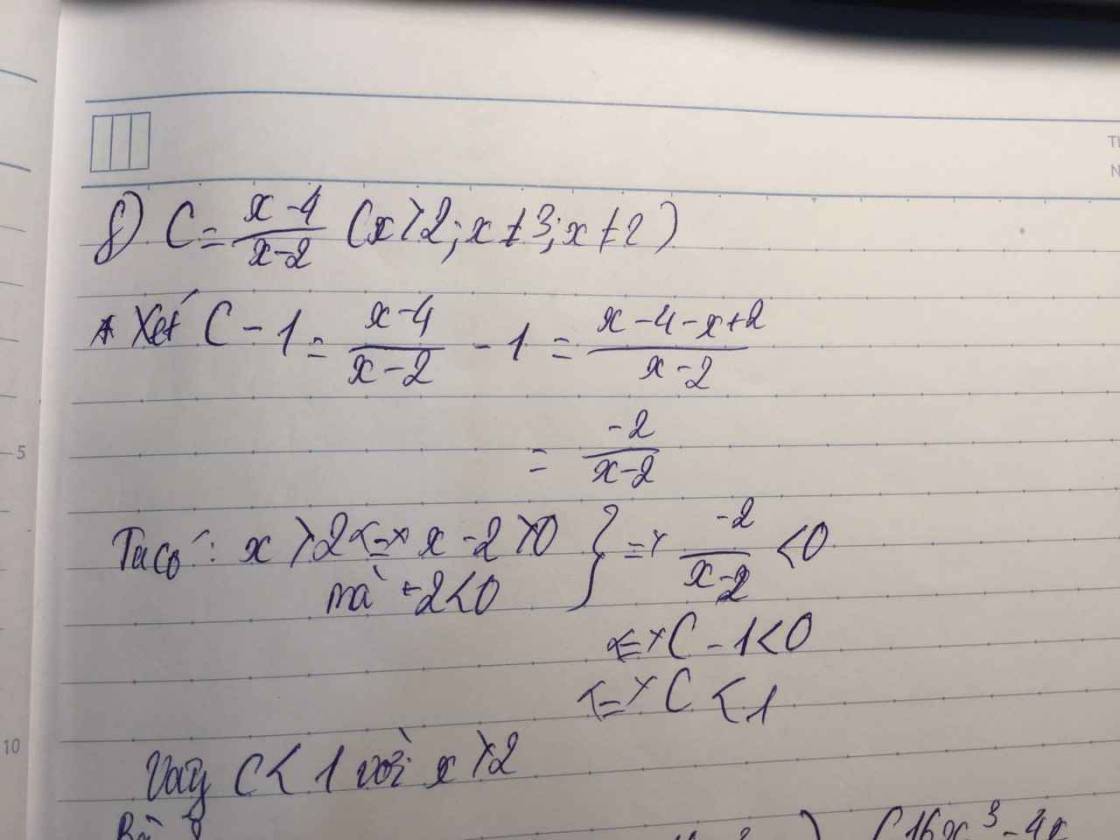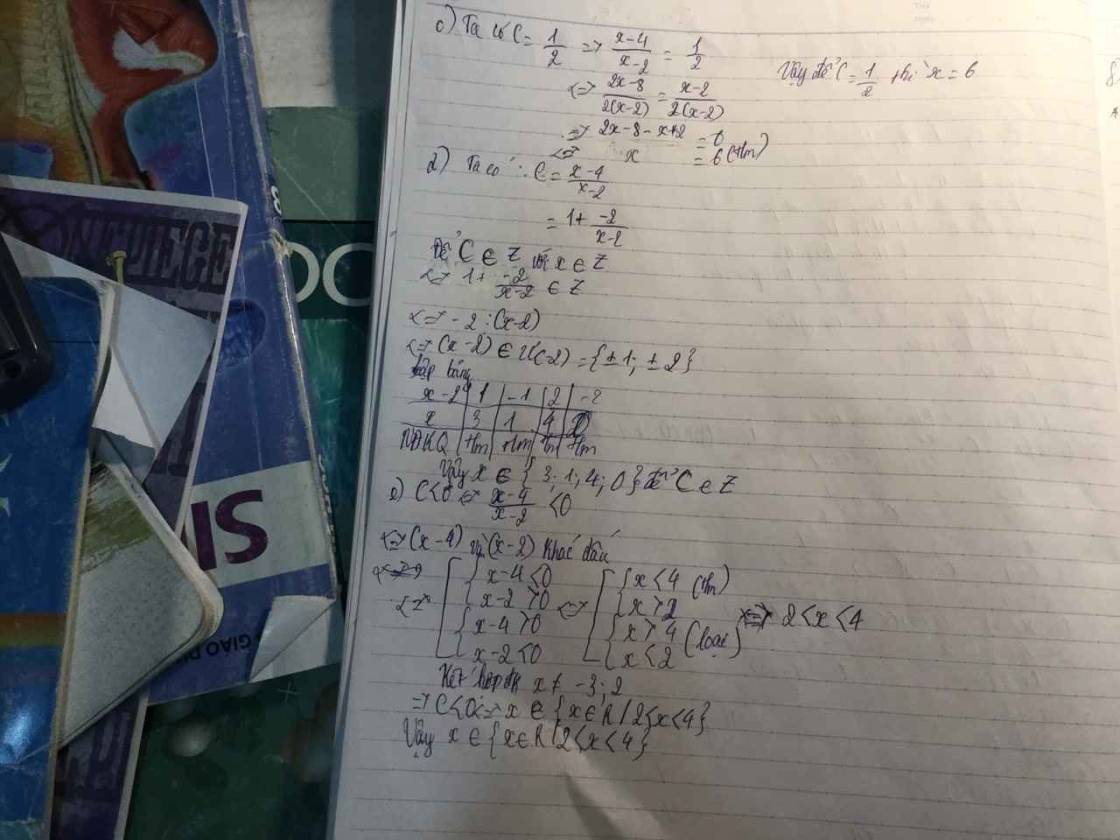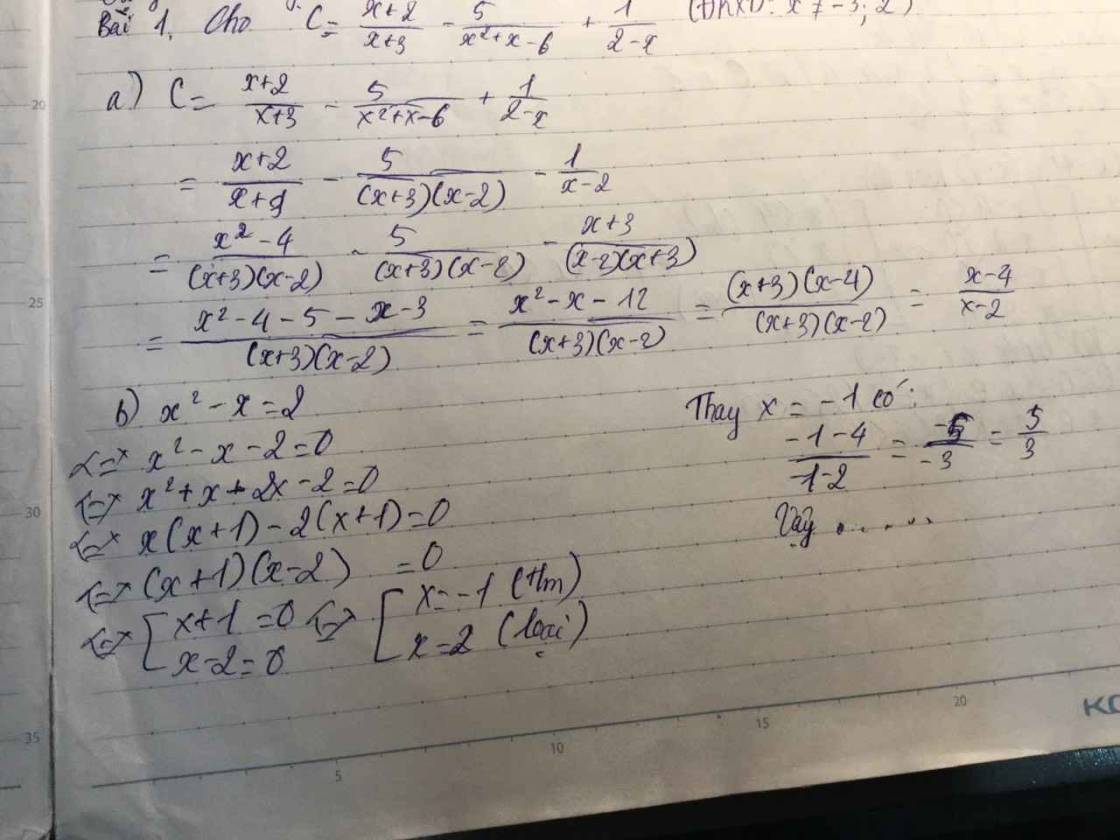Cho C=x^10-x^5+x^2-x+1. tìm x để C=0

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Cho \(C=x^{10}-x^5+x^2-x+1\) Tìm x để C = 0
TH1: Nếu \(x\le0\)\(\Rightarrow x^{10}\ge0\); \(-x^5\ge0\); \(x^2\ge0\); \(-x\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow x^{10}-x^5+x^2-x\ge0\)\(\Rightarrow C\ge1\)\(\Rightarrow\)C vô nghiệm
TH2: Nếu \(0< x< 1\)
Ta có: \(C=x^{10}-x^5+x^2-x+1=x^{10}+x^2-x^5+1-x\)
\(=x^{10}+x^2\left(1-x^3\right)+\left(1-x\right)\)
Vì \(0< x< 1\)\(\Rightarrow x^{10}>0\); \(x^2\left(1-x^3\right)>0\)( vì \(x^2>0\)và \(1-x^3>0\)) ; \(1-x>0\)
\(\Rightarrow C>0\)\(\Rightarrow\)C vô nghiệm
TH2: Nếu \(x\ge1\)
Ta có: \(C=\left(x^{10}-x^5\right)+\left(x^2-x\right)+1=x^5\left(x^5-1\right)+x\left(x-1\right)+1\)
Vì \(x\ge1\)\(\Rightarrow x^5\ge1\)và \(x-1\ge0\)\(\Rightarrow C\ge1\)\(\Rightarrow\)C vô nghiệm
Vậy không tìm được x để \(C=0\)
b1: cho phân thức:
P= (x+1/ x-1 + 2/ x^2-1 - x/ x+1 ) * x-1/ x+2
a, tìm ĐKXĐ
b, rút gọn
c, tính giá trị của P biết x^2 - 3x = 0
d, tìm x nguyên để P nhận giá trị nguyên
b2: cho phân thức:
Q= x^2+2x/2x+10 + x-5/x + 50-5x/2x(x+5)
a, tìm ĐKXĐ
b, tìm x để Q=0; Q=1/4
c,tìm x để Q>0; Q<0
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne\pm1;-2\)
\(P=\left(\frac{x+1}{x-1}+\frac{2}{x^2-1}-\frac{x}{x+1}\right).\frac{x-1}{x+2}\)
\(=\left(\frac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right).\left(x+1\right)}+\frac{2}{\left(x-1\right).\left(x+1\right)}-\frac{x\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x-1\right).\left(x+1\right)}\right).\frac{x-1}{x+2}\)
\(=\left(\frac{x^2+2x+1}{\left(x-1\right).\left(x+1\right)}+\frac{2}{\left(x-1\right).\left(x+1\right)}-\frac{x^2-x}{\left(x-1\right).\left(x+1\right)}\right).\frac{x-1}{x+2}\)
\(=\left(\frac{x^2+2x+1+2-x^2+x}{\left(x-1\right).\left(x+1\right)}\right).\frac{x-1}{x+2}\)
\(=\frac{3x+3}{\left(x-1\right).\left(x+1\right)}.\frac{x-1}{x+2}=\frac{3.\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right).\left(x+1\right)}.\frac{x-1}{x+2}=\frac{3}{x+2}\)
c. \(x^2-3x=0\Leftrightarrow x.\left(x-3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=3\end{cases}}\)
Nếu x=0 thì: \(P=\frac{3}{x+2}=\frac{3}{0+2}=\frac{3}{2}\)
Nếu x=3 thì: \(P=\frac{3}{x+2}=\frac{3}{3+2}=\frac{3}{5}\)
d. Ta có: \(P=\frac{3}{x+2}\inℤ\)
Vì \(x\inℤ\Rightarrow x+2\inℤ\Rightarrow x+2\inƯ\left\{3\right\}\Rightarrow x+2\in\left\{\pm1;\pm3\right\}\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{-3;-1;1;-5\right\}\)
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ \(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{-3;-5\right\}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho B=\(\dfrac{x^2+2x}{2x+10}+\dfrac{x-5}{x}-\dfrac{5x-50}{2x^2+10x}\)
a) Tìm điều kiện xác định và rút gọn B
b) Tìm x để B=0; B=\(\dfrac{1}{4}\)
c) Tính giá trị của B khi x=3
d) Tìm x để B<0; B>0
a) ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{0;-5\right\}\)
Ta có: \(B=\dfrac{x^2+2x}{2x+10}+\dfrac{x-5}{x}-\dfrac{5x-50}{2x^2+10x}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+2x}{2\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{x-5}{x}-\dfrac{5x-50}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3+2x^2}{2x\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{2\left(x+5\right)\left(x-5\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}-\dfrac{5x-50}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3+2x^2+2x^2-50-5x+50}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3+4x^2-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x^2+4x-5\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+5x-x-5}{2\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x+5\right)-\left(x+5\right)}{2\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x+5\right)\left(x-1\right)}{2\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-1}{2}\)
b) Để B=0 thì \(\dfrac{x-1}{2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1=0\)
hay x=1(nhận)
Vậy: Để B=0 thì x=1
Để \(B=\dfrac{1}{4}\) thì \(\dfrac{x-1}{2}=\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(x-1\right)=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x-4=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=6\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{3}{2}\)(nhận)
Vậy: Để \(B=\dfrac{1}{4}\) thì \(x=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
c) Thay x=3 vào biểu thức \(B=\dfrac{x-1}{2}\), ta được:
\(B=\dfrac{3-1}{2}=\dfrac{2}{2}=1\)
Vậy: Khi x=3 thì B=1
d) Để B<0 thì \(\dfrac{x-1}{2}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< 1\)
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ, ta được:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< 1\\x\notin\left\{0;-5\right\}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Để B<0 thì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< 1\\x\notin\left\{0;-5\right\}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Để B>0 thì \(\dfrac{x-1}{2}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1>0\)
hay x>1
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ, ta được: x>1
Vậy: Để B>0 thì x>1
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1 Cho biểu thức P =
\(\frac{x^2+2x}{2x+10}+\frac{x-5}{x}+\frac{50-5x}{2x.\left(x+5\right)}\)
a) Tìm ĐKXĐ
b)Tìm x để P =0
c)Tìm x để P>0;P<0
\(\frac{x^2+2x}{2x+10}+\frac{x-5}{x}+\frac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\frac{x\left(x^2+2x\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}+\frac{2\left(x+5\right)\left(x-5\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}+\frac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\frac{x^3+2x^2+2x^2-50+50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\frac{x^3+4x^2-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
a) ĐKXĐ: \(\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne0\\x\ne-5\end{cases}}\)
b) \(P=0\Leftrightarrow x^3+4x^2-5x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)x=0 ( ko tm đkxđ) hoặc x=1(tm đkxđ) hoặc x=-5(ktmdkxd)=> x=1
c)\(P=\frac{x\left(x+5\right)\left(x-1\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\frac{\left(x-1\right)}{2}\)
P>0 => x>1
P<0=> x<1
Chúc bạn học tốt :)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a,Tìm ĐKXĐ
\(2x+10\ne0\Rightarrow2\left(x+5\right)\ne0\Rightarrow x\ne-5\)
\(x\ne0\)
\(2x\left(x+5\right)\ne0\Rightarrow x\ne0;x\ne-5\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a) để phân thức P được xác định thì x\(\ne\pm2\)
b)rút gon P=3x(x-1)
Khi p=0 thì p=3x(x-1)=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}3x=0\\x-1=0\end{cases}}\:\:\:\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=1\end{cases}}\)
Để phân thức p=0 thì x=1
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
cho biểu thức
A=x^2+2x/2x+10 + x-5/x + 50-5x/2x(x+5)
a', tìm điều kiện xác định va rút gọn A
b, tìm x để A=0 , A=1/4
c, tính giá trị của A khi x=0 , x=2
d, tìm x để A>0 , A<0
e, tìm x để A nhận giá trị nguyên
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne-5;0\)
\(A=\frac{x^2+2x}{2x+10}+\frac{x-5}{x}+\frac{50-5x}{2x.\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\frac{\left(x^2+2x\right).x}{2x.\left(x+5\right)}+\frac{2.\left(x+5\right).\left(x-5\right)}{2x.\left(x+5\right)}+\frac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\frac{x^3+2x^2}{2x\left(x+5\right)}+\frac{2.\left(x^2-25\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}+\frac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\frac{x^3+2x^2+2x^2-50+50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\frac{x^3+4x^2-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\frac{x\left(x^2+4x-5\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\frac{x\left(x+5\right)\left(x-1\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\frac{x-1}{2}\)
b. \(A=0\Leftrightarrow\frac{x-1}{2}=0\Rightarrow x-1=0\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
\(A=\frac{1}{4}\Leftrightarrow\frac{x-1}{2}=\frac{1}{4}\Leftrightarrow4x-4=2\Leftrightarrow4x-6=0\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{3}{2}\)
c. Với x=0 thì \(A=\frac{0-1}{2}=-\frac{1}{2}\)
Với x=2 thì: \(A=\frac{2-1}{2}=\frac{1}{2}\)
d. \(A>0\Leftrightarrow\frac{x-1}{2}>0\Rightarrow\left(x-1\right).2>0\Rightarrow x-1>0\Leftrightarrow x>1\)
\(A< 0\Leftrightarrow\frac{x-1}{2}< 0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right).2< 0\Leftrightarrow x-1< 0\Leftrightarrow x< 1;x\ne-5,0\)
e. \(A=\frac{x-1}{2}\inℤ\Rightarrow x-1\in Z\Rightarrow x\inℤ\)
Và \(\left(x-1\right)⋮2\Rightarrow x:2dư1\)
Vậy \(A\in Z\Leftrightarrow x\inℤ\)và x chia 2 dư 1
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho biểu thức Cdfrac{x+2}{x+3}-dfrac{5}{x^2+x-6}+dfrac{1}{2-x}a) Rút gọn Cb) Tính C biết x^2-x2c) Tìm x biết Cdfrac{1}{2}d) Tím x để C nguyêne) Tìm x để C0f) Cho x2, Chứng minh C1Giúp mình với!
Đọc tiếp
Cho biểu thức \(C=\dfrac{x+2}{x+3}-\dfrac{5}{x^2+x-6}+\dfrac{1}{2-x}\)
a) Rút gọn C
b) Tính C biết \(x^2-x=2\)
c) Tìm \(x\) biết \(C=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
d) Tím \(x\) để C nguyên
e) Tìm \(x\) để \(C>0\)
f) Cho \(x>2\), Chứng minh \(C>1\)
Giúp mình với!
a) Cho a>0, b>0. CMR 1/a + 1/b >= 4/a+b
b) Cho x>0. CMR x+ 1/x >= 2, từ đó tìm GTNN của x+1/x
c) tìm x để biểu thức x2-4x+5 đạt GTNN
d) CMR (-x2+4x-10)/(x2+2018) <0
a, Ta có :
\(\frac{1}{a}+\frac{1}{b}\ge\frac{4}{a+b}\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{(a+b)}{ab}\ge\frac{4}{(a+b)}\)
\(\Rightarrow(a+b)^2\ge4ab\)
\(\Rightarrow(a-b)^2\ge0(đpcm)\)
Mình để cho dấu lớn bằng để dễ hiểu nha bạn
c,Ta có : \(x^2-4x+5=(x^2-4x+4)+1=(x-2)^2+1\ge1\)
Dấu " = "xảy ra khi : \((x-2)^2=0\Rightarrow x=x-2=0\Rightarrow x=2\)
Rồi bạn tự suy ra.Mk chắc đúng không nữa nên bạn thông cảm
Còn câu b và d bạn tự làm nhé
Chúc bạn học tốt
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(a,\frac{1}{a}+\frac{1}{b}\ge\frac{4}{a+b}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{a+b}{ab}-\frac{4}{a+b}\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{a^2+2ab+b^2-4ab}{ab\left(a+b\right)}\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{a^2-2ab+b^2}{ab\left(a+b\right)}\ge0\Leftrightarrow\frac{\left(a-b\right)^2}{ab\left(a+b\right)}\ge0\)(luôn đúng vì a>0,b>0)
dấu ''='' xảy ra khi và chỉ khi a=b
\(b,x+\frac{1}{x}\ge2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-2+\frac{1}{x}\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x^2-2x+1}{x}\ge0\Leftrightarrow\frac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{x}\ge0\)(luôn đúng)
dấu''='' xảy ra khi và chỉ khi x=1
áp dụng\(x+\frac{1}{x}\ge2\)(c/m trên) =>GTNN là 2
dấu ''='' xay ra khi và chỉ khi x=1
\(c,\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2+1\ge1\)
=> GTNN là 1 tại x=2
\(d,\frac{-\left(x^2+4x+4+6\right)}{x^2+2018}=\frac{-\left(x+2\right)-6}{x^2+2018}< 0\)
vì -(x+2 )-6 <-6
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho biểu thức \(P=\dfrac{x^2+2x}{2x+10}+\dfrac{x-5}{x}+\dfrac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
a, Tìm điều kiện của x để giá trị của phân thức xác định
b, Tìm x để P = 0
c, Tìm x để \(P=-\dfrac{1}{4}\)
d, Tìm x để P > 0 ; P < 0
a) P xác định \(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne0\\x+5\ne0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne0\\x\ne-5\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy P xác định \(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne0\\x\ne-5\end{cases}}\)
b) \(P=\frac{x^2+2x}{2x+10}+\frac{x-5}{x}+\frac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{x\left(x+2\right)}{2\left(x+5\right)}+\frac{x-5}{x}+\frac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{x^2\left(x+2\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}+\frac{\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)2}{2x\left(x+5\right)}+\frac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{x^3+2x^2+2x^2-50+50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{x^3+4x^2-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
Có: \(P=0\)
\(\Rightarrow P=\frac{x^3+4x^2-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=0\Leftrightarrow x\left(x^2+4x-5\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x^2+4x-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-x\right)+\left(5x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-1\right)+5\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-1=0\\x+5=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=-5\end{cases}}\)
Vậy \(P=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=-5\end{cases}}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho biểu thức P = ( x + 2x) / (2x + 10) + (x - 5)/x + (50 - 5x)/[2x.(x + 5 )
a) tìm điều kiện của biến để biểu thức xác định
b)tìm x để P = 0
c) tìm x để P = 1/4
d) Tìm x để P>0; P < 0
( p/s: các bạn nhanh nhé mai mình nộp bài)