Cho log 2 x 2 + y 2 = 1 + log 2 x y x y > 0 Chọn khẳng định đúng trong các khẳng định sau ?
A. x > y
B. x = y
C. x < y
D. x = y 2
Cho các số thực dương x, y ≠ 1 và thoả mãn logxy=logyx, logx(x-y)=logy(x+y). Giá trị của x2+xy+y2bằng:
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne y\)
\(log_xy=\frac{1}{log_xy}\Leftrightarrow log_x^2y=1\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}log_xy=1\\log_xy=-1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=y\left(l\right)\\x=\frac{1}{y}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(log_x\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)=log_{x^{-1}}\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)\Leftrightarrow log_x\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)=-log_x\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_x\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-\frac{1}{x^2}=1\Leftrightarrow x^4-x^2-1=0\Rightarrow x^2=\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2}\Rightarrow y^2=\frac{1}{x^2}=\frac{-1+\sqrt{5}}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+xy+y^2=\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2}+1+\frac{-1+\sqrt{5}}{2}=\sqrt{5}+1\)
Cho các số thực dương x, y ≠ 1 và thoả mãn logxy=logyx, logx(x-y)=logy(x+1). Giá trị của x2+xy+y2 bằng:
\(log_xy=log_yx=\frac{1}{log_xy}\Rightarrow\left(log_xy\right)^2=1\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}log_xy=1\\log_xy=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=y\\x=\frac{1}{y}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Do \(log_x\left(x-y\right)\) tồn tại \(\Rightarrow x-y\ne0\Rightarrow x\ne y\Rightarrow x=\frac{1}{y}\)
\(log_x\left(x-y\right)=log_y\left(x+1\right)\Leftrightarrow log_x\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)=-log_x\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_x\left[\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)\left(x+1\right)\right]=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)\left(x+1\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=x\Leftrightarrow x^3+x^2-2x-1=0\)
Pt này nghiệm xấu, đề bài có vấn đề
Cho đồ thị của hàm số \(y = {\log _2}x\) và y = 2 như Hình 6.8. Tìm khoảng giá trị của x mà đồ thị hàm số \(y = {\log _2}x\) nằm phía trên đường thẳng y = 2 và từ đó suy ra tập nghiệm của bất phương trình \({\log _2}x > 2.\)
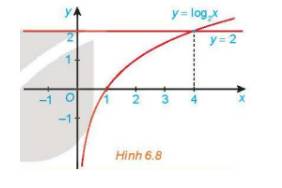
Khoảng giá trị của x mà đồ thị hàm số \(y=log_2x\) nằm phía trên đường thẳng y = 2 là \(\left(4;+\infty\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Tập nghiệm của bất phương trình \(log_2x>2\) là \(\left(4;+\infty\right)\)
Trong các hàm số sau, những hàm số nào là hàm số lôgarit? Khi đó hãy chỉ ra cơ số.
a) \(y = {\log _{\sqrt 3 }}x;\)
b) \(y = {\log _{{2^{ - 2}}}}x;\)
c) \(y = {\log _x}2;\)
d) \(y = {\log _{\frac{1}{x}}}5.\)
Hàm số a,b là các hàm số logarit
a: \(log_{\sqrt{3}}x\)
Cơ số là \(\sqrt{3}\)
b: \(log_{2^{-2}}x\)
Cơ số là \(2^{-2}=\dfrac{1}{4}\)
70. Cho 2 số dương x và y thỏa mãn log2(x+1) + log2(y+1) ≥ 6. Giá trị nhỏ nhất của S = x + y ?
Viết công thức biểu thị \(y\) theo \(x\), biết \(2{\log _2}y = 2 + \frac{1}{2}{\log _2}x\).
\(2log_2y=2+\dfrac{1}{2}log_2x\)
=>\(log_2y^2=log_22^2+log_2x^{\dfrac{1}{2}}\)
=>\(log_2y^2=log_2\left(2^2\cdot x^{\dfrac{1}{2}}\right)\)
=>\(y^2=4\cdot x^{\dfrac{1}{2}}=4\sqrt{x}\)
Tìm tập xác định của các hàm số sau :
a) \(y=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{4^x-2}}\)
b) \(y=\log_6\dfrac{3x+2}{1-x}\)
c) \(y=\sqrt{\log x+\log\left(x+2\right)}\)
d) \(y=\sqrt{\log\left(x-1\right)+\log\left(x+1\right)}\)
Với các số thực dương xyz đôi một khác nhau thỏa xyz=1 và x,y,z khác 1 tìm minP=logx\(\dfrac{y}{z}\)+logy\(\dfrac{z}{x}\)+logz\(\dfrac{x}{y}\)+2(log\(\dfrac{y}{z}\)(x)+log\(\dfrac{z}{x}\)(y)+log\(\dfrac{x}{y}\)(z))
Tìm tập xác định của các hàm số:
a) \(y = 12{}^x\)
b) \(y = {\log _5}(2x - 3)\)
c) \(y = {\log _{\frac{1}{5}}}\left( { - {x^2} + 4} \right)\)
\(a,D=R\\ b,2x-3>0\\ \Rightarrow x>\dfrac{3}{2}\\ \Rightarrow D=(\dfrac{3}{2};+\infty)\\ c,-x^2+4>0\\ \Rightarrow x^2< 4\\ \Leftrightarrow-2< x< 2\\ \Rightarrow D=\left(-2;2\right)\)
Cho x,y >0, x,y khác 1,logyx+ logxy =\(\dfrac{10}{3}\) và xy=144,vậy \(\dfrac{x+y}{2}\)=?
A.24 B.30 C.12\(\sqrt{2}\) D.13\(\sqrt{3}\)
Lời giải:
Đặt \(\log_yx=a,\log_xy=b\). Khi đó ta có:
\(\left\{\begin{matrix} a+b=\frac{10}{3}\\ ab=\log_xy.\log_yx=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Áp dụng định lý Viete đảo thì \(a,b\) là nghiệm của PT:
\(x^2-\frac{10}{3}x+1=0\) . PT trên có hai nghiệm \(3,\frac{1}{3}\)
Giả sử \(a=\log_yx=3\) và \(b=\log_xy=\frac{1}{3}\)
\(\left\{\begin{matrix} \log_y\left(\frac{144}{y}\right)=3\\ \log_x\left(\frac{144}{x}\right)=\frac{1}{3} \end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} x=24\sqrt{3}\\ y=2\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow \frac{x+y}{2}=13\sqrt{3}\). Đáp án D