Giúp mình với mn ơi mình cần gấp


Những câu hỏi liên quan
mn ơi giúp mình với ạ, mình cần gấp,mình cảm ơn mn
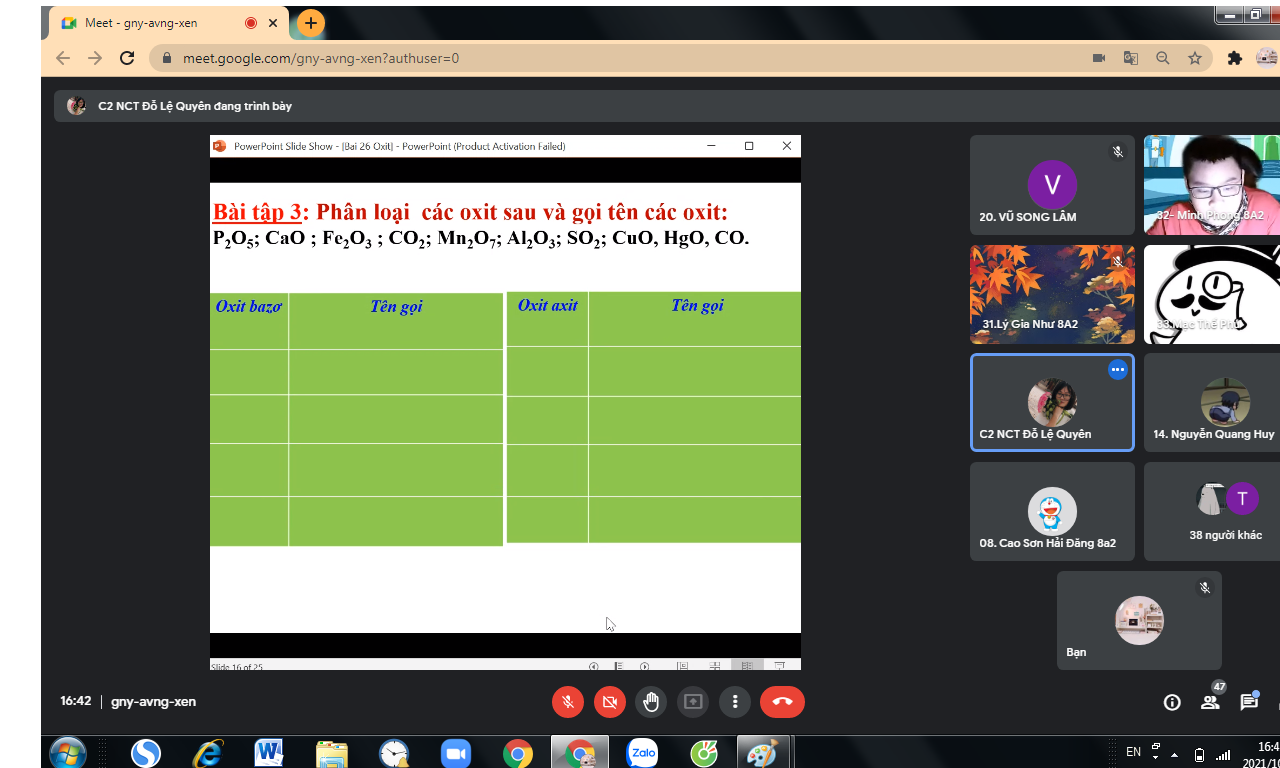
mn ơi giúp mình với ! (mình cần gấp :() 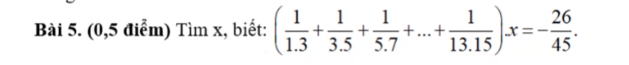
\(\left(\dfrac{1}{1.3}+\dfrac{1}{3.5}+...+\dfrac{1}{13.15}\right).x=\dfrac{-26}{45}\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(\dfrac{2}{1.3}+\dfrac{2}{3.5}+...+\dfrac{2}{13.15}\right).x=\dfrac{-52}{45}\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(1-\dfrac{1}{3}+\dfrac{1}{3}-\dfrac{1}{5}+...+\dfrac{1}{13}-\dfrac{1}{15}\right).x=\dfrac{-52}{45}\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(1-\dfrac{1}{15}\right).x=\dfrac{-52}{45}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{14}{15}.x=\dfrac{-52}{45}\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{26}{21}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
(11.3+13.5+...+113.15).x=−2645⇔(21.3+23.5+...+213.15).x=−5245⇔(1−13+13−15+...+113−115).x=−5245⇔(1−115).x=−5245⇔1415.x=−5245⇔x=−2621
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giúp mình với mn ơi , mình cần gấp!
Giúp mình với mn ơi,mình cần gấp
giúp mình với mn ơi , mình cần gấp lắm
Mn ơi giúp mình với mình cần gấp ạ 
\(a,A=\dfrac{x+2\sqrt{x}+1+x-2\sqrt{x}+1-3\sqrt{x}-1}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\\ A=\dfrac{2x-3\sqrt{x}+1}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(2\sqrt{x}-1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}=\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}-1}{\sqrt{x}+1}\\ b,A=\dfrac{2\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)-3}{\sqrt{x}+1}=2-\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{x}+1}\in Z\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}+1\inƯ\left(3\right)=\left\{1;3\right\}\left(\sqrt{x}+1\ge1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}\in\left\{0;2\right\}\\ \Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{0;4\right\}\left(tm\right)\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
a) \(A=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-1}+\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-1}{\sqrt{x}+1}-\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}+1}{x-1}\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)^2}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}+\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)^2}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}-\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}+1}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{x+2\sqrt{x}+1}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}+\dfrac{x-2\sqrt{x}+1}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}-\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}+1}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{x+2\sqrt{x}+1+x-2\sqrt{x}+1-3\sqrt{x}-1}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{2x-3\sqrt{x}+1}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{\left(2x-2\sqrt{x}\right)-\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)-\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{\left(2\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}-1}{\sqrt{x}+1}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Mn ơi giúp mình với mình đang cần gấp

1. that - because
2. that
3. that - who
4. That - so
5. Where - what - who
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1 that - because
2 that
3 that - who
4 That - so
5 Where - what - who
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Mn ơi giúp mình với ạ mình cần gấp ạ
1 his illness, he cannot come
2 her busyness, she couldn't help us
3 his illness, he tries to go to school on time
4 the bad weather, we tried to finish the work on the road
5 the bad weather, we got to the station late
6 the old house, she liked it
7 not wearing any shoes, Carol ran outside to see what was happening
8 being afraid of flying, Fiona had to get on the plane
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Giúp mình bài 2 với Mn ơi
Mình cần gấp!!! 
Bài 2:
a: Xét ΔABC có
BI,CI là các đường phân giác
BI cắt CI tại I
Do đó: I là tâm đường tròn nội tiếp ΔABC
b: Ta có: \(\widehat{DIB}=\widehat{IBC}\)(hai góc so le trong, DI//BC)
\(\widehat{DBI}=\widehat{IBC}\)(BI là phân giác của góc DBC)
Do đó: \(\widehat{DIB}=\widehat{DBI}\)
=>ΔDIB cân tại D
c: Ta có: \(\widehat{EIC}=\widehat{ICB}\)(hai góc so le trong, EI//BC)
\(\widehat{ECI}=\widehat{ICB}\)(CI là phân giác của góc ECB)
Do đó: \(\widehat{EIC}=\widehat{ECI}\)
=>ΔEIC cân tại E
d: Ta có: ΔDIB cân tại D
=>DB=DI
Ta có: ΔEIC cân tại E
=>EI=EC
Ta có: DI+IE=DE
mà DI=DB
và EC=EI
nên DB+EC=DE
Bài 1:
a: Xét ΔABC có
BE,CF là các đường phân giác
BE cắt CF tại I
Do đó: I là tâm đường tròn nội tiếp ΔABC
=>AI là phân giác của góc BAC
b: ta có: \(\widehat{ABE}=\widehat{CBE}=\dfrac{\widehat{ABC}}{2}\)(BE là phân giác của góc ABC)
\(\widehat{ACF}=\widehat{FCB}=\dfrac{\widehat{ACB}}{2}\)(CF là phân giác của góc ACB)
mà \(\widehat{ABC}=\widehat{ACB}\)
nên \(\widehat{ABE}=\widehat{EBC}=\widehat{ACF}=\widehat{FCB}\)
c: ta có: \(\widehat{EBC}=\widehat{FCB}\)
=>\(\widehat{IBC}=\widehat{ICB}\)
=>ΔIBC cân tại I
d: Xét ΔABE và ΔACF có
\(\widehat{ABE}=\widehat{ACF}\)
AB=AC
\(\widehat{BAE}\) chung
Do đó: ΔABE=ΔACF
=>BE=CF
e:
Ta có: ΔAEB=ΔAFC
=>AE=AF
Ta có: AE+EC+AC
AF+FB=AB
mà AE=AF
và AC=AB
nên EC=FB
Xét ΔFIB và ΔEIC có
FB=EC
\(\widehat{FBI}=\widehat{ECI}\)
BI=CI
Do đó: ΔFIB=ΔEIC
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)























