Tìm GTNN của P = xᒾ+2x+1/x- 1 khi x>1

Những câu hỏi liên quan
A(x)=2x⁴+3x +xᒾ+2x-6 B(x)=5xᒾ-3x+2x⁴-6x²+1 a)Tính A(1) b)Thu gọn và sắp xếp theo các hạng tử của mỗi đa thức trên theo lũy thừa giảm dần c)Tính P(x)=A(x)+B(x) Q(x)=A(x)-B(x)
a: A(x)=2x^4+x^2+5x-6
A(1)=2+1+5-6=2
b: B(x)=2x^4-x^2-3x+1
c: P(x)=A(x)+B)(x)=4x^4+2x-5
Q(x)=2x^2+8x-7
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
P=x2+xx2−2x+1:(x+1x+1x−1+2−x2x2−x)
a) Rút gọn P
b) Tìm x để P< 1
c)tìm gtnn của p khi x>1
cho M= x^2+x/x^2-2x+1:(x+1/x-1/1-x +2x^2/x^2-x)
Rút gọn M
tìm x thuộc z để M thuộc z
tìm x để M<1
tìm GTNN của M khi x>1
Rút gọn:
\(M=\frac{x^2+x}{x^2-2x+1}:\left(\frac{x+1}{x}-\frac{1}{1-x}+\frac{2x^2}{x^2-x}\right)\)
\(M=\frac{x\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\cdot\frac{x\left(x-1\right)}{x^2-1+1+2x^2}\)
\(M=\frac{x\left(x+1\right)}{x-1}\cdot\frac{x}{3x^3}\)
\(M=\frac{x+1}{3x\left(x-1\right)}\)
Tìm GTLN (max), GTNN (min) của
y
x
2
-
x
+
2
x
-
1
khi
x
∈
3
2
;
3
Đọc tiếp
Tìm GTLN (max), GTNN (min) của y = x 2 - x + 2 x - 1 khi x ∈ 3 2 ; 3
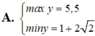
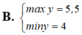
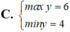
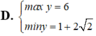
1. tìm GTNN của A= x(x+2)(x+4)(x+6)+8
2. tìm GTLN của B=5+(1-x)(x+2)(x+3)(x+6)3
3.tìm GTNN của C=(x+3)4 + (x-7)4
4. Cho x>0. Tìm GTNN của P=\(\dfrac{4x^2+1}{2x}\)
1.
$x(x+2)(x+4)(x+6)+8$
$=x(x+6)(x+2)(x+4)+8=(x^2+6x)(x^2+6x+8)+8$
$=a(a+8)+8$ (đặt $x^2+6x=a$)
$=a^2+8a+8=(a+4)^2-8=(x^2+6x+4)^2-8\geq -8$
Vậy $A_{\min}=-8$ khi $x^2+6x+4=0\Leftrightarrow x=-3\pm \sqrt{5}$
Đúng 4
Bình luận (0)
2.
$B=5+(1-x)(x+2)(x+3)(x+6)=5-(x-1)(x+6)(x+2)(x+3)$
$=5-(x^2+5x-6)(x^2+5x+6)$
$=5-[(x^2+5x)^2-6^2]$
$=41-(x^2+5x)^2\leq 41$
Vậy $B_{\max}=41$. Giá trị này đạt tại $x^2+5x=0\Leftrightarrow x=0$ hoặc $x=-5$
Đúng 4
Bình luận (0)
3.
Đặt $x+3=a; 7-x=b$ thì $a+b=10$
$C=a^4+b^4$
Áp dụng BĐT Bunhiacopxky:
$(a^4+b^4)(1+1)\geq (a^2+b^2)^2$
$\Rightarrow C\geq \frac{(a^2+b^2)^2}{2}$
$(a^2+b^2)(1+1)\geq (a+b)^2=100$
$\Rightarrow a^2+b^2\geq 50$
$\Rightarrow C\geq \frac{50^2}{2}=1250$
Vậy $C_{\min}=1250$
Giá trị này đạt tại $a=b=5\Leftrightarrow x=2$
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Cho A=$\sqrt{x^2+2x+1}$ + $\sqrt{x^2-2x+1}$
tìm GTNN của A, giá trị đó đạt được khi x bằng bao nhiêu?
\(A=\sqrt{x^2+2x+1}+\sqrt{x^2-2x+1}=\sqrt{\left(x+1\right)^2}+\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
\(=\left|x+1\right|+\left|x-1\right|=\left|x+1\right|+\left|1-x\right|\)
Áp dụng bđt \(\left|A\right|+\left|B\right|\ge\left|A+B\right|\) ta có:
\(A\ge\left|x+1+1-x\right|=2\)
Vậy GTNN của A là 2 khi \(-1\le x\le1\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (4)
Ta có
\(A=\sqrt{x^2+2x+1}+\sqrt{x^2-2x+1}\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\sqrt{\left(x+1\right)^2}+\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\left|x+1\right|+\left|x-1\right|\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\left|x+1\right|+\left|1-x\right|\)
Vì \(\begin{cases}\left|x+1\right|\ge x+1\\\left|1-x\right|\ge1-x\end{cases}\)\(\Rightarrow\left|x+1\right|+\left|1-x\right|\ge x+1+1-x\)
\(\Rightarrow\left|x+1\right|+\left|1-x\right|\ge2\)
Dấu " = " xảy ra khi \(\begin{cases}x+1\ge0\\1-x\ge0\end{cases}\)\(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}x\ge-1\\x\le1\end{cases}\)
Vậy MINA=2 khi \(-1\le x\le1\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (1)
1) cho x>0,y>0 thỏa mãn x+y=1.tìm GTNN của biểu thức P= 1/xy+2/x^2+y^2
2)cho x>0,y>0 và x+y=1.tìm GTNN của M=3/xy+2/x^2+y^2
3)tìm GTNN và GTLN của
N= 2x+1/x^2+2
Q= 2x^2-2x+9/x^2+2x+5
R=2(x^2+x+1)/x^2+1
Cho biểu thức:
\(A=\dfrac{x^2+x}{x^2-2x+1}:\left(\dfrac{x+1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{x-1}+\dfrac{2-x^2}{x^2-x}\right)\)
a) Tìm điều kiện xác định của A
b) Rút gọn A
c) Tìm GTNN của A khi x > 1
a: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{0;1;-1\right\}\)
b: \(A=\dfrac{x^2+x}{x^2-2x+1}:\left(\dfrac{x+1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{x-1}+\dfrac{2-x^2}{x^2-x}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2}:\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)+x+2-x^2}{x\left(x-1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\cdot\dfrac{x\left(x-1\right)}{x^2-1+x+2-x^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{x^2}{x-1}\)
c: \(A=\dfrac{x^2}{x-1}=\dfrac{x^2-1+1}{x-1}=x+1+\dfrac{1}{x-1}\)
=>\(A=x-1+\dfrac{1}{x-1}+2>=2\cdot\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)\cdot\dfrac{1}{x-1}}+2=2+2=4\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi (x-1)2=1
=>x-1=1 hoặc x-1=-1
=>x=0(loại) hoặc x=2(nhận)
Vậy: \(A_{min}=4\) khi x=2
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)
Cho \(P=\left(\dfrac{x^2-2x}{2x^2+8}-\dfrac{2x^2}{8-4x+2x^2-x^3}\right)\left(1-\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{2}{x^2}\right)\)
a) Rút gọn.
b) Tìm GTNN của P khi x>1
Em cần câu b ạ. Cảm ơn ạ.
a) Ta có: \(P=\left(\dfrac{x^2-2x}{2x^2+8}-\dfrac{2x^2}{8-4x+2x^2-x^3}\right)\left(1-\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{2}{x^2}\right)\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{x^2-2x}{2\left(x^2+4\right)}-\dfrac{2x^2}{4\left(2-x\right)+x^2\left(2-x\right)}\right)\left(1-\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{2}{x^2}\right)\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{x^2-2x}{2\left(x^2+4\right)}-\dfrac{2x^2}{\left(2-x\right)\left(x^2+4\right)}\right)\left(1-\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{2}{x^2}\right)\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{\left(x^2-2x\right)\left(x-2\right)}{2\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+4\right)}+\dfrac{4x^2}{2\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+4\right)}\right)\cdot\left(1-\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{2}{x^2}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3-x^2-2x^2+4x+4x^2}{2\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+4\right)}\cdot\left(1-\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{2}{x^2}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3+x^2+4x}{2\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+4\right)}\cdot\dfrac{x^2-x-2}{x^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x^2+x+4\right)}{2\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+4\right)}\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}{x^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x^2+x+4\right)\left(x+1\right)}{2x\left(x^2+4\right)}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)


















