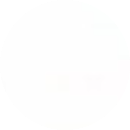
giải pt sau:x/x+1-1/x-2=3x-11/(x+1).(x-2)

Những câu hỏi liên quan
giải các pt sau:
x(x+3) - (2x-1) . (x+3) = 0
x(x-3) - 5 (x-3) = 0
3x + 12 = 0
2x (x-2) + 5 (x-2) = 0
`x(x+3) - (2x-1) . (x+3) = 0`
`<=>(x+3)(x-2x+1)=0`
`<=>(x+3)(-x+1)=0`
`** x+3=0`
`<=>x=-3`
`** -x+1=0`
`<=>x=1`
`x(x-3) - 5 (x-3) = 0`
`<=>(x-3)(x-5)=0`
`** x-3=0`
`<=>x=3`
`** x-5=0`
`<=>x=5`
`3x + 12 = 0`
`<=>3x=-12`
`<=> x=-4`
`2x (x-2) + 5 (x-2) = 0`
`<=>(x-2)(2x+5)=0`
`** x-2=0`
`<=>x=2`
`** 2x+5=0`
`<=> x= -5/2`
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
giải phương trình sau:x(x+3)2-3x=(x+2)3+1
x(x2+6x+9) - 3x= x3+6x2+12x+8+1
\(\Leftrightarrow\)x3+6x2+9x-3x=x3+6x2+12x+9
\(\Leftrightarrow\)6x=12x+9
\(\Leftrightarrow\)6x=-9
\(\Leftrightarrow\)x=-3/2
Vậy phương trình có 1 nghiệm duy nhất x=-3/2
x(x + 3)^2 - 3x = (x + 2)^3 + 1
<=> x(x^2 + 6x + 9) = x^3 + 6x^2 + 12x + 8 + 1
<=> x^3 + 6x^2 + 9x = x^3 + 6x^2 + 12x + 9
<=> 3x + 9 = 0
<=> 3x = -9
<=> x = -3
\(x\left(x+3\right)^2-3x=\left(x+2\right)^3+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x^2+6x+9\right)=x^3+6x^2+12x+8+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3+6x^2+9x=x^3+6x^2+12x+9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x+9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=-9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-3\)
`1.` giải pt :
`a)|-7x|=3x+16`
`b)(x-1)/(x+2)-x/(x-2)=(5x-8)/(x^2-4)`
`2.` giải bất phương trình sau và biểu diễn nghiệm trên trục số
`7x+5<3x-11`
1.a)|−7x|=3x+16
Vì |-7x| ≥ 0 nên 3x+16 ≥ 0 ⇔ x ≥ \(\dfrac{-16}{3}\) (*)
Với đk (*), ta có: |-7x|=3x+16
\(\left[\begin{array}{} -7x=3x+16\\ -7x=-3x-16 \end{array} \right.\) ⇔ \(\left[\begin{array}{} -7x-3x=16\\ -7x+3x=-16 \end{array} \right.\)
⇔ \(\left[\begin{array}{} x=-1,6 (t/m)\\ x= 4 (t/m) \end{array} \right.\)
b) \(\dfrac{x-1}{x+2}\) - \(\dfrac{x}{x-2}\) = \(\dfrac{5x-8}{x^2-4}\)
⇔ \(\dfrac{(x-1)(x-2)}{x^2-4}\) - \(\dfrac{x(x+2)}{x^2-4}\) = \(\dfrac{5x-8}{x^2-4}\)
⇒ x2 - 2x - x + 2 - x2 - 2x = 5x - 8
⇔ -5x - 5x = -8 - 2
⇔ -10x = -10
⇔ x=1
2.7x+5 < 3x−11
⇔ 7x - 3x < -11 - 5
⇔ 4x < -16
⇔ x < -4
bạn tự biểu diễn trên trục số nha !
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải pt
\(11\sqrt{4-x}-26=-7x+2\sqrt{1+x}+\sqrt{4+3x-x^2}\)
đang gấp, giúp e với ạ
bài 1: giải các pt sau: a, 1/x-2+3=7-x/x-2
b, x^2-x/x+3-x^2/x-3=7x^2-3x/9-x^2
c, x/2x-1 + x+1/x+2=0
d, 2/x+1 - 1/x-2 = 3x-11/(x+1)(x-2)
a: =>1+3x-6=7-x
=>3x-5=7-x
=>4x=12
=>x=3(nhận)
b: \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2-x}{x+3}-\dfrac{x^2}{x-3}=\dfrac{-7x^2+3x}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
=>\(x^3-3x^2-x^2+3x-x^3-3x^2=-7x^2+3x\)
=>\(-7x^2+3x=-7x^2+3x\)
=>0x=0(luôn đúng)
Vậy: S=R\{3;-3}
c: =>x(x+2)+(2x-1)(x+1)=0
=>2x^2+2x-x-1+x^2+2x=0
=>3x^2+3x-1=0
\(x=\dfrac{-3\pm\sqrt{21}}{6}\)
d: =>2(x-2)-x-1=3x-11
=>3x-11=2x-4-x-1=x-5
=>2x=6
=>x=3(nhận)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (1)
Giải PT: \(4\sqrt{x+1}-11=3x+2\sqrt{1-x}+\sqrt{1-x^2}\)
(1) giải pt quy về ax^2+bx+c01) x^23x 2) x^2-3x4 3) x^4-5x^2+60 4) x^39x5) left(x+2right)left(x-3right)x^2-4 6) dfrac{x+11}{x^2-1}-dfrac{x-1}{x+1}dfrac{2left(x+7right)}{x+1}giúp mk vs mk cần gấp
Đọc tiếp
(1) giải pt quy về \(ax^2+bx+c=0\)
1) \(x^2=3x\) 2) \(x^2-3x=4\)
3) \(x^4-5x^2+6=0\) 4) \(x^3=9x\)
5) \(\left(x+2\right)\left(x-3\right)=x^2-4\) 6) \(\dfrac{x+11}{x^2-1}-\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}=\dfrac{2\left(x+7\right)}{x+1}\)
giúp mk vs mk cần gấp
1)
<=> \(x^2-3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-3\right)=0\)
x= 0
x = 3
2) <=> \(x\left(x-3\right)=4\)
=> \(x=\dfrac{4}{x}+3\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
\(2,x^2-3x=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x-4=0\)
\(\Delta=b^2-4ac=\left(-3\right)^2-4\left(-4\right)=25>0\)
\(\Rightarrow\)Pt có 2 nghiệm pb
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{-b+\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{3+5}{2}=4\\x_2=\dfrac{-b-\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{-3-5}{2}=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{4;-1\right\}\)
\(3,x^4-5x^2+6=0\)
Đặt \(t=x^2\left(t\ge0\right)\)
Pt trở thành
\(t^2-5t+6=0\)
\(\Delta=b^2-4ac=\left(-5\right)^2-4.6=1>0\)
\(\Rightarrow\)Pt ó 2 nghiệm pb
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{-b+\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{5+1}{2}=3\\x_2=\dfrac{-b-\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{-5-1}{2}-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow t=x^2\Leftrightarrow t=\pm\sqrt{3}\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{\pm\sqrt{3}\right\}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
\(4,x^3=9x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-9x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x^2-9\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x^2-9=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x^2=9\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\pm3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{0;\pm3\right\}\)
\(5,\left(x+2\right)\left(x-3\right)=x^2-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x+2x-6-x^2+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-2\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{-2\right\}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Giải pt \(\left(x^2-3x+2\right)\sqrt{\frac{x+3}{x-1}}=-\frac{1}{2}x^3+\frac{15}{2}x-11\)
ĐKXĐ: \(x\le-3\)hoặc 1 < x
(x2 - 3x +2)\(\sqrt{\frac{x+3}{x-1}}\)=\(\frac{-1}{2}x^3+\frac{15}{2}x-11\)
<=> (x - 1)(x - 2)\(\sqrt{\frac{x+3}{x-1}}\)=\(\frac{-1}{2}\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+2x-11\right)\) (1)
+ TH1: x = 2 là nghiệm của phương trình (1).
+ TH2: \(x\ne2\). Lấy 2 vế của phương trình (1) chia cho (x - 2), ta được:
(x - 1)\(\sqrt{\frac{x+3}{x-1}}\)=\(\frac{-1}{2}\left(x^2+2x-11\right)\)
Đến đây bạn tự giải tiếp.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giai pt sau:x-1/2013+x-2/2012+x-3/2011=x-4/2010+x-5/2009+x-6/2008
=> 3x-(1/2013+2/2012+3/2011)=3x-(4/2010+5/2009+6/2008)=>6x=-4/2010-5/2009-6/2008+1/2013+2/2012+3/2011 =>x=... làm tiếp đi bạn
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
giải pt và bất pt
a) |x+5|=3x+1
b)\(\frac{3\left(x-1\right)}{4}+1\ge\frac{x+2}{3}\)
c)\(\frac{x-2}{x+2}-\frac{3}{x-2}=\frac{2\left(x-11\right)}{x^2-4}\)