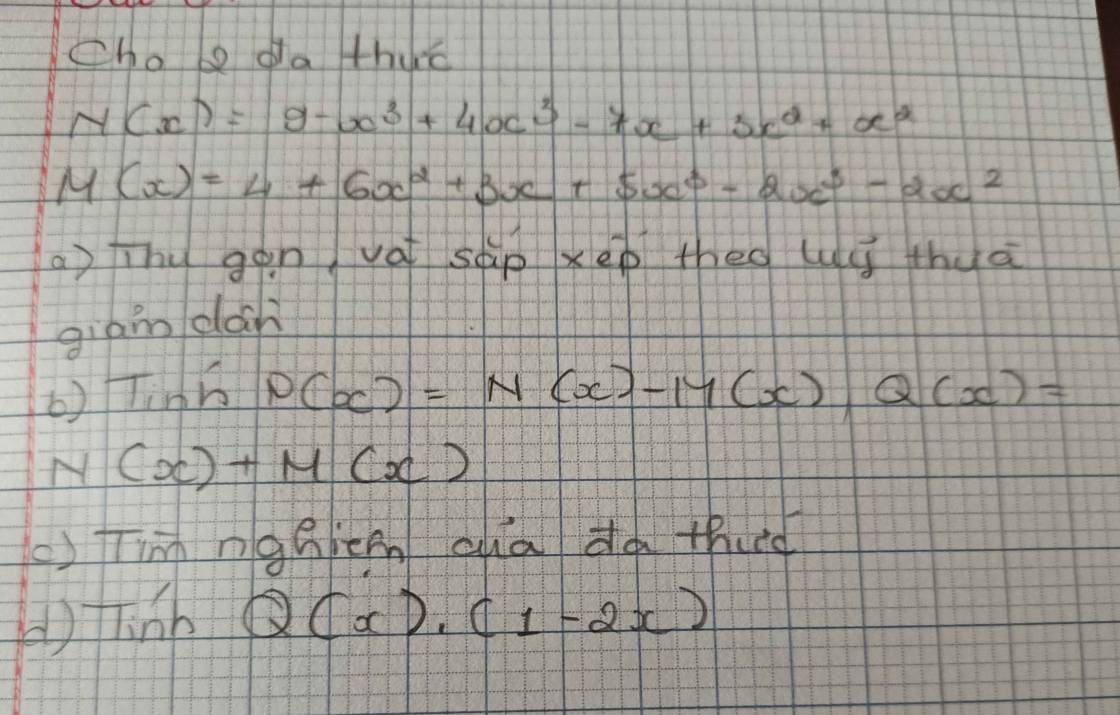 giúp e câu c,d với ạ
giúp e câu c,d với ạ

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Giúp e câu c vs d với ạ
Giúp em với ạ câu C,D,E
c) 108(12 + 13 ) + 25 . 92
= 2700 + 2300
= 5000
d) 2.169.12 - 3.68.8 - 24
= ( 2 .12 ) . 169 - (3.8) . 68 - 24
= 24 . 169 - 24 . 68 - 24
= 24(169 - 68 ) - 24
= 2424 - 24 = 2400
e) 2.56.24 - 3.36.16 + 4.12.95 + 6.3.8.5
= ( 2 . 24 ) . 56 - ( 3.16 ) . 36 + (4.12) .95 + (6.8) . 3 . 5
= 48 . 56 - 48 . 36 + 48 . 95 + 48 . 15
= 48(56 - 36 + 95 + 15 )
= 6240
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
c) 108.12+25.92+13.108
=(108+12)+(25.13)+(108+92)
=120+325+200
=645
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giúp mình câu c, d, e với ạ
a: \(A=\dfrac{x\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)^2}:\dfrac{x^2-4+x+6-x^2}{x\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x+2\right)}{x-2}\cdot\dfrac{x}{x+2}=\dfrac{x^2}{x-2}\)
c: A<0
=>x-2<0
=>x<2
d: B nguyên
=>x^2-4+4 chia hết cho x-2
=>x-2 thuộc {1;-1;2;-2;4;-4}
=>x thuộc {3;1;4;6}
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giúp mik câu c,d,e với ạ mik đag cần gấp ạ
\(c,\Rightarrow\left|x-\dfrac{1}{9}\right|=-\dfrac{4}{5}\\ \Rightarrow x\in\varnothing\left(\left|x-\dfrac{1}{9}\right|\ge0>-\dfrac{4}{5}\right)\\ d,\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x-2=0\\4y-7=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\y=\dfrac{7}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\\ e,\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+1=0\\x-y=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=y=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow x=y=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)

GIÚP MIK CÂU C,D,E,H VỚI Ạ
Để phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt thì:
\(\Delta>0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(-5\right)^2-4.1.\left(m+4\right)>0\\ \Leftrightarrow25-4m-16>0\\\Leftrightarrow9-4m>0\\ \Leftrightarrow m< \dfrac{9}{4}\)
Theo viét:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=5\\x_1x_2=m+4\end{matrix}\right.\)
c,
\(\left|x_1-x_2\right|=3\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x_1-x_2\right)^2=9\\ \Leftrightarrow x_1^2-2x_1x_2+x_2^2=9\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-4x_1x_2=9\\ \Leftrightarrow5^2-4\left(m+4\right)=9\\ \Leftrightarrow25-4m-16=9\\ \Leftrightarrow m=0\left(nhận\right)\)
d.
\(\left|x_1\right|+\left|x_2\right|=4\\ \)
Xét trường hợp 1: hai nghiệm đều dương:
ta có:
\(x_1+x_2=4\)
5 = 4 (vô lý)
Loại trường hợp này.
Xét trường hợp 2: hai nghiệm đều âm, tương tự ta loại trường hợp này.
Xét trường hợp 3:
\(x_1< 0< x_2\)
=> \(x_2-x_1=4\)
<=> \(x_2+x_1-2x_1=4\)
=> \(5-2x_1=4\)
=> \(x_1=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(x_2< 0< x_1\)
\(x_1-x_2=4\\ \Leftrightarrow x_1+x_2-2x_2=4\\ \Leftrightarrow5-2x_2=4\\ \Rightarrow x_2=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Có: \(x_1x_2=m+4\\\)
<=> \(\dfrac{1}{2}.\dfrac{1}{2}=m+4\)
=> m = -3,75 (nhận)
e.
Theo viét và theo đề ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x_1+4x_2=6\left(1\right)\\x_1+x_2=5\left(2\right)\\x_1x_2=m+4\left(3\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Từ (1) có \(x_1=\dfrac{6-4x_2}{3}=2-\dfrac{4}{3}x_2\) (x)
Thế (x) vào (2) được \(2-\dfrac{4}{3}x_2+x_2=5\)
=> \(x_2=-9\) (xx)
Thế (xx) vào (1) được \(3x_1+4.\left(-9\right)=6\)
=> \(x_1=14\) (xxx)
Thế (xx) và (xxx) vào (3) được:
\(14.\left(-9\right)=m+4\)
=> m = -130 (nhận)
h.
\(x_1\left(1-3x_2\right)+x_2\left(1-3x_1\right)=m^2-23\)
<=> \(x_1-3x_1x_2+x_2-3x_1x_2=m^2-23\)
<=> \(x_1+x_2-6x_1x_2=m^2-23\)
<=> \(5-6.\left(m+4\right)=m^2-23\)
<=> \(5-6m-20-m^2+23=0\)
<=> \(-m^2-6m+8=0\)
\(\Delta=\left(-6\right)^2-4.\left(-1\right).8=68\)
\(m_1=\dfrac{6+\sqrt{68}}{2.\left(-1\right)}=-3-\sqrt{17}\left(nhận\right)\)
\(m_2=\dfrac{6-\sqrt{68}}{2.\left(-1\right)}=-3+\sqrt{17}\left(nhận\right)\)
☕T.Lam
Mình không chắc chắn ở câu d, mình lên đây để ôn bài thi tiện thể giúp được bạn phần nào.
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
 giúp mình làm bài 1 câu c,d ,e với ạ
giúp mình làm bài 1 câu c,d ,e với ạ
Đây là nội dung của bài 1 câu c, d, e:
**Câu c:**
\[
\begin{cases}
2x - 3y = 11 \\
-4x + 6y = 5
\end{cases}
\]
**Câu d:**
\[
\begin{cases}
3x + 2y = 1 \\
2x - y = 3
\end{cases}
\]
**Câu e:**
\[
\begin{cases}
2x + 5y = 2 \\
6x - 15y = 6
\end{cases}
\]
3: \(\begin{cases}2x-3y=11\\ -4x+6y=5\end{cases}\Rightarrow\begin{cases}4x-6y=22\\ -4x+6y=5\end{cases}\)
=>\(\begin{cases}4x-6y-4x+6y=22+5\\ 2x-3y=11\end{cases}\Rightarrow\begin{cases}0x=27\\ 2x-3y=11\end{cases}\)
=>(x;y)∈∅
4: \(\begin{cases}3x+2y=1\\ 2x-y=3\end{cases}\Rightarrow\begin{cases}3x+2y=1\\ 4x-2y=6\end{cases}\)
=>\(\begin{cases}3x+2y+4x-2y=1+6=7\\ 2x-y=3\end{cases}\Rightarrow\begin{cases}7x=7\\ y=2x-3\end{cases}\)
=>\(\begin{cases}x=1\\ y=2\cdot1-3=2-3=-1\end{cases}\)
5: \(\begin{cases}2x+5y=2\\ 6x-15y=6\end{cases}\Rightarrow\begin{cases}6x+15y=6\\ 6x-15y=6\end{cases}\)
=>\(\begin{cases}6x+15y+6x-15y=6+6=12\\ 2x+5y=2\end{cases}=.\begin{cases}12x=12\\ 5y=2-2x\end{cases}\)
=>\(\begin{cases}x=1\\ 5y=2-2\cdot1=0\end{cases}\Rightarrow\begin{cases}x=1\\ y=0\end{cases}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
GIÚP EM BÀI GIẢI PT VÀ CÂU C,D,E BÀI 2 VỚI Ạ..
\(b,B=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+2}{\sqrt{x}-3}+\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-8}{x-5\sqrt{x}+6}\left(x\ge0;x\ne4;x\ne9\right)\\ B=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)+\sqrt{x}-8}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)}\\ B=\dfrac{x-4+\sqrt{x}-8}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)}=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-4\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)}=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-4}{\sqrt{x}-2}\)
\(c,B< A\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-4}{\sqrt{x}-2}< \dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-2}\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-4}{\sqrt{x}-2}-\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-2}< 0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{-5}{\sqrt{x}-2}< 0\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}-2>0\left(-5< 0\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow x>4\\ d,P=\dfrac{B}{A}=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-4}{\sqrt{x}-2}:\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-2}=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-4}{\sqrt{x}+1}=1-\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+1}\in Z\\ \Leftrightarrow5⋮\sqrt{x}+1\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}+1\inƯ\left(5\right)=\left\{-5;-1;1;5\right\}\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}\in\left\{-6;-2;0;4\right\}\\ \Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{0;16\right\}\left(\sqrt{x}\ge0\right)\)
\(e,P=1-\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+1}\)
Ta có \(\sqrt{x}+1\ge1,\forall x\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+1}\ge5\Leftrightarrow1-\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+1}\le-4\)
\(P_{max}=-4\Leftrightarrow x=0\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
giúp e giải bài này với ạ
câu b c d thui nha mng

b: Thay x=-1 và y=-3 vào (d1), ta được:
-3=-1+2
=>-3=1(loại)
=>A ko thuộc (d1)
Thay x=-1 và y=1 vào (d1), ta đc:
-1+2=1
=>1=1
=>B thuộc (d1)
c: Tọa độ C là:
x+2=-1/2x+2 và y=x+2
=>x=0 và y=2
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)


















