.cíu mình với mn

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Các bạn ơi cíu mình với, thanks mn nha
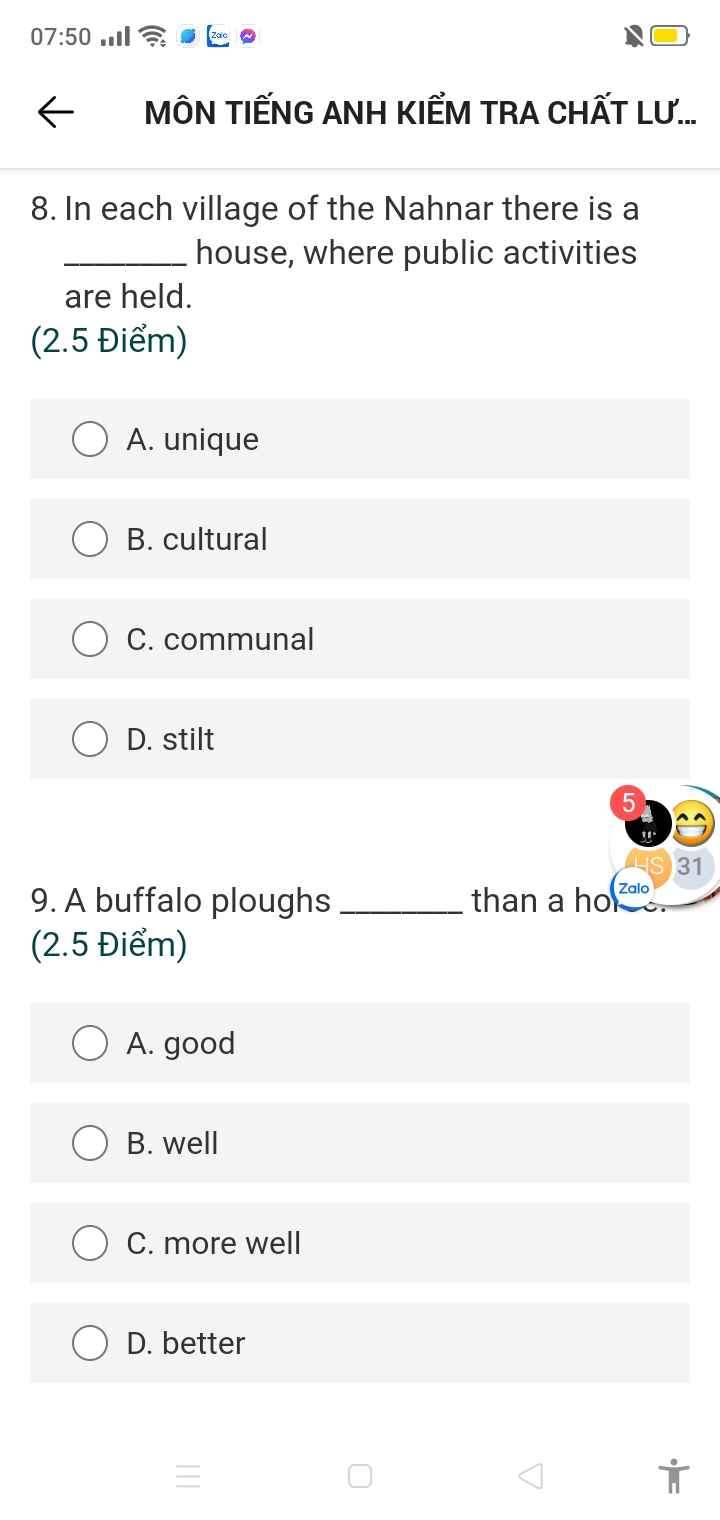
1 lived
2 wasn't hearing - was thinking
3 walked - was
4 were you doing - phoned
5 was reading - heard
6 was walking - saw
7 had watched - wrote
8 met
9 had you done - moved
10 was - didn't attend
II
1 when we were having lunch
2 had read the instruction, I started the machine
3 went out for a rest, we had finished our assignment
4 she left, it was raining
5 learning English
6 to help me
7 the man to open the briefcase
8 my friend break the bottle
9 him fall off the bike
10 a foreign language in a short time is not easy
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
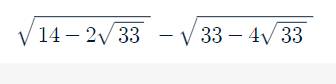 Cíu mình dới mn ơi huhu
Cíu mình dới mn ơi huhu
cần chi tiết ko bạn
hay mỗi đáp án nhợ![]()
Đúng 0
Bình luận (1)
Ta có:\(\sqrt{14-2\sqrt{33}}\)=1,584573983
\(\sqrt{33-4\sqrt{33}}\)=3,165714677
=>1,584573983\(-\)3,165714677=-1,581140694
nhé bạn![]()
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
(-3).7 cíu mình,cầu xin,vái lạy mn
Xem thêm câu trả lời

CÍU TUI BÀI 5 VỚI Ạ. THANK MN!
\(=\dfrac{35\cdot0.1\cdot154\cdot243\cdot50}{35\cdot154\cdot0.1\cdot121.5\cdot100}\)
\(=\dfrac{243}{121.5}\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}=1\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
(−53).x2−1125. cíu với mn ơi pls
Đọc tiếp
. cíu với mn ơi pls
(-5)3.\(x^2\) = - 1125
\(x^2\) = (-1125) : (-53)
\(x^2\) = 9
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\) \(\in\) {-3; 3}
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(\left(-5\right)^3.x^2=-1125\)
\(x^2=-1125:\left(-5\right)^3\)
\(x^2=-1125:\left(-125\right)\)
\(x^2=9\)
\(x^2=3^2\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇒ Vậy \(x\in\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3\\-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
mn cíu e với ạ. e cảm ơn nhaa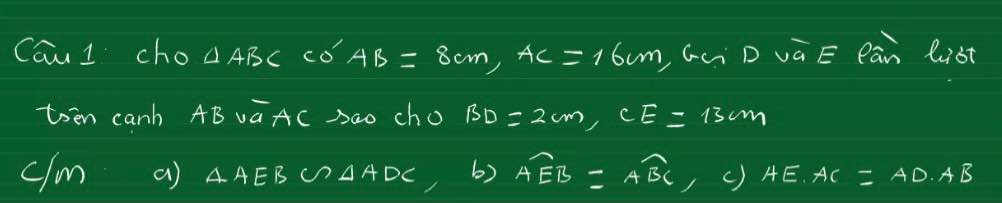
Mn ơi , giúp mình đc ko , SOS !!!
2x+1 là ước của 3x+2
ai trả lời nhanh tick cho nha , cíu!!!!!!
2x+1 là ước của 3x+2
⇔3x+2 ⋮ 2x+1
⇒2(3x+2) ⋮ 2x+1
⇔6x+4 ⋮ 2x+1
⇔(2x+1)+(2x+1)+(2x+1)+1 ⋮ 2x+1
Để 3x+2 ⋮ 2x+1 thì 2x+1 ∈ Ư(1)
Ta có:
Ư(1)={±1}
⇒2x+1∈{±1}
⇒x∈{0;-1}
Vậy x={0;-1)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Ta có : 2x + 1 là ước của 3x + 2
=> 3x + 2 ⋮ 2x + 1
=> 2(3x + 2) ⋮ 2x + 1
=> 6x + 4 ⋮ 2x + 1
=> (6x + 3) + 1 ⋮ 2x + 1
=> 3(2x + 1) + 1 ⋮ 2x + 1
Vì 3(2x + 1) ⋮ 2x + 1 nên 1 ⋮ 2x + 1
=> 2x + 1 ∈ Ư(1) ∈ {-1;1}
=> x ∈ {-1;0}
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
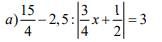 Cíu mình với=(((
Cíu mình với=(((
a, \(\dfrac{15}{4}\) - 2,5 : |\(\dfrac{3}{4}\)\(x\) + \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)| = 3
3,75 - 2,5:|\(\dfrac{3}{4}\)\(x\) + \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)| = 3
2,5:|\(\dfrac{3}{4}\)\(x\) + \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)| = 3,75 - 3
2,5 : |\(\dfrac{3}{4}\)\(x\) + \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)| = 0,75
|\(\dfrac{3}{4}\)\(x\) + \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)| = 2,5 : 0,75
|\(\dfrac{3}{4}\)\(x\) + \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)| = \(\dfrac{10}{3}\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3}{4}x+\dfrac{1}{2}=-\dfrac{10}{3}\\\dfrac{3}{4}x+\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{10}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3}{4}x=-\dfrac{10}{3}-\dfrac{1}{2}\\\dfrac{3}{4}x=\dfrac{10}{3}-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3}{4}x=-\dfrac{26}{3}\\\dfrac{3}{4}x=\dfrac{17}{6}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{46}{9}\\x=\dfrac{34}{9}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cíu mình với ạ
a. Ta có: $\sin x\in [-1;1]$ nên $|\sin x|\in [0;1]$
$\Rightarrow 1\leq 3-2|\sin x|\leq 3$
Vậy $y_{\min}=1; y_{\max}=3$
b.
$y=\frac{1-\cos 2x}{2}-\frac{3}{2}\sin 2x+1$
$2y=3-\cos 2x-3\sin 2x$
$3-2y=\cos 2x+3\sin x$
Áp dụng định lý Bunhiacopxky:
$(3-2y)^2\leq (\cos ^22x+\sin ^22x)(1+3^2)=10$
$\Rightarrow -\sqrt{10}\leq 3-2y\leq \sqrt{10}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{3-\sqrt{10}}{2}\leq y\leq \frac{3+\sqrt{10}}{2}$
Vậy $y_{\max}=\frac{1+\sqrt{10}}{2}; y_{\min}=\frac{1-\sqrt{10}}{2}$
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
c.
\(y=\sqrt{5-\frac{1}{4}(2\sin x\cos x)^2}=\sqrt{5-\frac{1}{2}\sin ^22x}\)
Vì $\sin 2x\in [-1;1]$
$\Rightarrow \sin ^22x\in [0;1]$
$\Rightarrow \frac{3\sqrt{2}}{2}\leq \sqrt{5-\frac{1}{2}\sin ^22x}\leq \sqrt{5}$
d.
$\cos (x+\frac{\pi}{3})\in [-1;1]$
$\Rightarrow 2(-1)+3\leq 2\cos (x+\frac{\pi}{3})+3\leq 2.1+3$
$\Rightarrow 1\leq y\leq 5$
$\Rightarrow y_{\min}=1; y_{\max}=5$
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
e.
\(y=2\sin ^2x-\cos 2x=1-\cos 2x-\cos 2x=1-2\cos 2x\)
Vì $\cos 2x\in [-1;1]$ nên:
$-1\leq 1-2\cos 2x\leq 3$
Vậy $y_{\min}=-1; y_{\max}=3$
f.
$y=(\sin ^2x+\cos ^2x)^2-2(\sin x\cos x)^2$
$=1-\frac{1}{2}\sin ^22x$
Vì $-1\leq \sin 2x\leq 1\Rightarrow 0\leq \sin ^22x\leq 1$
$\Rightarrow \frac{1}{2}\leq y\leq 1$
Vậy $y_{\min}=\frac{1}{2};y_{\max}=1$
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời



























