Mn giải giúp mình câu 1 vs ạ. Mình cảm ơn nhiều

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Mn giải giúp mình c4 vs ạ. Mình cảm ơn nhiều
Gọi O là trung điểm IK \(\Rightarrow OI=OK=\dfrac{1}{2}IK\)
\(\left(\overrightarrow{MI}+\overrightarrow{IA}\right)\left(\overrightarrow{MI}+\overrightarrow{IB}\right)+\left(\overrightarrow{MK}+\overrightarrow{KC}\right)\left(\overrightarrow{MK}+\overrightarrow{KD}\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}Ik^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow MI^2-IA^2+MK^2-KC^2=\dfrac{1}{2}IK^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\overrightarrow{MO}+\overrightarrow{OI}\right)^2+\left(\overrightarrow{MO}+\overrightarrow{OK}\right)^2=IA^2+KC^2+\dfrac{1}{2}IK^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2MO^2+2OI^2=IA^2+KC^2+\dfrac{1}{2}IK^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2MO^2+\dfrac{1}{2}IK^2=IA^2+KC^2+\dfrac{1}{2}IK^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow MO^2=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(IA^2+KC^2\right)=\dfrac{1}{8}\left(AB^2+CD^2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow MO=\dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{2}}\sqrt{AB^2+CD^2}\)
Tập hợp M là đường tròn tâm O bán kính \(\dfrac{\sqrt{AB^2+CD^2}}{2\sqrt{2}}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Mn giải giúp mình câu 2 vs ạ. Mìn cảm ơn nhiều
Đk:\(y^2-2x-5y+6\ge0\)
Pt (1)\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-1\right)-\left(xy-y\right)+\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)-y\left(x-1\right)+\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2-y\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=x+2\end{matrix}\right.\)
TH1: Thay x=1 vào pt (2) ta đc: \(3\sqrt{y^2-5y+4}=y+9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y+9\ge0\\9\left(x^2-5y+4\right)=y^2+18y+81\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y\ge-9\\8y^2-63y-45=0\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{63+3\sqrt{601}}{16}\\y=\dfrac{63-3\sqrt{601}}{16}\end{matrix}\right.\) (tm)
TH2: Thay y=x+2 vào pt (2) ta đc:
\(\left(x-1\right)^2+3\sqrt{\left(x+2\right)^2-2x-5\left(x+2\right)+6}=x+2+9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x-10+3\sqrt{x^2-3x}=0\)
Đặt \(t=\sqrt{x^2-3x}\left(t\ge0\right)\)
Pttt: \(t^2-10+3t=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=2\left(tm\right)\\t=-5\left(ktm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow2=\sqrt{x^2-3x}\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}y=6\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\) (tm)
Vậy \(\left(x;y\right)=\text{}\left\{\left(1;\dfrac{63+3\sqrt{601}}{16}\right);\left(1;\dfrac{63-3\sqrt{601}}{16}\right),\left(4;6\right),\left(-1;1\right)\right\}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Xét pt đầu:
\(\left(x^2+x-2\right)-y\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)-y\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2-y\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=x+2\end{matrix}\right.\)
- Với \(x=1\) thay xuống pt dưới:
\(3\sqrt{y^2-5y+4}=y+9\) \(\left(y\ge-9\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9\left(y^2-5y+4\right)=y^2+18y+81\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8y^2-63y-45=0\)
\(\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{63\pm3\sqrt{601}}{16}\) (thỏa mãn)
- Với \(y=x+2\) thay xuống pt dưới:
\(\left(x-1\right)^2+3\sqrt{x^2-3x}=x+11\) (ĐKXĐ: ....)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x+3\sqrt{x^2-3x}-10=0\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{x^2-3x}=t\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow t^2+3t-10=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=2\\t=-5\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{x^2-3x}=2\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow...\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Mn giải giúp mình vs ạ. Mình cảm ơn nhiều
- Xét : \(x^2+8x-20\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow-10\le x\le2\)
Mà \(x>0\)
\(\Rightarrow0< x\le2\)
- Xét \(x^2-2\left(m+3\right)x+m^2-2m< 0\)
Có : \(\Delta^,=b^{,2}-ac=\left(m+3\right)^2-\left(m^2-2m\right)\)
\(=m^2+6m+9-m^2+2m=8m+9\)
- Để bất phương trình có nghiệm
\(\Leftrightarrow\Delta>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m>-\dfrac{9}{8}\)
=> Bất phương trình có nghiệm \(S=\left(x_1;x_2\right)\)
Mà \(0< x\le2\)
\(\Rightarrow0< x_1< x_2\le2\)
\(TH1:x=2\)
\(\Rightarrow4-4\left(m+3\right)+m^2-2m< 0\)
\(\Rightarrow3-\sqrt{17}< m< 3+\sqrt{17}\)
\(TH2:0< x_1< x_2< 2\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m^2-2m>0\\m^2-6m-8>0\\0< 2\left(m+3\right)< 2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left[{}\begin{matrix}m< 0\\m>2\end{matrix}\right.\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}m>3+\sqrt{17}\\m< 3-\sqrt{17}\end{matrix}\right.\\-3< m< -2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(3-\sqrt{7}< m< 3+\sqrt{7}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (4)
Từ pt đầu \(\Rightarrow-10\le x\le2\) (1)
Để BPT chứa m có nghiệm thì \(\Delta'>0\Rightarrow m...\) (2)
Gọi 2 nghiệm của pt chứa m là \(x_1;x_2\Rightarrow\) miền nghiệm của BPT dưới là \(D=\left(x_1;x_2\right)\)
Do (1) chỉ chứa 2 số nguyên dương là 1 và 2, nên để hệ có nghiệm nguyên dương thì D cần chứa ít nhất 1 trong 2 giá trị 1 hoặc 2
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x_1< 1< x_2\\x_1< 2< x_2\end{matrix}\right.\) (các trường hợp trùng lặp 2 điều kiện ví dụ \(x_1< 1< 2< x_2\) không thành vấn đề vì cuối cùng ta cũng hợp nghiệm)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}f\left(1\right)< 0\\f\left(2\right)< 0\end{matrix}\right.\) (3) với \(f\left(x\right)=x^2-2\left(m+3\right)x+m^2-2m\)
Lấy giao nghiệm của (2) và (3) sẽ được khoảng m cần tìm
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Mn giải giúp mình vs ạ. Mình cảm ơn nhiều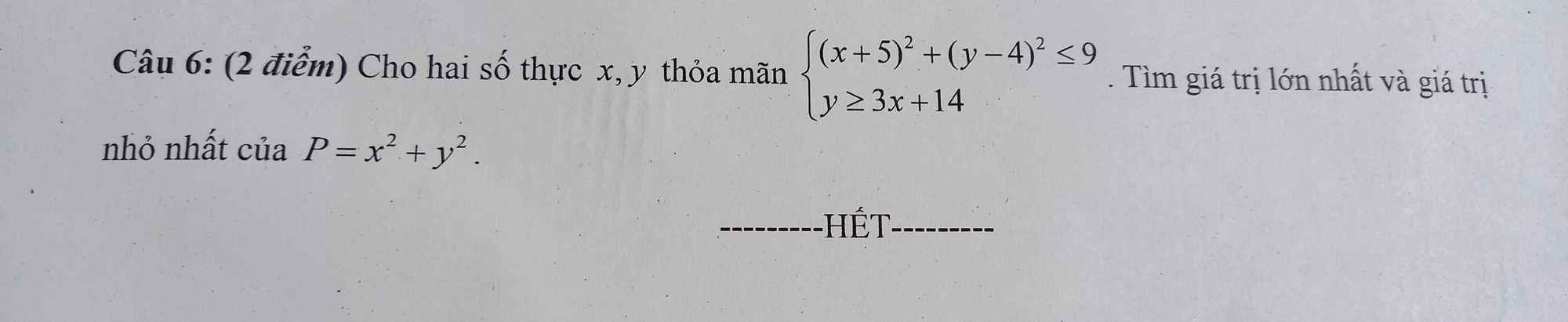
Nếu \(y\le0\Rightarrow\left(y-4\right)^2\ge16>9\left(ktm\right)\Rightarrow y>0\)
Nếu \(x\ge0\Rightarrow\left(x+5\right)^2\ge25>9\left(ktm\right)\Rightarrow x< 0\)
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-x=a>0\\y=b>0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(a-5\right)^2+\left(b-4\right)^2\le9\\3a+b\ge14\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có:
\(14^2\le\left(3a+b\right)^2\le\left(3^2+1\right)\left(a^2+b^2\right)\Rightarrow a^2+b^2\ge\dfrac{196}{10}=\dfrac{98}{5}\)
\(P_{min}=\dfrac{98}{5}\) khi \(\left(a;b\right)=\left(\dfrac{21}{5};\dfrac{7}{5}\right)\) hay \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(-\dfrac{21}{5};\dfrac{7}{3}\right)\)
Lại có:
\(\left(a-5\right)^2+\left(b-4\right)^2\le9\Leftrightarrow a^2+b^2\le10a+8b-32\le\sqrt{\left(10^2+8^2\right)\left(a^2+b^2\right)}-32\)
\(\Rightarrow P\le2\sqrt{41}\sqrt{P}-32\Leftrightarrow P-2\sqrt{41}\sqrt{P}+32\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(\sqrt{P}-3-\sqrt{41}\right)\left(\sqrt{P}-3+\sqrt{41}\right)\le0\) (1)
Do \(P\ge\dfrac{98}{5}\Rightarrow\sqrt{P}-3+\sqrt{41}>0\)
Nên (1) tương đương: \(\sqrt{P}-3-\sqrt{41}\le0\Rightarrow P\le50+6\sqrt{41}\)
\(P_{max}=50+6\sqrt{41}\) khi \(\left(a;b\right)=\left(5+\dfrac{15}{\sqrt{41}};4+\dfrac{12}{\sqrt{41}}\right)\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Mình đang gấp lắm mn ơi, nhờ mn giúp mình câu 3 vs ạ, nếu đc cả câu 4 nữa thì mình cảm ơn mn nhiều.

 Mn giải giúp mik vs ạ 🥺 mình đang cần gấp. Cảm ơn mn nhiều
Mn giải giúp mik vs ạ 🥺 mình đang cần gấp. Cảm ơn mn nhiều
Mn ơi giải câu này giúp mình vs ;-;;; Cảm ơn mn ạ
Mọi người giải giúp mình vs ạ. Chiều nay mình phải nộp r 🥺Cảm ơn mn nhiều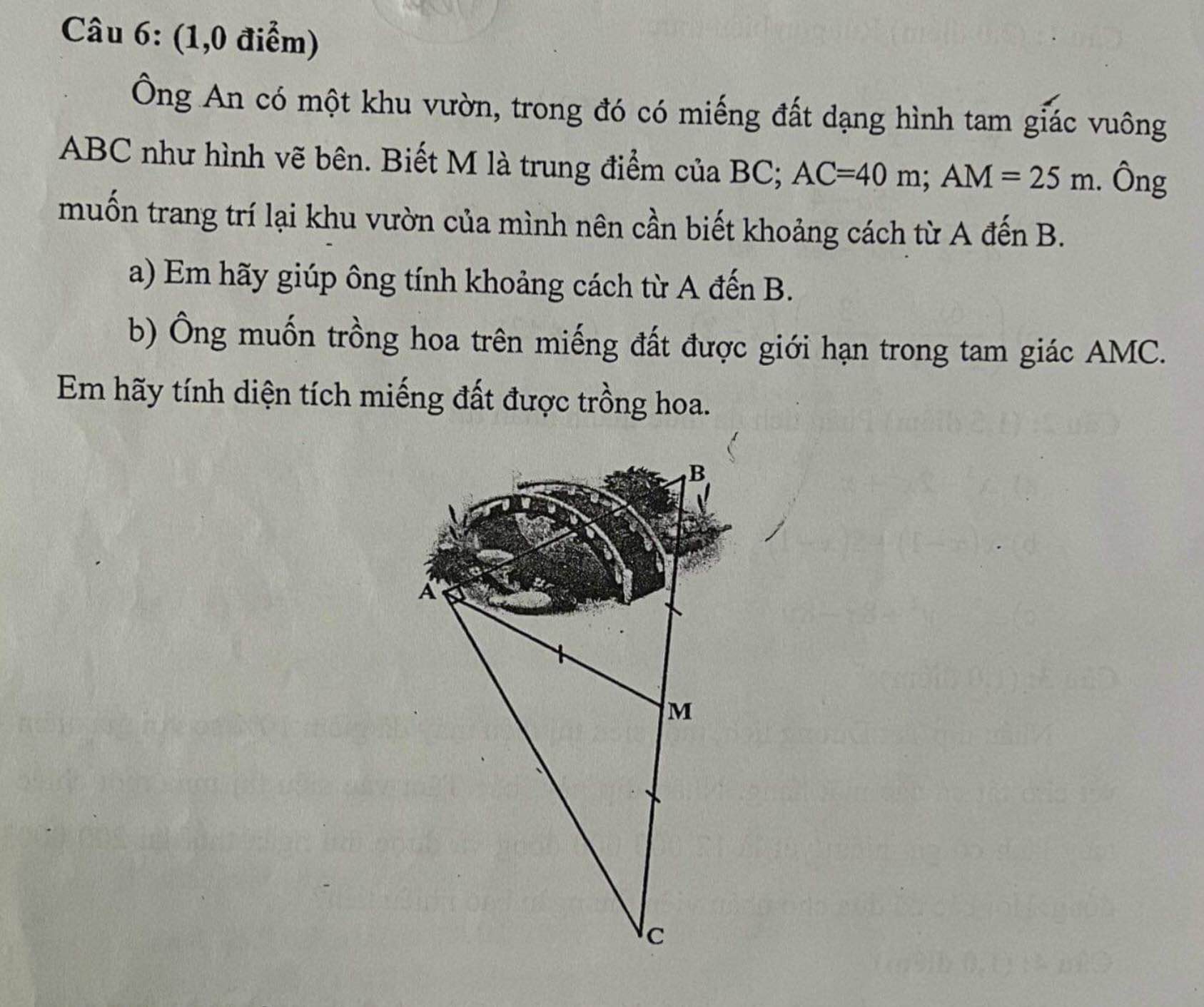
Tam giác ABC vuông tại A có AM là trung tuyến ứng với cạnh huyền
\(\Rightarrow AM=\dfrac{1}{2}BC\Rightarrow BC=2AM=50\left(m\right)\)
a. Áp dụng định lý Pitago:
\(AB=\sqrt{BC^2-AC^2}=30\left(m\right)\)
b. Kẻ \(MH\perp AC\Rightarrow MH||AB\) (cùng vuông góc AC)
Mà M là trung điểm BC \(\Rightarrow MH\) là đường trung bình tam giác ABC
\(\Rightarrow MH=\dfrac{1}{2}AB=15\left(m\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow S_{AMC}=\dfrac{1}{2}MH.AC=\dfrac{1}{2}.15.40=300\left(m^2\right)\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (1)
Mn ơi giúp mình câu 4 phần 3 vs giải thích giúp mình cách làm của nó như thế nào vs mình cảm ơn mn nhiều.
3: góc AMN=góic ACM
=>AM là tiếp tuyến của đường tròn ngoại tiếp ΔECM
=>góc AMB=90 độ
=>Tâm o1 của đường tròn ngoại tiếp ΔECM nằm trên BM
NO1 min khi NO1=d(N;BM)
=>NO1 vuông góc BM
Gọi O1 là chân đường vuông góc kẻ từ N xuống BM
=>O1 là tâm đường tròn ngoại tiếp ΔECM có bán kính là O1M
=>d(N;tâm đường tròn ngoại tiếp ΔECM) nhỏ nhất khi C là giao của (O1;O1M) với (O) với O1 ;là hình chiếu vuông góc của N trên BM
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)













