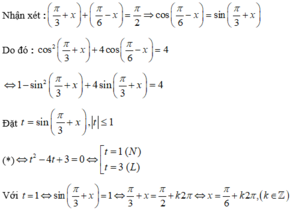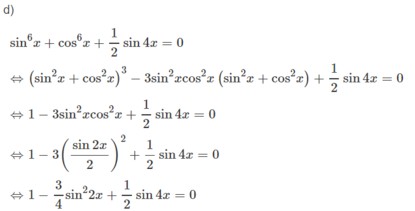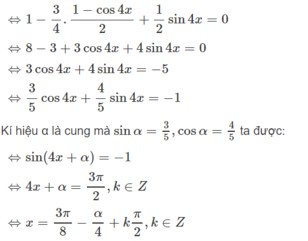Giải phương trình: cos2x + cos6x + cos10x=0

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Giải các phương trình sau: sin6x + cos6x
15
8
cos2x –
1
2
A. x ±
π
6
+ k2π, k ∈ Z B. x ±
5
π
6
+ k2π, k ∈ Z C. x
-
π
4
+ k2π, x
-
π
6
+ k2π, k ∈ Z D. Cả A và B đún...
Đọc tiếp
Giải các phương trình sau: sin6x + cos6x = 15 8 cos2x – 1 2
A. x = ± π 6 + k2π, k ∈ Z
B. x = ± 5 π 6 + k2π, k ∈ Z
C. x = - π 4 + k2π, x = - π 6 + k2π, k ∈ Z
D. Cả A và B đúng
Giải phương trình
1, cos2x + cos6x + cos3x + cos5x = 0
2, sinx + sin2x + sin3x = 0
3, sinx + sin2x + sin3x + sin4x = 0
\( 2)\sin x + \sin 2x + \sin 3x = 0\\ \Leftrightarrow 2\sin 2x.\cos x + \sin 2x = 0\\ \Leftrightarrow \sin 2x\left( {2\cos x + 1} \right) = 0\\ \Leftrightarrow \left[ \begin{array}{l} \sin 2x = 0\\ 2\cos x + 1 = 0 \end{array} \right. \Leftrightarrow \left[ \begin{array}{l} 2x = k\pi \\ \cos x = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{2} \end{array} \right. \Leftrightarrow \left[ \begin{array}{l} x = \dfrac{{k\pi }}{2}\\ x = \pm \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3} + k2\pi \end{array} \right.\left( {k \in \mathbb{Z} } \right) \)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\( 3)\sin x + \sin 2x + \sin 3x + \sin 4x = 0\\ \Leftrightarrow \left( {\sin x + \sin 4x} \right) + \left( {\sin 2x + \sin 3x} \right) = 0\\ \Leftrightarrow 2\sin \dfrac{{5x}}{2}.\cos \dfrac{{3x}}{2} + 2\sin \dfrac{{5x}}{2}.\cos \dfrac{x}{2} = 0\\ \Leftrightarrow \sin \dfrac{{5x}}{2}.\left( {\cos \dfrac{{3x}}{2} + \cos \dfrac{x}{2}} \right) = 0\\ \Leftrightarrow \sin \dfrac{{5x}}{2}.2\cos x.\cos \dfrac{x}{2} = 0\\ \Leftrightarrow \left[ \begin{array}{l} \sin \dfrac{{5x}}{2} = 0\\ 2\cos x = 0\\ \cos \dfrac{x}{2} = 0 \end{array} \right. \Leftrightarrow \left[ \begin{array}{l} x = \dfrac{{2k\pi }}{5}\\ x = \dfrac{\pi }{2} + k\pi \\ x = \pi + 2k\pi \end{array} \right.\left( {k \in \mathbb{Z}} \right) \)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
giải phương trình:
cos2x + cos4x + cos6x = cosx.cos2x.cos3x + 2
\(\Leftrightarrow2cos4x.cos2x+cos4x=\frac{1}{2}cos2x\left(cos4x+cos2x\right)+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3cos4x.cos2x+2cos4x=cos^22x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3cos2x\left(2cos^22x-1\right)+2\left(2cos^22x-1\right)=cos^22x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2cos^22x+cos^22x-cos2x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(cos2x-1\right)\left(2cos^22x+3cos2x+2\right)=0\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
9. Rút gọn các biểu thức sau
A= cos7x - cos8x - cos9x + cos10x / sin7x - sin8x - sin9x + sin10x
B = sin2x + 2sin3x + sin4x / sin3x +2sin4x + sin5x
C= 1+cosx + cos2x + cos3x / cosx + 2cos^2 . x -1
D = sin4x + sin5x + sin6x / cos4x + cos5x + cos6x
\(D=\frac{sin4x+sin5x+sin6x}{cos4x+cos5x+cos6x}\)
\(=\frac{\left(sin4x+sin6x\right)+sin5x}{\left(cos4x+cos6x\right)+cos5x}\)
\(=\frac{2sin\frac{4x+6x}{2}.cos\frac{4x-6x}{2}+sin5x}{2cos\frac{4x+6x}{2}.cos\frac{4x-6x}{2}+cos5x}\)
\(=\frac{2sin5x.cos\left(-x\right)+sin5x}{2cos5x.cos\left(-x\right)+cos5x}=\frac{sin5x\left(2.cos\left(-x\right)+1\right)}{cos5x\left(2.cos\left(-x\right)+1\right)}=\frac{sin5x}{cos5x}=tan5x\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
giải phương trình: 2sin^2 2x-1+cos6x=0
Giải các phương trình sau sin 6 x + cos 6 x + sin 4 x / 2 = 0
Giải phương trình lượng giác:
24) \(\cos2x-\cos6x+4\left(3\sin x-4\sin^3x+1\right)=0\)
25) \(\sin^2x-2\sin x+2=\sin^23x\)
SGP.Capheny - Trang của SGP.Capheny - Học toán với OnlineMath
@SGP.Capheny
30. \(\tan x+\cot x=2\sin\left(x+\frac{\pi}{4}\right)\)
ĐK: \(x\ne\frac{k\pi}{2}\)
pt <=> \(\frac{1}{\sin x.\cos x}=2\sin\left(x+\frac{\pi}{4}\right)\)
<=> \(\frac{1}{\sin2x}=\sin\left(x+\frac{\pi}{4}\right)\)
Đánh giá: \(-1\le\sin2x\le1\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}\frac{1}{\sin2x}\le-1\\\frac{1}{\sin2x}\ge1\end{cases}}\)
\(-1\le\sin\left(x+\frac{\pi}{4}\right)\le1\)
Như vậy dấu "=" xảy ra <=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}\frac{1}{\sin2x}=\sin\left(x+\frac{\pi}{4}\right)=-1\\\frac{1}{\sin2x}=\sin\left(x+\frac{\pi}{4}\right)=1\end{cases}}\)
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}\sin2x=\sin\left(x+\frac{\pi}{4}\right)=-1\\\sin2x=\sin\left(x+\frac{\pi}{4}\right)=1\end{cases}}\)
TH1: \(\sin2x=\sin\left(x+\frac{\pi}{4}\right)=-1\)
<=> \(\hept{\begin{cases}2x=-\frac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\\x+\frac{\pi}{4}=-\frac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=-\frac{\pi}{4}+k\pi\\x=-\frac{3\pi}{4}+k2\pi\end{cases}}\)loại
TH2:
\(\sin2x=\sin\left(x+\frac{\pi}{4}\right)=1\)
<=> \(\hept{\begin{cases}2x=\frac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\\x+\frac{\pi}{4}=\frac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=\frac{\pi}{4}+k\pi\\x=\frac{\pi}{4}+k2\pi\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{\pi}{4}+k2\pi\)
Vậy ...
29) \(\sin x-2\sin2x-\sin3x=2\sqrt{2}\)
<=> \(\left(\sin x-\sin3x\right)-2\sin2x=2\sqrt{2}\)
<=> \(-2.\sin x\cos2x-2\sin2x=2\sqrt{2}\)
<=> \(\sin x\cos2x+\sin2x=-\sqrt{2}\)
Ta có: \(\left(\sin x\cos2x+\sin2x\right)^2\le\left(\sin^2x+1\right)\left(\sin^22x+\cos^22x\right)=\sin^2x+1\le2\)
( theo bunhia)
=> \(-\sqrt{2}\le\sin x\cos2x+\sin2x\le\sqrt{2}\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra <=> \(\frac{\sin x}{1}=\frac{\cos2x}{\sin2x}\)(1) và \(\sin x\cos2x+\sin2x=-\sqrt{2}\)(2)
(1) <=> \(\frac{\sin x.\cos2x}{1}=\frac{\cos^22x}{\sin2x}\)=> (2) <=> \(\frac{\cos^22x}{\sin2x}+\sin2x=-\sqrt{2}\)
<=> \(\frac{1}{\sin2x}=-\sqrt{2}\)<=> \(\sin2x=-\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\)<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-\frac{\pi}{8}+k\pi\\x=-\frac{3\pi}{8}+k\pi\end{cases}}\)
(1) <=> \(\sin x.\sin2x=\cos2x\)=> (2) <=> \(\sin x.\sin x.\sin2x+\sin2x=-\sqrt{2}\)
<=> \(\frac{\sin^2x}{2}+\frac{1}{2}=+1\Leftrightarrow\sin^2x=1\)=> \(\cos^2x=0\)loại vì \(\sin2x=-\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\)
Vậy pt vô nghiệm
28. \(\sqrt{5+\sin^23x}=\sin x+2\cos x\)
có: \(\sqrt{5+\sin^23x}\ge\sqrt{5}\)
\(\left(\sin x+2\cos x\right)^2\le\left(1^2+2^2\right)\left(\sin^2x+\cos^2x\right)=5\)
<=> \(\sin x+2\cos x\le\sqrt{5}\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra <=> \(\hept{\begin{cases}\sin3x=0\\\frac{1}{2}=\frac{\sin x}{\cos x}\\\sin x+2\cos x=\sqrt{5}\end{cases}}\)hệ vô nghiệm
Xem thêm câu trả lời
cos6x. cos2x+ 1/2=0
cos6x . cos2x + \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) = 0
⇔ 2cos6x . cos2x + 1 = 0
⇔ cos8x + cos4x + 1 = 0
⇔ 2cos24x + cos4x = 0
⇔ \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}cos4x=0\\cos4x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm số nghiệm của phương trình cos22x + 3cos18x + 3cos14x + cos10x = 0 thuộc khoảng 0 ; π 2
A. 6
B. 7
C. 8
D. 9