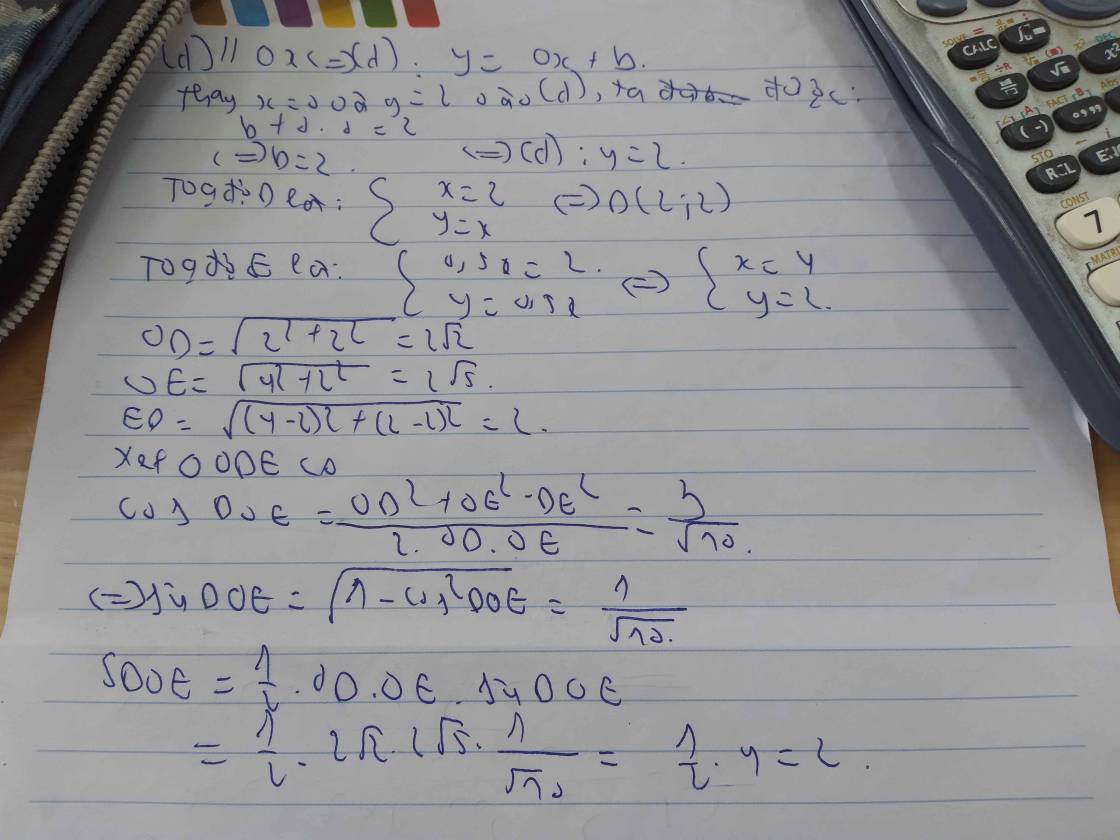Cho 2 đường thẳng: (d1): y = (m2 - 2)x + 2 và (d2): y = - x + 3 . Hai đường thẳng (d) và (D) song song khi:

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Cho các đường thẳng (d1): y= (m2+1)x +m và (d2): y=5x+2. Tìm m để hai đường thẳng song song
`(d1) //// (d2) <=> {(a = a'),(b \ne b'):}`
`<=>{(m^2 + 1 = 5),(1 \ne 2\text{ (Luôn đúng)}):}`
`<=> m^2 = 4`
`<=>m = +-2`
Vậy `m = +-2` thì `(d1) //// (d2)`
Đúng 2
Bình luận (2)
TK
(d1)//(d2)⇔{a=a'b≠b'(d1)//(d2)⇔{a=a′b≠b′
⇔{m2+1=51≠2 (Luôn đúng)⇔{m2+1=51≠2 (Luôn đúng)
⇔m2=4⇔m2=4
⇔m=±2⇔m=±2
Vậy m=±2m=±2 thì (d1)//(d2)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho hai đường thẳng y = ax +b (d1) và y= x+ 2 (d2)
Tìm a, b biết đường thẳng (d1) song song với đường thẳng (d2) và qua A(-1; 2)
Lời giải:
Vì $(d_1)\parallel (d_2)$ nên $a=1$
$A\in (d_1)$ nên $y_A=ax_A+b\Leftrightarrow 2=a(-1)+b$
$\Leftrightarrow b=2+a=2+1=3$
Vậy $a=1; b=3$
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Cho đường thẳng (d1): y=(m-1)x+m-2 và đường thẳng (d2): y=-2x+3. Tìm giá trị của m để hai đoạn thẳng (d1) và (d2) song song với nhau
Để (d1 ) và (d2 ) song song thì
+) b≠b'
⇔m-2≠3
⇔m≠5
+) a=a'
⇔m-1=-2
⇔m=-1 (thỏa mãn điều kiện)
Vậy tại m=-1 thì (d1) // (d2)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 2. Cho đường thẳng (d): y (m – 1)x + m – 2.a) Vẽ đường thẳng (d1) khi m 3.b) Viết phương trình đường thẳng (d2) song song với đường thẳng (d1) và thỏa mãnkhoảng cách từ gốc tọa độ O đến đường thẳng (d2) bằng 1.c) Tìm tọa độ điểm cố định mà đường thẳng (d) luôn đi qua với mọi m. Xác định m đểđường thẳng (d) tạo với tia đối của các tia Ox và Oy một tam giác có diện tích nhỏ nhất.
Đọc tiếp
Bài 2. Cho đường thẳng (d): y = (m – 1)x + m – 2.
a) Vẽ đường thẳng (d1) khi m = 3.
b) Viết phương trình đường thẳng (d2) song song với đường thẳng (d1) và thỏa mãn
khoảng cách từ gốc tọa độ O đến đường thẳng (d2) bằng 1.
c) Tìm tọa độ điểm cố định mà đường thẳng (d) luôn đi qua với mọi m. Xác định m để
đường thẳng (d) tạo với tia đối của các tia Ox và Oy một tam giác có diện tích nhỏ nhất.
\(a,m=3\Leftrightarrow\left(d_1\right):y=2x+1\\ b,\text{Gọi PT cần tìm là }\left(d_2\right):y=ax+b\left(a\ne0\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=2\\b\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left(d_2\right):y=2x+b\\ \text{PT giao }Ox:y=0\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{b}{2}\Leftrightarrow A\left(-\dfrac{b}{2};0\right)\Leftrightarrow OA=\left|\dfrac{b}{2}\right|\\ \text{PT giao }Oy:x=0\Leftrightarrow y=b\Leftrightarrow B\left(0;b\right)\Leftrightarrow OB=\left|b\right|\)
Gọi H là chân đường cao từ O tới \(\left(d_2\right)\Leftrightarrow OH=1\)
Áp dụng HTL: \(\dfrac{1}{OH^2}=\dfrac{1}{OA^2}+\dfrac{1}{OB^2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4}{b^2}+\dfrac{1}{b^2}=1\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5}{b^2}=1\Leftrightarrow b^2=5\Leftrightarrow b=\pm\sqrt{5}\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy \(\left(d_2\right)\) có dạng \(\left(d_2\right):y=2x+\sqrt{5}\) hoặc \(\left(d_2\right):y=2x-\sqrt{5}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
\(c,\text{Gọi điểm cần tìm là }A\left(x_0;y_0\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow y_0=mx_0-x_0+m-2\\ \Leftrightarrow m\left(x_0+1\right)-\left(x_0+y_0+2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_0+1=0\\x_0+y_0+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_0=-1\\y_0=-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow A\left(-1;-1\right)\\ \text{Vậy }A\left(-1;-1\right)\text{ là điểm cố định mà }\left(d\right)\text{ đi qua với mọi }m\)
\(\text{PT giao }Ox:y=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{2-m}{m-1}\Leftrightarrow A\left(\dfrac{2-m}{m-1};0\right)\Leftrightarrow OA=\left|\dfrac{m-2}{m-1}\right|\\ \text{PT giao }Oy:x=0\Leftrightarrow y=m-2\Leftrightarrow B\left(0;m-2\right)\Leftrightarrow OB=\left|m-2\right|\\ \text{Ta có }S_{OAB}=\dfrac{1}{2}OA\cdot OB=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot\left|\dfrac{m-2}{m-1}\right|\cdot\left|m-2\right|\\ \Leftrightarrow S_{OAB}=\dfrac{\left(m-2\right)^2}{2\left|m-1\right|}\)
Đặt \(S_{OAB}=t\)
Với \(m\ge1\Leftrightarrow t=\dfrac{\left(m-2\right)^2}{2\left(m-1\right)}\Leftrightarrow2mt-2t=m^2-4m+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2-2m\left(2-t\right)+2t+4=0\)
PT có nghiệm \(\Leftrightarrow\Delta'=\left(2-t\right)^2-\left(2t+4\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t^2-6t\ge0\Leftrightarrow t\left(t-6\right)\ge0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t\le0\\t\ge6\end{matrix}\right.\left(1\right)\)
Với \(m< 1\Leftrightarrow t=\dfrac{\left(m-2\right)^2}{2\left(1-m\right)}\Leftrightarrow2t-2mt=m^2-4m+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2+2m\left(t-2\right)+4-2t=0\)
PT có nghiệm \(\Leftrightarrow\Delta'=\left(t-2\right)^2-\left(4-2t\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t^2-2t\ge0\Leftrightarrow t\left(t-2\right)\ge0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t\le0\\t\ge2\end{matrix}\right.\left(2\right)\)
\(\left(1\right)\left(2\right)\Leftrightarrow t\ge6\)
Vậy \(\left(S_{OAB}\right)_{min}=6\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(m-2\right)^2}{2\left|m-1\right|}=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12\left|m-1\right|=m^2-4m+4\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}12\left(m-1\right)=m^2-4m+4\left(m\ge1\right)\\12\left(1-m\right)=m^2-4m+4\left(m< 1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m^2-16m+16=0\\m^2+8m-8=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=8\pm4\sqrt{3}\\m=-4\pm2\sqrt{6}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
cho hai đường thẳng d1:y=-x+2 và d2:y=-x/3-1/2
a) vẽ trên cùng một mặt phẳng Oxy hai đường thẳng d1; d2
b) viết pt đường thẳng đi qua điểm N ∈ d2 có hoành độ Xn = 3/4 đồng thời song song với đường thẳng d1
b: \(y_N=-\dfrac{3}{4}:3-\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{-1}{4}-\dfrac{1}{2}=-\dfrac{3}{8}\)
Vì (d)//(d1) nên a=-1
Vậy: (d): y=-x+b
Thay x=3/4 và y=-3/8 vào (d), ta được:
b-3/4=-3/8
hay b=3/8
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho 2 đường thẳng
(d1) y=x-7 (d2) y=-2x-1 viết phương trình đường thẳng (d) đi qua giao điểm của (d1) và (d2) đồng thời song song với đường thẳng x-2x+1
Cho (d1): y=x, (d2): y=0,5x. Đường thẳng (d) song song với trục Ox và cắt trục tung Oy tại điểm C có tung độ bằng 2. Đường thẳng (d) lần lượt cắt (d1) và (d2) tại D và E. Tính diện tích tam giác ODE
Cho 2 đường thẳng: y=2x-1(d1) và y=-x+2(d2)
a) Tìm tọa độ giao điểm M của (d1)và (d2)
b)viết pt đường thẳng (d) qua M nói trên và cắt trục Oy tại điểm có tung độ bằng 4
C)viết pt đường thẳng (d')qua gốc tọa độ O và song song với (d1)
a: tọa độ giao điểm M là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-1=-x+2\\y=2x-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1/Cho hai đường thẳng (d1):y = x + 4 và (d2):y = - 2x - 2 a) Vẽ đồ thị (d1) và (d2) trên cùng một mặt phẳng tọa độ. b) Cho đường thẳng (d3): y = ax + b . Xác định a và b biết đường thẳng (d3) song song với đường thẳng (d1) và (d3) cắt (d2)tại điểm A có hoành độ là -3.
\(b,\left(d_3\right)\text{//}\left(d_1\right)\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=1\\b\ne4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left(d_3\right):y=x+b\)
PT hoành độ giao điểm \(\left(d_2\right);\left(d_3\right)\) là \(x+b=-2x-2\)
Mà 2 đt cắt tại hoành độ \(-3\) nên \(x=-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow b-3=4\Leftrightarrow b=7\)
Vậy \(\left(d_3\right):y=x+7\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)