Giải bất phương trình sau:
\(\dfrac{A^1_n}{P_n+2}< \dfrac{143}{4P_n-1}\)
Giải bất phương trình sau:
\(\dfrac{x}{x+2}< \dfrac{x}{x+1}\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{x}{x+2}< \dfrac{x}{x+1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x}{x+2}-\dfrac{x}{x+1}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2+x-x^2-2x}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{-x}{\left(x+2\right)\cdot\left(x+1\right)}< 0\)
Trường hợp 1: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-x>0\\\left(x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< 0\\-2< x< -1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow-2< x< -1\)
Trường hợp 2: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-x< 0\\\left(x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>0\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< -2\\x>-1\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x>0\)
Giải bất phương trình sau
a)\(\dfrac{2-x}{3}\)\(-x-2\le\dfrac{x-17}{2}\)
b) \(\dfrac{2x+1}{3}-\dfrac{x-4}{4}\le\dfrac{3x+1}{6}-\dfrac{x-4}{12}\)
a) \(\dfrac{2-x}{3}-x-2\le\dfrac{x-17}{2}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(6\left(\dfrac{2-x}{3}-x-2\right)\le6\left(\dfrac{x-17}{2}\right)\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) 4-2x-6x-12\(\le\)3x-51 \(\Leftrightarrow\) -2x-6x-3x\(\le\)-51-4+12 \(\Leftrightarrow\) -11x\(\le\)-43 \(\Rightarrow\) x\(\ge\)43/11.
b) \(\dfrac{2x+1}{3}-\dfrac{x-4}{4}\le\dfrac{3x+1}{6}-\dfrac{x-4}{12}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(12\left(\dfrac{2x+1}{3}+\dfrac{4-x}{4}\right)\le12\left(\dfrac{3x+1}{6}+\dfrac{4-x}{12}\right)\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) 8x+4+12-3x\(\le\)6x+2+4-x \(\Leftrightarrow\) 8x-3x-6x+x\(\le\)2+4-4-12 \(\Leftrightarrow\) 0x\(\le\)-10 (vô lí).
a) \(\dfrac{2-x}{3}-x-2\le\dfrac{x-17}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(2-x\right)-6\left(x+2\right)\le3\left(x-17\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4-2x-6x-12\le3x-51\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-11x\le-43\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ge\dfrac{43}{11}\)
Vậy S = {\(x\) | \(x\ge\dfrac{43}{11}\) }
b) \(\dfrac{2x+1}{3}-\dfrac{x-4}{4}\le\dfrac{3x+1}{6}-\dfrac{x-4}{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(2x+1\right)-3\left(x-4\right)\le2\left(3x+1\right)-\left(x-4\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8x+4-3x+12\le6x+2-x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0x\le-10\) (vô lý)
Vậy \(S=\varnothing\)
Giải bất phương trình sau:
\(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2x^2+3x-5}}\) ≥ \(\dfrac{1}{2x-1}\)
a) giải phương trình: 8x-3=5x+12
b) giải bất phương trình sau và biểu diễn tập hợp nghiệm trên trục số: \(\dfrac{8-11x}{4}\)< 13
c) Chứng minh rằng: (\(\dfrac{x}{x^2-36}\)- \(\dfrac{x-6}{x^2+6x}\)): \(\dfrac{2x-6}{x^2+6x}\)+ \(\dfrac{x}{6-x}\)= 1
a:=>3x=15
=>x=5
b: =>8-11x<52
=>-11x<44
=>x>-4
c: \(VT=\left(\dfrac{x^2-\left(x-6\right)^2}{x\left(x+6\right)\left(x-6\right)}\right)\cdot\dfrac{x\left(x+6\right)}{2x-6}+\dfrac{x}{6-x}\)
\(=\dfrac{12x-36}{2x-6}\cdot\dfrac{1}{x-6}-\dfrac{x}{x-6}=\dfrac{6}{x-6}-\dfrac{x}{x-6}=-1\)
Giải các bất phương trình sau
a) (x-4)2<x(x-8)
b) x+\(\dfrac{1}{2}\)\(\overset{>}{-}\)\(\dfrac{3-5x}{-3}\)
c) \(\dfrac{x-7}{-4}\)\(\overset{< }{-}\)\(\dfrac{4-2x}{-3}\)
a: =>x^2-8x+16<x^2-8x
=>16<0(loại)
b: =>\(x+\dfrac{1}{2}>=\dfrac{5x-3}{3}\)
=>x+1/2>=5/3x-1
=>-2/3x>=-3/2
=>x<=3/2:2/3=9/4
c: =>\(\dfrac{7-x}{4}< =\dfrac{2x-4}{3}\)
=>21-3x<=8x-16
=>-11x<=-37
=>x>=37/11
giải bất phương trình sau và biểu diễn tập nghiệm trên trục số:
\(\dfrac{x-2}{2}+1\)≤\(\dfrac{x-1}{3}\)
\(\dfrac{x-2}{2}+1\le\dfrac{x-1}{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3\left(x-2\right)}{6}+\dfrac{1.6}{6}\le\dfrac{2\left(x-1\right)}{6}\)
`<=> 3x - 6 + 6 <= 2x-2`
`<=> 3x <= 2x-2`
`<=> 3x -2x <= -2`
`<=> x <= -2`
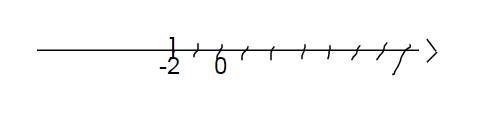
\(\dfrac{x-2}{2}\)+1≤\(\dfrac{x-1}{3}\)
<=>\(\dfrac{3x-6}{6}\)+\(\dfrac{6}{6}\)≤\(\dfrac{2x-1}{6}\)
<=>3x-6+6≤2x-1
<=>x<-1
giải các bất phương trình sau:
1) \(\dfrac{x^2-2x+5}{x-2}-x+1\ge0\) 2) \(\dfrac{2x-3}{x+1}-2< 0\)
1) \(ĐK:x\ne2\)
Nếu \(x>2\)
BPT ⇔ \(x^2-2x+5-\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\ge0\) ⇔ \(x^2-2x+5-\left(x^2-3x+3\right)\ge0\)
⇔\(x+2\ge0\) ⇔\(x\ge-2\) ⇒ Lấy \(x\ge2\)
Nếu \(x< 2\)
BPT ⇔\(\dfrac{-\left(x^2-2x+5\right)}{x-2}-x+1\ge0\) ⇔\(-x^2+2x-5-\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\ge0\)
⇔\(-x^2+2x-5-x^2+3x-2\ge0\)
⇔\(-2x^2+5x-7\ge0\)
⇔\(x^2-\dfrac{5}{2}x+\dfrac{7}{2}\le0\)
⇔\(\left(x-\dfrac{5}{4}\right)^2\le\dfrac{11}{4}\)
⇔\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-\dfrac{5}{4}\le\dfrac{11}{4}\\x-\dfrac{5}{4}\le\dfrac{-11}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\) ⇔\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\le4\\x\le\dfrac{-3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\) ⇔ \(x\le\dfrac{-3}{2}\)
S= [2;+∞)U(-∞;\(\dfrac{-3}{2}\)]
2) \(ĐK:x\ne-1\)
Nếu \(x>-1\)
BPT ⇔ \(2x-3-2\left(x+1\right)< 0\) ⇔\(2x-3-2x-2< 0\)
⇔\(-5< 0\) ( luôn đúng với mọi \(x>-1\))
Nếu \(x< -1\)
BPT⇔\(\dfrac{-\left(2x-3\right)}{x+1}-2< 0\) ⇔\(-\left(2x-3\right)-2\left(x+1\right)< 0\) ⇔\(-4x+1< 0\) ⇔ \(x>\dfrac{-1}{4}\)
Vậy S=....
\(\dfrac{1-2x}{2}-\dfrac{x+1}{3}\le2\) . Giải bất phương trình sau và biểu diễn tập nghiệm trên trục số
\(\Leftrightarrow3\left(1-2x\right)-2\left(x+1\right)< =6\)
=>3-6x-2x-2<=6
=>-8x+1<=6
=>-8x<=5
hay x>=5/8