Giúp mik câu này nữa ạ

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Các bạn giúp mik với
X2 = 9/25
Ai làm đc thì giúp lun mik câu này nữa
Căn bậc √2x =2
Bạn nào tốt giúp mik lốt câu này với ạ
X2 = 0.09
Làm ơn giúp mik với
\(x^2=9/25 x=0,6 hoặc x=(-0,6); x^2=0,09 x=0,3 hoặc (-0,3); căn bậc 2x=2 x=2\)
Mọi người ơi giúp mik với, mik đg cần gấp 2 câu này lắm !!! 20 p nữa thôi mik học rồi mà chx xong, cho mik câu trả lời chi tiết các bước, đúng kết quả nhất với ạ !! xong mik se tick ! mik cam on !! SOS!!! 

11)
\(\dfrac{2x}{x+2}\) \(\times\) \(\dfrac{x^{2^{ }}-4}{4}\) - \(\dfrac{x}{2}\)
= \(\dfrac{2x}{x+2}\) \(\times\) \(\dfrac{x^2-2^2}{4}\) - \(\dfrac{x}{2}\)
= \(\dfrac{2x}{x+2}\) \(\times\) \(\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}{4}\) - \(\dfrac{x}{2}\)
= \(\dfrac{x\left(x-3\right)}{2}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
I waited for them _____ they arrived
A. after
B. because
C. when
Giúp mik câu này nữa ạ
Xem thêm câu trả lời
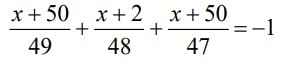
Giúp em câu này nữa ạ ;-;
\(\dfrac{x+50}{49}+\dfrac{x+2}{48}+\dfrac{x+50}{47}=-1\)
\(\dfrac{x+50}{49}+\left(\dfrac{x+2}{48}+1\right)+\dfrac{x+50}{47}=0\)
\(\dfrac{x+50}{49}+\dfrac{x+50}{48}+\dfrac{x+50}{47}=0\)
\(\left(x+50\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{49}+\dfrac{1}{48}+\dfrac{1}{47}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-50\) Vì \(\left(\dfrac{1}{49}+\dfrac{1}{48}+\dfrac{1}{47}\right)>0\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
làm hộ mik câu 1.2, 2.2(CÂU NÀY LÀM BẰNG PP CHẶN GIÚP MIK Ạ) , 3.2 nha
MIK CẢM ƠN Ạ
MIK ĐANG CẦN RẤT GẤP NÊN MỌI NGƯỜI GIÚP MIK Ạ

1.2 với \(x\ge0,x\in Z\)
A=\(\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}+7}{\sqrt{x}+2}=2+\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{x}+2}\in Z< =>\sqrt{x}+2\inƯ\left(3\right)=\left(\pm1;\pm3\right)\)
*\(\sqrt{x}+2=1=>\sqrt{x}=-1\)(vô lí)
*\(\sqrt{x}+2=-1=>\sqrt{x}=-3\)(vô lí
*\(\sqrt{x}+2=3=>x=1\)(TM)
*\(\sqrt{x}+2=-3=\sqrt{x}=-5\)(vô lí)
vậy x=1 thì A\(\in Z\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Cả câu này nữa ạ giúp e với
\(\dfrac{-188}{2017}< 0;\dfrac{1}{3678}>0\\ \Rightarrow\dfrac{-188}{2017}< \dfrac{1}{3678}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
vì\(\dfrac{-188}{2017}\)bé hơn 0 nên \(\dfrac{-188}{2017}\)<\(\dfrac{1}{3678}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Các bạn giúp mik vẽ hình cho bài này nữa với ạ😥😥😥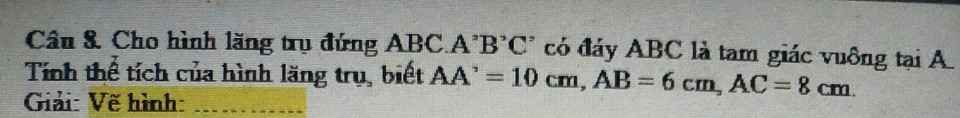
người ơi giúp mik với mik đg cần gấp lắm ạ!! Còn 20p nữa là mik học rồi nhưng mik vẫn còn 3 câu chx tính xong, mọi người giúp mik với ạ, cho mik câu trả lời chi tiết và rõ ràng các bước nhất với ạ!, mi cảm ơn! Xong thì mik sẽ tick ạ( cái ảnh thứ nhất là cách làm ạ.)
Đọc tiếp
người ơi giúp mik với mik đg cần gấp lắm ạ!! Còn 20p nữa là mik học rồi nhưng mik vẫn còn 3 câu chx tính xong, mọi người giúp mik với ạ, cho mik câu trả lời chi tiết và rõ ràng các bước nhất với ạ!, mi cảm ơn! Xong thì mik sẽ tick ạ( cái ảnh thứ nhất là cách làm ạ.)
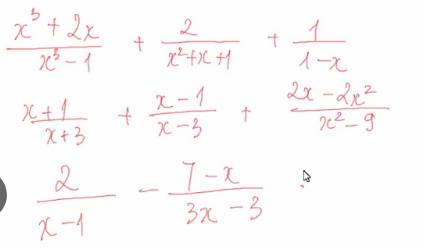
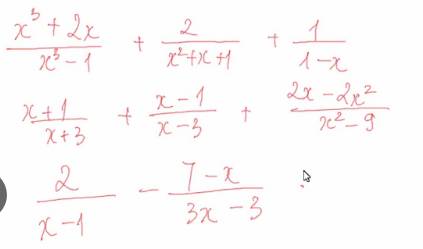
a: \(=\dfrac{x^3+2x+2x-2-x^2-x-1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3-x^2+3x-3}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}=\dfrac{x^2+3}{x^2+x+1}\)
b: \(=\dfrac{x^2-2x-3+x^2+2x-3+2x-2x^2}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x-6}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\dfrac{2}{x+3}\)
c: \(=\dfrac{6-7+x}{3\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{x-1}{3\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
d: \(=\dfrac{x^3+2x+2x-2-x^2-x-1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}=\dfrac{x^3-x^2+3x-3}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}=\dfrac{x^2+3}{x^2+x+1}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
 giúp em câu này nữa ạ, làm phiền mấy anh chị rồi ạ, xl :)
giúp em câu này nữa ạ, làm phiền mấy anh chị rồi ạ, xl :)
Bài 3:
theo đề bài ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2a-3b=0\\5b-7c=0\\3a-7b+5c=30\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=42\\b=28\\c=20\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (2)
Bài 4:
Đặt \(\dfrac{x}{4}=\dfrac{y}{5}=\dfrac{z}{6}=k\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=4k\\y=5k\\z=6k\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có: \(x^2-2y^2+z^2=18\)
\(\Leftrightarrow16k^2-50k^2+36k^2=18\)
\(\Leftrightarrow k^2=9\)
Trường hợp 1: k=3
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=4k=4\cdot3=12\\y=5k=5\cdot3=15\\z=6k=6\cdot3=18\end{matrix}\right.\)
Trường hợp 2: k=-3
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=4k=-3\cdot4=-12\\y=5k=-3\cdot5=-15\\z=6k=-3\cdot6=-18\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)