 + 4 = 0 b ) 2 x 4 − 3 x 2 − 2 = 0 c ) 3 x 4 + 10 x 2 + 3 = 0
a) x 4 – 5 x 2 + 4 = 0 ( 1 )
Đặt x 2 = t, điều kiện t ≥ 0.
Khi đó (1) trở thành : t 2 – 5 t + 4 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2) : Có a = 1 ; b = -5 ; c = 4 ⇒ a + b + c = 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm t 1 = 1 ; t 2 = c / a = 4
Cả hai giá trị đều thỏa mãn điều kiện.
+ Với t = 1 ⇒ x 2 = 1 ⇒ x = 1 hoặc x = -1;
+ Với t = 4 ⇒ x 2 = 4 ⇒ x = 2 hoặc x = -2.
Vậy phương trình (1) có tập nghiệm S = {-2 ; -1 ; 1 ; 2}.
b) 2 x 4 – 3 x 2 – 2 = 0 ; ( 1 )
Đặt x 2 = t , điều kiện t ≥ 0.
Khi đó (1) trở thành : 2 t 2 – 3 t – 2 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2) : Có a = 2 ; b = -3 ; c = -2
⇒ Δ = ( - 3 ) 2 - 4 . 2 . ( - 2 ) = 25 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm
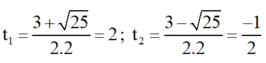
Chỉ có giá trị t 1 = 2 thỏa mãn điều kiện.
+ Với t = 2 ⇒ x 2 = 2 ⇒ x = √2 hoặc x = -√2;
Vậy phương trình (1) có tập nghiệm S = {-√2 ; √2}.
c) 3 x 4 + 10 x 2 + 3 = 0 ( 1 )
Đặt x 2 = t , điều kiện t ≥ 0.
Khi đó (1) trở thành : 3 t 2 + 10 t + 3 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2) : Có a = 3; b' = 5; c = 3
⇒ Δ ’ = 5 2 – 3 . 3 = 16 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt
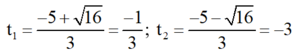
Cả hai giá trị đều không thỏa mãn điều kiện.
Vậy phương trình (1) vô nghiệm.