Giải phương trình sau 3x2+21x+18+2√(x2+7x+7)=2

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Giúp vs ạBài 1 giải các bất phương trình saua.x2 - x - 6 0b.2x2 - 7x + 5 0c.3x2 - 9x + 6 ≥ 0d.2x2 - 5x + 3 0Bài 2 Giải phương trình sauA.√x2 + x + 5 √2x2 - 4x + 1B.√11x2 -14x - 12 √3x2 + 4x - 7
Đọc tiếp
Giúp vs ạ
Bài 1 giải các bất phương trình sau
a.x2 - x - 6 = 0
b.2x2 - 7x + 5 < 0
c.3x2 - 9x + 6 ≥ 0
d.2x2 - 5x + 3 < 0
Bài 2 Giải phương trình sau
A.√x2 + x + 5 = √2x2 - 4x + 1
B.√11x2 -14x - 12 = √3x2 + 4x - 7
Bài 2:
a: =>2x^2-4x+1=x^2+x+5
=>x^2-5x-4=0
=>\(x=\dfrac{5\pm\sqrt{41}}{2}\)
b: =>11x^2-14x-12=3x^2+4x-7
=>8x^2-18x-5=0
=>x=5/2 hoặc x=-1/4
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
giải phương trình vô tỉ sau:
\(\sqrt{2x^2+5x-7}+\sqrt{3x^2-21x+18}=\sqrt{7x^2-6x-1}\)
TXĐ: \(x\le\dfrac{-7}{2};x\ge6;x=1\)
\(\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)\left(2x+7\right)}+\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)\left(3x-18\right)}=\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)\left(7x+1\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x-1}=0\\\sqrt{2x+7}+\sqrt{3x-18}=\sqrt{7x+1}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Pt1: \(\sqrt{x-1}=0\Rightarrow x=1\)
Pt2: \(\sqrt{2x+7}+\sqrt{3x-18}=\sqrt{7x+1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x-11+2\sqrt{\left(2x+7\right)\left(3x-18\right)}=7x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(2x+7\right)\left(3x-18\right)}=x+6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+6\ge0\\\left(2x+7\right)\left(3x-18\right)=\left(x+6\right)^2\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge-6\\5x^2-27x-162=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=9\\x=\dfrac{-18}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy pt có 3 nghiệm: \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=9\\x=\dfrac{-18}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (2)
Giải phương trình bằng cách đưa về phương trình tích :
3x2 + 2x - 1 = 0
x2 - 5x + 6 = 0
3x2 + 7x + 2 = 0
x2 - 4x + 1 = 0
2x2 - 6x + 1 = 0
3x2 + 4x - 4 = 0
3x2 + 2x - 1 = 0
=> 3x2 + 3x - x - 1 = 0
=> 3x(x + 1) - (x + 1) = 0
=> (3x - 1)(x + 1) = 0
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}3x-1=0\\x+1=0\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{1}{3}\\x=-1\end{cases}}\)
x2 - 5x + 6 = 0
=> x2 - 2x - 3x + 6 = 0
=> x(x - 2) - 3(x - 2) = 0
=> (x - 3)(x - 2) = 0
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x-3=0\\x-2=0\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=3\\x=2\end{cases}}\)
3x2 + 7x + 2 = 0
=> 3x2 + 6x + x + 2 = 0
=> 3x(x + 2) + (x + 2) = 0
=> (3x + 1)(x + 2) = 0
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}3x+1=0\\x+2=0\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-\frac{1}{3}\\x=-2\end{cases}}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1, \(3x^2+2x-1=0\Leftrightarrow3x^2+3x-x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x+1\right)-\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(3x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+1=0\\3x-1=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-1\\x=\frac{1}{3}\end{cases}}}\)
2, \(x^2-5x+6=0\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-3x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-2\right)-3\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-2=0\\x-3=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2\\x=3\end{cases}}}\)
3, \(3x^2+7x+2=0\Leftrightarrow3x^2+6x+x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x+2\right)+\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(3x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+2=0\\3x+1=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-2\\x=-\frac{1}{3}\end{cases}}}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(x^2-4x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-4x+4\right)=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\sqrt{3}+2;x=2-\sqrt{3}\)
\(2x^2-6x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-12x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-3\right)^2=7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{\sqrt{7}+3}{2};x=\frac{3-\sqrt{7}}{2}\)
\(3x^2+4x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-2x+6x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(3x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-2;x=\frac{2}{3}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình: 3x2−7x−43�2−7�−4 0
Đọc tiếp
Giải phương trình: = 0
\(3x^2-7x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-3x+4x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x-1\right)+4\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(3x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\3x+4=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{4}{3}\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
1. Phân tích thành nhân tửa) x2 + 7x + 10; b) x2 – 21x + 110; c) 3x2 + 12x + 9; d) 2ax2 - 16ax + 30a.2. Phân tích thành nhân tửa) x2 + x – 6; b) x2 – 2x – 15; c) 4x2 - 12x - 160; d) 5x2y - 10xy - 15y.3. Phân tích thành nhân tửa) x2 – xy – 20y2 ; b) 3x4 + 6x2y2 – 45y4 ; c) 2bx2 – 4bxy - 70y24. Giải phương trìnha) x2 + x 72; b) 3x2 – 6x 24 c) 5x3 – 10x2 120x.5. Phân tích thành nhân tửa) 3x2 -11x + 6; b) 8x2 + 10x – 3 ; c) 8x2 -2x -1 .
Đọc tiếp
1. Phân tích thành nhân tử
a) x2 + 7x + 10; b) x2 – 21x + 110; c) 3x2 + 12x + 9; d) 2ax2 - 16ax + 30a.
2. Phân tích thành nhân tử
a) x2 + x – 6; b) x2 – 2x – 15; c) 4x2 - 12x - 160; d) 5x2y - 10xy - 15y.
3. Phân tích thành nhân tử
a) x2 – xy – 20y2 ; b) 3x4 + 6x2y2 – 45y4 ; c) 2bx2 – 4bxy - 70y2
4. Giải phương trình
a) x2 + x = 72; b) 3x2 – 6x = 24 c) 5x3 – 10x2 = 120x.
5. Phân tích thành nhân tử
a) 3x2 -11x + 6; b) 8x2 + 10x – 3 ; c) 8x2 -2x -1 .
Phương trình nào sau đây tương đương,không tương đương
a) 2(x-5)=2(2x-3)-2x và -3x2-7=0
b) 2x-3 phần 5 - 7x-2 phần 4 =3 và x2-4x-4=0
\(a,2\left(x-5\right)=2\left(2x-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-10-4x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-2\)
\(-3x^2-7=0\Leftrightarrow x^2=-\dfrac{7}{3}\Leftrightarrow\) pt vô nghiệm
Vậy 2 pt ko tương đương
\(b,\dfrac{2x-3}{5}-\dfrac{7x-2}{4}=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(2x-3\right)-5\left(7x-2\right)-3.20=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8x-12-35x+10-60=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-27x=62\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{62}{27}\)
\(x^2-4x-4=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
Vậy 2 pt ko tương đương
Đúng 0
Bình luận (2)
a: 2(2x-3)-2x=2(x-5)
=>4x-6-2x=2x-10
=>2x-6=2x-10
=>-6=-10(loại)
=>PTVN
-3x^2-7=0
=>3x^2+7=0
=>x^2=-7/3(loại)
=>PTVN
=>Hai phương trình tương đương
b: \(\dfrac{2x-3}{5}-\dfrac{7x-2}{4}=3\)
=>4(2x-3)-5(7x-2)=60
=>8x-12-35x+10=60
=>-27x-2=60
=>-27x=62
=>x=-62/27
x^2-4x-4=0
=>x^2-4x+4-8=0
=>(x-2)^2-8=0
=>x=2 căn 2+2 hoặc x=-2 căn 2+2
=>Hai phương trình ko tương đương
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình bằng cách đưa về phương trình tích:
a
)
3
x
2
−
7
x
−
10
⋅
2
x
2...
Đọc tiếp
Giải phương trình bằng cách đưa về phương trình tích:
a ) 3 x 2 − 7 x − 10 ⋅ 2 x 2 + ( 1 − 5 ) x + 5 − 3 = 0 b ) x 3 + 3 x 2 − 2 x − 6 = 0 c ) x 2 − 1 ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) = 0 , 6 x 2 + x d ) x 2 + 2 x − 5 2 = x 2 − x + 5 2
a) 3 x 2 − 7 x − 10 ⋅ 2 x 2 + ( 1 − 5 ) x + 5 − 3 = 0
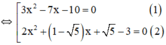
+ Giải (1):
3 x 2 – 7 x – 10 = 0
Có a = 3; b = -7; c = -10
⇒ a – b + c = 0
⇒ (1) có hai nghiệm x 1 = - 1 v à x 2 = - c / a = 10 / 3 .
+ Giải (2):
2 x 2 + ( 1 - √ 5 ) x + √ 5 - 3 = 0
Có a = 2; b = 1 - √5; c = √5 - 3
⇒ a + b + c = 0
⇒ (2) có hai nghiệm:
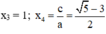
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 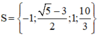
b)
x 3 + 3 x 2 - 2 x - 6 = 0 ⇔ x 3 + 3 x 2 - ( 2 x + 6 ) = 0 ⇔ x 2 ( x + 3 ) - 2 ( x + 3 ) = 0 ⇔ x 2 - 2 ( x + 3 ) = 0
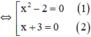
+ Giải (1): x 2 – 2 = 0 ⇔ x 2 = 2 ⇔ x = √2 hoặc x = -√2.
+ Giải (2): x + 3 = 0 ⇔ x = -3.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = {-3; -√2; √2}
c)
x 2 − 1 ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) = 0 , 6 x 2 + x ⇔ x 2 − 1 ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) = x ⋅ ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) ⇔ x 2 − 1 ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) − x ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) = 0 ⇔ ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) x 2 − 1 − x = 0
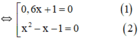
+ Giải (1): 0,6x + 1 = 0 ⇔ 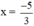
+ Giải (2):
x 2 – x – 1 = 0
Có a = 1; b = -1; c = -1
⇒ Δ = ( - 1 ) 2 – 4 . 1 . ( - 1 ) = 5 > 0
⇒ (2) có hai nghiệm 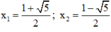
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 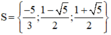
d)
x 2 + 2 x − 5 2 = x 2 − x + 5 2 ⇔ x 2 + 2 x − 5 2 − x 2 − x + 5 2 = 0 ⇔ x 2 + 2 x − 5 − x 2 − x + 5 ⋅ x 2 + 2 x − 5 + x 2 − x + 5 = 0 ⇔ ( 3 x − 10 ) 2 x 2 + x = 0
⇔ (3x-10).x.(2x+1)=0
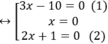
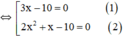
+ Giải (1): 3x – 10 = 0 ⇔ 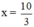
+ Giải (2):
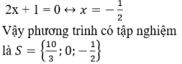
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình
\(\frac{x\left(x2-56\right)}{4-7x}-\frac{21x+22}{x3+2}=4\)
1.Giải các phương trình sau : a,7x+35=0 b, 8-x/x-7 -8 =1/x-7 2.giải bất phương trình sau : 18-3x(1-x)_< 3x^2-3x
a: 7x+35=0
=>7x=-35
=>x=-5
b: \(\dfrac{8-x}{x-7}-8=\dfrac{1}{x-7}\)
=>8-x-8(x-7)=1
=>8-x-8x+56=1
=>-9x+64=1
=>-9x=-63
hay x=7(loại)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
a, \(7x=-35\Leftrightarrow x=-5\)
b, đk : x khác 7
\(8-x-8x+56=1\Leftrightarrow-9x=-63\Leftrightarrow x=7\left(ktm\right)\)
vậy pt vô nghiệm
2, thiếu đề
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1.
\(a,7x+35=0\\ \Rightarrow7x=-35\\ \Rightarrow x=-5\\ b,ĐKXĐ:x\ne7\\ \dfrac{8-x}{x-7}-8=\dfrac{1}{x-7}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{8-x}{x-7}-\dfrac{8\left(x-7\right)}{x-7}-\dfrac{1}{x-7}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{8-x-8x+56-1}{x-7}=0\\ \Rightarrow-9x+63=0\\ \Leftrightarrow-9x=-63\\ \Leftrightarrow x=7\left(ktm\right)\)
2.đề thiếu
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
























