Tìm x, biết:
a, x2 - 10x + 9 = 0 (làm bằng 2 cách)
b, 8x2 - 2x - 15 = 0 (làm bằng 2 cách)
c, 2x2 + 8x - 7 = 0
d, 3x2 - 15x + 3 = 0
e, 16x2 - 24x - 4 = 0
f, -5x2 + 6x + 3 = 0
i, 6x2 - 9x + 40 = 0
Giải các phương trình sau:
a, x2 - 9x +20 = 0
b, x2 - 3x - 18 = 0
c, 2x2 - 9 x + 9 = 0
d, 3x2 - 8x + 4 = 0
e, 3x3 - 6x2 - 9x = 0
f, x(x - 5) - 2 + x = 0
g, x3 + 32 + 6x +8 = 0
h, 2x(x - 2) - 2 + x = 0
i, 5x(1 - x) + x - 1 = 0
k, 4 - 9(x - 1)2 = 0
l, (x - 2)2 - 36(x + 3)2 = 0
\(a)x^2-9x+20=0 \\<=>(x-4)(x-5)=0 \\<=>x=4\ hoặc\ x=5 \\b)x^2-3x-18=0 \\<=>(x+3)(x-6)=0 \\<=>x=-3\ hoặc\ x=6 \\c)2x^2-9x+9=0 \\<=>(x-3)(2x-3)=0 \\<=>x=3\ hoặc\ x=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
d: \(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-6x-2x+4=0\)
=>(x-2)(3x-2)=0
=>x=2 hoặc x=2/3
e: \(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x^2-2x-3\right)=0\)
=>x(x-3)(x+1)=0
hay \(x\in\left\{0;3;-1\right\}\)
f: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x-2+x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2=6\)
hay \(x\in\left\{\sqrt{6}+2;-\sqrt{6}+2\right\}\)
Tìm x, biết:
a, x2 - 10x + 9 = 0 (làm bằng 2 cách)
b, 8x2 - 2x - 15 = 0 (làm bằng 2 cách)
c, 2x2 + 8x - 7 = 0
d, 3x2 - 15x + 3 = 0
e, 16x2 - 24x - 4 = 0
f, -5x2 + 6x + 3 = 0
i, 6x2 - 9x + 40 = 0
a)
Cách 1:
Ta có: \(x^2-10x+9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x-9x+9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-1\right)-9\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-9\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\x-9=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=9\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={1;9}
Cách 2:
Ta có: \(x^2-10x+9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-10x+25-16=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)^2=16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-5=4\\x-5=-4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=9\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={9;1}
b)
Cách 1:
Ta có: \(8x^2-2x-15=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8x^2-12x+10x-15=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x\left(2x-3\right)+5\left(2x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-3\right)\left(4x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-3=0\\4x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=3\\4x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\frac{3}{2}\\x=\frac{-5}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\frac{3}{2};\frac{-5}{4}\right\}\)
Cách 2:
Ta có: \(8x^2-2x-15=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8\left(x^2-\frac{1}{4}x-\frac{15}{8}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-\frac{1}{4}x-\frac{15}{8}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2\cdot x\cdot\frac{1}{8}+\frac{1}{64}-\frac{121}{64}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\frac{1}{8}\right)^2=\frac{121}{64}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-\frac{1}{8}=\frac{11}{8}\\x-\frac{1}{8}=-\frac{11}{8}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\frac{12}{8}=\frac{3}{2}\\x=\frac{-11+1}{8}=\frac{-10}{8}=\frac{-5}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\frac{3}{2};\frac{-5}{4}\right\}\)
c) Ta có: \(2x^2+8x-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(x^2+4x-\frac{7}{2}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+4x+4-\frac{15}{2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)^2=\frac{15}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+2=\sqrt{\frac{15}{2}}\\x+2=-\sqrt{\frac{15}{2}}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\sqrt{\frac{15}{2}}-2\\x=-\sqrt{\frac{15}{2}}-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\sqrt{\frac{15}{2}}-2;-\sqrt{\frac{15}{2}}-2\right\}\)
d) Ta có: \(3x^2-15x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\left(x^2-5x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2\cdot x\cdot\frac{5}{2}+\frac{25}{4}-\frac{21}{4}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\frac{5}{2}\right)^2=\frac{21}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-\frac{5}{2}=\frac{\sqrt{21}}{2}\\x-\frac{5}{2}=-\frac{\sqrt{21}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\frac{\sqrt{21}+5}{2}\\x=\frac{-\sqrt{21}+5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\frac{\sqrt{21}+5}{2};\frac{-\sqrt{21}+5}{2}\right\}\)
e) Ta có: \(16x^2-24x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(4x^2-6x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-6x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x\right)^2-2\cdot2x\cdot\frac{3}{2}+\frac{9}{4}-\frac{13}{4}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-\frac{3}{2}\right)^2=\frac{13}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-\frac{3}{2}=\frac{\sqrt{13}}{2}\\2x-\frac{3}{2}=-\frac{\sqrt{13}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=\frac{3+\sqrt{13}}{2}\\2x=\frac{3-\sqrt{13}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\frac{3+\sqrt{13}}{2}:2=\frac{3+\sqrt{13}}{4}\\x=\frac{3-\sqrt{13}}{2}:2=\frac{3-\sqrt{13}}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\frac{3+\sqrt{13}}{4};\frac{3-\sqrt{13}}{4}\right\}\)
f) Ta có: \(-5x^2+6x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-5\left(x^2-\frac{6}{5}x-\frac{3}{5}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-\frac{6}{5}x-\frac{3}{5}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2\cdot x\cdot\frac{3}{5}+\frac{9}{25}-\frac{24}{25}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\frac{3}{5}\right)^2=\frac{24}{25}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-\frac{3}{5}=\frac{2\sqrt{6}}{5}\\x-\frac{3}{5}=\frac{-2\sqrt{6}}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\frac{3+2\sqrt{6}}{5}\\x=\frac{3-2\sqrt{6}}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\frac{3+2\sqrt{6}}{5};\frac{3-2\sqrt{6}}{5}\right\}\)
i) Ta có: \(6x^2-9x+40=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6\left(x^2-\frac{3}{2}x+\frac{20}{3}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-\frac{3}{2}x+\frac{20}{3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2\cdot x\cdot\frac{3}{4}+\frac{9}{16}+\frac{293}{48}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\frac{3}{4}\right)^2+\frac{293}{48}=0\)(vô lý)
Vậy: \(S=\varnothing\)
Bài 5: Giải các phương trình sau:
a. (3x - 1)2 - (x + 3)2 = 0
b. x3 = \(\dfrac{x}{49}\)
c. x2 - 7x + 12 = 0
d. 4x2 - 3x -1 = 0
e. x3 - 2x - 4 = 0
f. x3 + 8x2 + 17x +10 = 0
g. x3 + 3x2 + 6x + 4 = 0
h. x3 - 11x2 + 30x = 0
a. (3x - 1)2 - (x + 3)2 = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1+x+3\right)\left(3x-1-x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x+2\right)\left(2x-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x+2=0\) hoặc \(2x-4=0\)
1. \(4x+2=0\Leftrightarrow4x=-2\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
2. \(2x-4=0\Leftrightarrow2x=4\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
S=\(\left\{-\dfrac{1}{2};2\right\}\)
b. \(x^3=\dfrac{x}{49}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow49x^3=x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow49x^3-x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(49x^2-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(7x+1\right)\left(7x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=0\) hoặc \(7x+1=0\) hoặc \(7x-1=0\)
1. x=0
2. \(7x+1=0\Leftrightarrow7x=-1\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{7}\)
3. \(7x-1=0\Leftrightarrow7x=1\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{7}\)
*Cách khác:
a) Ta có: \(\left(3x-1\right)^2-\left(x+3\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)^2=\left(x+3\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x-1=-x-3\\3x-1=x+3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}4x=-2\\2x=4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{1}{2};2\right\}\)
Tìm X:
a) 16x2-24x+9=25
b) x2+10x+9=0
c) x2-4x-12=0
d) x2-5x-6=0
e) 4x2-3x-1=0
f) x4+4x2-5=0
`a)16x^2-24x+9=25`
`<=>(4x-3)^2=25`
`+)4x-3=5`
`<=>4x=8<=>x=2`
`+)4x-3=-5`
`<=>4x=-2`
`<=>x=-1/2`
`b)x^2+10x+9=0`
`<=>x^2+x+9x+9=0`
`<=>x(x+1)+9(x+1)=0`
`<=>(x+1)(x+9)=0`
`<=>` \(\left[ \begin{array}{l}x=-9\\x=-1\end{array} \right.\)
`c)x^2-4x-12=0`
`<=>x^2+2x-6x-12=0`
`<=>x(x+2)-6(x+2)=0`
`<=>(x+2)(x-6)=0`
`<=>` \(\left[ \begin{array}{l}x=-2\\x=6\end{array} \right.\)
`d)x^2-5x-6=0`
`<=>x^2+x-6x-6=0`
`<=>x(x+1)-6(x+1)=0`
`<=>(x+1)(x-6)=0`
`<=>` \(\left[ \begin{array}{l}x=6\\x=-1\end{array} \right.\)
`e)4x^2-3x-1=0`
`<=>4x^2-4x+x-1=0`
`<=>4x(x-1)+(x-1)=0`
`<=>` \(\left[ \begin{array}{l}x=1\\x=-\dfrac14\end{array} \right.\)
`f)x^4+4x^2-5=0`
`<=>x^4-x^2+5x^2-5=0`
`<=>x^2(x^2-1)+5(x^2-1)=0`
`<=>(x^2-1)(x^2+5)=0`
Vì `x^2+5>=5>0`
`=>x^2-1=0<=>x^2=1`
`<=>` \(\left[ \begin{array}{l}x=1\\x=-1\end{array} \right.\)
Dùng công thức nghiệm của phương trình bậc hai để giải các phương trình sau:
a ) 2 x 2 − 7 x + 3 = 0 b ) 6 x 2 + x + 5 = 0 c ) 6 x 2 + x − 5 = 0 d ) 3 x 2 + 5 x + 2 = 0 e ) y 2 − 8 y + 16 = 0 f ) 16 z 2 + 24 z + 9 = 0
a) Phương trình bậc hai
2 x 2 – 7 x + 3 = 0
Có: a = 2; b = -7; c = 3;
Δ = b 2 – 4 a c = ( - 7 ) 2 – 4 . 2 . 3 = 25 > 0
Áp dụng công thức nghiệm, phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt là:
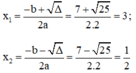
Vậy phương trình có hai nghiệm là 3 và 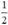
b) Phương trình bậc hai 6 x 2 + x + 5 = 0
Có a = 6; b = 1; c = 5;
Δ = b 2 – 4 a c = 12 – 4 . 5 . 6 = - 119 < 0
Vậy phương trình vô nghiệm.
c) Phương trình bậc hai 6 x 2 + x – 5 = 0
Có a = 6; b = 1; c = -5;
Δ = b 2 – 4 a c = 12 – 4 . 6 . ( - 5 ) = 121 > 0
Áp dụng công thức nghiệm, phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt là:
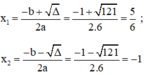
Vậy phương trình có hai nghiệm là -1 và 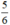
d) Phương trình bậc hai 3 x 2 + 5 x + 2 = 0
Có a = 3; b = 5; c = 2;
Δ = b 2 – 4 a c = 5 2 – 4 . 3 . 2 = 1 > 0
Áp dụng công thức nghiệm, phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt là:
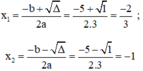
Vậy phương trình có hai nghiệm là -1 và 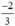
e) Phương trình bậc hai y 2 – 8 y + 16 = 0
Có a = 1; b = -8; c = 16; Δ = b 2 – 4 a c = ( - 8 ) 2 – 4 . 1 . 16 = 0 .
Áp dụng công thức nghiệm ta có phương trình có nghiệm kép :
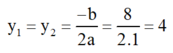
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm kép y = 4.
f) Phương trình bậc hai 16 z 2 + 24 z + 9 = 0
Có a = 16; b = 24; c = 9; Δ = b 2 – 4 a c = 24 2 – 4 . 16 . 9 = 0
Áp dụng công thức nghiệm ta có phương trình có nghiệm kép:
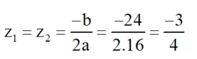
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm kép 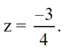
Kiến thức áp dụng
Phương trình ax2 + bx + c = 0 (a ≠ 0) có biệt thức Δ = b2 – 4ac.
+ Nếu Δ > 0, phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt 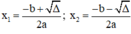
+ Nếu Δ = 0, phương trình có nghiệm kép 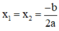 ;
;
+ Nếu Δ < 0, phương trình vô nghiệm.
Tìm x:
a) 36x3-4x=0
b) 3x(x-2)-2+x=0
c) (x3-x2)-4x2+8x-4=0
d) x2-6x-16=0
e) x4-6x2-7=0
1. x2+3x-8=0; 2). 8x2-2x-5=0 3). 2x2+7x+6=0 4). 3x2 -10x+8=0
5). 2x(8x-1)2(4x-1)=9
Phân tích
a,(x2 + x + 2)3 - (x+1)3 = x6 +1 b,(x2 + 10x + 8)2 - (8x + 4)(x2 + 8x+7)
c, A= x4 + 2x3 + 3x2 + 2x+4 d,B= x4 + 4x3 + +8x2 + 8x + 4
e, C= x4 - 2x3 + 5x2 - 4x + 4
Tìm x:
a) 36x3-4x=0
b) 3x(x-2)-2+x=0
c) (x3-x2)-4x2+8x-4=0
d) x2-6x-16=0
e) x4-6x2-7=0
(Mình cần gấp ạ)
a) Ta có: \(36x^3-4x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x\left(9x^2-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(3x-1\right)\left(3x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\dfrac{1}{3}\\x=\dfrac{-1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) Ta có: \(3x\left(x-2\right)+x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(3x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{-1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
d) Ta có: \(x^2-6x-16=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-8\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=8\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
e) Ta có: \(x^4-6x^2-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-7\right)\left(x^2+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{\sqrt{7};-\sqrt{7}\right\}\)