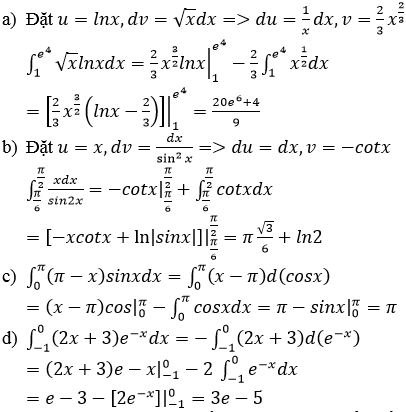Tính các tích phân sau: ∫ 1 2 1 e x e 2 x - 1 d x

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Tính các tích phân sau: 1) 2 ln e e x dx ; 2) 1 3 2 0 4 x dx x ; 3) /2 /4 1 tan dx x ; 4) 1 0 x e dx ; 5) 2 1 x xe dx ; 6) 0 1 3 4 dx x ; 7) 2 1 4 4 5 dx x x ; 8) 2 0 ln 1 x dx x (HD: 1 u x ) ĐS: 1) 2 e ; 2) 16 7 5 3 ; 3) ln 2 ; 4) 2
PHÂN TÍCH CÁC BIỂU THỨC SAU THÀNH PHÂN TỬ :
E) 2X2(x+1)+4(X+1) F) -3x - 6xy + 9xz
e) \(2x^2\left(x+1\right)+4\left(x+1\right)\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)\left(2x^2+4\right)\)
\(=2\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+2\right)\)
f) \(-3x-6xy+9xz\)
\(=-3\left(x+2y-3z\right)\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
nhờ giải giupws em với a
1. Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử:
a) 5x2 – 10xy
b) 3x(x – y) – 6(x – y)
c) 2x(x – y) – 4y(y – x)
d) 9x2 – 9y2
e) x2 – xy – x + y
f) xy – xz – y + z
2. Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử:
a)a2 – 4b2 b) x2 – y2 + 6y - 9
c) (2a + b)2 – a2 d) 16(x – 1)2 – 25(x + y)2
e)x2 + 10x + 25 f) 25x2 – 20xy + 4y2
...
Đọc tiếp
nhờ giải giupws em với a
1. Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử:
a) 5x2 – 10xy
b) 3x(x – y) – 6(x – y)
c) 2x(x – y) – 4y(y – x)
d) 9x2 – 9y2
e) x2 – xy – x + y
f) xy – xz – y + z
2. Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử:
a)a2 – 4b2 b) x2 – y2 + 6y - 9
c) (2a + b)2 – a2 d) 16(x – 1)2 – 25(x + y)2
e)x2 + 10x + 25 f) 25x2 – 20xy + 4y2
g)9x4 + 24x2 + 16 h) x3 – 125
i)x6 – 1 k) x3 + 15x2 + 75x + 125
3. Tìm x biết :
a) 3x2 + 8x = 0 b) 9x2 – 25 = 0 c) x3 – 16x = 0 d) x3 + x = 0.
4. Chứng minh rằng với mọi số nguyên a thì: a3 – a chia hết cho 6
Bài `1`
\(a,5x^2-10xy=5x\left(x-2y\right)\\ b,3x\left(x-y\right)-6\left(x-y\right)=\left(x-y\right)\left(3x-6\right)\\ =3\left(x-y\right)\left(x-2\right)\\ c,2x\left(x-y\right)-4y\left(y-x\right)=2x\left(x-y\right)+4y\left(x-y\right)\\ =\left(x-y\right)\left(2x+4y\right)=2\left(x-y\right)\left(x+2y\right)\\ d,9x^2-9y^2=\left(3x\right)^2-\left(3y\right)^2=\left(3x-3y\right)\left(3x+3y\right)\\ f,xy-xz-y+z=\left(xy-xz\right)-\left(y-z\right)\\ =x\left(y-z\right)-\left(y-z\right)=\left(y-z\right)\left(x-1\right)\)
Bài `3`
\(a,3x^2+8x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(3x+8\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\3x+8=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\3x=-8\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-\dfrac{8}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(b,9x^2-25=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3x\right)^2-5^2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3x-5\right)\left(3x+5\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x-5=0\\3x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x=5\\3x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5}{3}\\x=-\dfrac{5}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(c,x^3-16x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(x^2-16\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x-4=0\\x+4=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=4\\x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(d,x^3+x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(x^2+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2+1\in\varnothing\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow x=0\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Tính diện tích các hình phẳng giới hạn bởi các đường sau: y = x - 1 + lnx x , y = x - 1 và x = e
Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử:a/ y2 - 2y b/ 3x4 – 6x3 + 3x2 c/ 27x2 ( y – 1) – 9x3 ( 1 - y) d/y3 – 2y2 + y e/ x3 + 6x2 + 9x f/ x3 – 2x2y + xy2g/ x( 2- x) – x + 2 h/ 3x ( x – 1) + 6( 1 – x)
Đọc tiếp
Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử:
a/ y2 - 2y b/ 3x4 – 6x3 + 3x2
c/ 27x2 ( y – 1) – 9x3 ( 1 - y) d/y3 – 2y2 + y
e/ x3 + 6x2 + 9x f/ x3 – 2x2y + xy2
g/ x( 2- x) – x + 2 h/ 3x ( x – 1) + 6( 1 – x)
\(a,=y\left(y-2\right)\\ b,=3x\left(x^2-2x+1\right)=3x\left(x-1\right)^2\\ c,=\left(y-1\right)\left(27x^2+9x^3\right)=9x^2\left(x+3\right)\left(y-1\right)\\ d,=y\left(y^2-2y+1\right)=y\left(y-1\right)^2\\ e,=x\left(x^2+6x+9\right)=x\left(x+3\right)^2\\ f,=x\left(x^2-2xy+y^2\right)=x\left(x-y\right)^2\\ g,=\left(2-x\right)\left(x+1\right)\\ h,=\left(x-1\right)\left(3x-6\right)=3\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
a: =y(y-2)
b: \(=3x^2\left(x^2-2x+1\right)=3x^2\left(x-1\right)^2\)
d: \(=y\left(y^2-2y+1\right)=y\left(y-1\right)^2\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử:
a) \({\left( {x - 1} \right)^2} - 4\)
b) \(4{x^2} + 12x + 9\)
c) \({x^3} - 8{y^6}\)
d) \({x^5} - {x^3} - {x^2} + 1\)
e) \( - 4{x^3} + 4{x^2} + x - 1\)
f) \(8{x^3} + 12{x^2} + 6x + 1\)
\(a,\left(x-1\right)^2-2^2=\left(x-1-2\right)\left(x-1+2\right)=\left(x-3\right)\left(x+1\right)\\ b,=\left(2x\right)^2+2.2x.3+3^2\\ =\left(2x+3\right)^2\\ c,=x^3-\left(2y\right)^3\\ =\left(x-2y\right)\left(x^2+2xy+4y^2\right)\\ d,=x^3\left(x^2-1\right)-\left(x^2-1\right)\\ =\left(x^3-1\right)\left(x^2-1\right)\\ =\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\\ =\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)\)
\(e,=-4x^2\left(x-1\right)+\left(x-1\right)\\ =\left(1-4x^2\right)\left(x-1\right)\\ =\left(1-2x\right)\left(1+2x\right)\left(x-1\right)\)
\(f,=\left(2x\right)^3+3.\left(2x\right)^2.1+3.2x.1^2+1^3\\ =\left(2x+1\right)^3\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử:
\(e,x^2-y^2+2x+1\)
\(f,x^3+2x^2+2x+1\)
\(e,x^2-y^2+2x+1=\left(x^2+2x+1\right)-y^2\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)^2-y^2=\left(x+1-y\right)\left(x+1+y\right)\)
\(f,x^3+2x^2+2x+1=\left(x^3+1\right)+\left(2x^2+2x\right)\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)+2x\left(x+1\right)\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1+2x\right)\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(x^2-y^2+2x+1\)
\(=\left(x^2+2x+1\right)-y^2\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)^2-y^2\)
\(=\left(x-y+1\right)\left(x+y+1\right)\)
hk tốt
^^
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tính các tích phân sau bằng phương pháp tính tích phân từng phần :
a) \(\int\limits^{e^4}_1\sqrt{x}\ln xdx\)
b) \(\int\limits^{\dfrac{\pi}{2}}_{\dfrac{\pi}{6}}\dfrac{xdx}{\sin^2x}\)
c) \(\int\limits^{\pi}_0\left(\pi-x\right)\sin xdx\)
d) \(\int\limits^0_{-1}\left(2x+3\right)e^{-x}dx\)
Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử:
b) x^2-4y^2+2x+4y
e) 6x^2-150y^2+60y-6
f) x^2(x+1)+x(x+2)-4(x+1)
g) x^35+x^34+x^33+...+x^2+x+1
Tính các tích phân sau:
∫
0
π
4
x
sin
x
+
(
x
+
1
)
cos
x
xsinx
+
cosx...
Đọc tiếp
Tính các tích phân sau: ∫ 0 π 4 x sin x + ( x + 1 ) cos x xsinx + cosx d x