Read the text again and fill the table below.
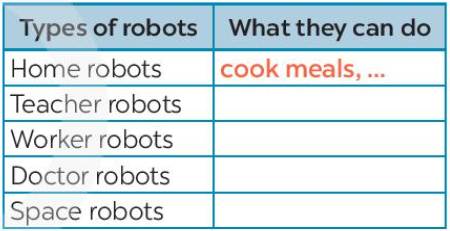
Read the text below and fill in the blank.
Question 4
A. taking
B. eating
C. baking
D. cooking
Đáp án: D
Dịch: Nhiều người Việt Nam chuẩn bị cho Tết bằng cách nấu các món ăn ngày lễ đặc biệt và dọn dẹp nhà cửa.
Read the text below and fill in the blank.
Question 3
A. calendar
B. paper
C. year
D. decade
Read the text below and fill in the blank.
Question 8
A. coming up
B. upcoming
C. come up
D. upcome
Đáp án: B
Vị trí trống cần tính từ. Upcoming: sắp tới
Read the text below and fill in the blank.
Question 6
A. on
B. at
C. in
D. by
Đáp án: A
On the+ số thứ tự
On the first day: vào ngày đầu tiên
Read the text below and fill in the blank.
Question 7
A. celebrating
B. meeting
C. worshipping
D. decorating
Đáp án: C
Ancestral worshipping: việc thờ cúng tổ tiên
Read the text below and fill in the blank.
Question 2
A. takes part
B. takes care of
C. takes place
D. takes turn
Read the text below and fill in the blank.
Question 5
A. prepared
B. practiced
C. performed
D. done
Đáp án: B
Dịch: Có rất nhiều phong tục tập quán trong dịp Tết…
Read the text and complete the comparison table below.
BACTERIA AND VIRUSES
Both bacteria and viruses can cause diseases, but they are different in many ways. Bacteria are living organisms. They can live in many places, such as soil, water, and the human body. The smallest bacteria are about 0.4 micron* in diameter. Some bacteria in our bodies are helpful, but some can cause infectious diseases such as tuberculosis** or food poisoning. Antibiotics are often used to treat infections caused by bacteria.
*7 metre = 1 million microns
**a serious lung disease
Viruses are tiny germs that cause diseases in people, animals, and plants. They can cause a range of illnesses, from the common cold or the flu to more serious diseases such as AIDS and Covid-19. As they are very small (0.02 to 0.25 micron), viruses can get into our bodies easily. They are not living things, so they need to enter our bodies to become active. Then, they start to grow and cause the infected cell to make millions of copies of the virus. Vaccines are often used to prevent the spread of diseases caused by viruses.
| Bacteria | Viruses |
1. Living or not when entering the human body? |
|
|
2. Which is smaller? |
|
|
3. Examples of diseases they can cause |
|
|
4. How to treat/prevent diseases caused by them? |
|
|
Read the text and complete the comparison table below.
BACTERIA AND VIRUSES
Both bacteria and viruses can cause diseases, but they are different in many ways. Bacteria are living organisms. They can live in many places, such as soil, water, and the human body. The smallest bacteria are about 0.4 micron* in diameter. Some bacteria in our bodies are helpful, but some can cause infectious diseases such as tuberculosis** or food poisoning. Antibiotics are often used to treat infections caused by bacteria.
*7 metre = 1 million microns
**a serious lung disease
Viruses are tiny germs that cause diseases in people, animals, and plants. They can cause a range of illnesses, from the common cold or the flu to more serious diseases such as AIDS and Covid-19. As they are very small (0.02 to 0.25 micron), viruses can get into our bodies easily. They are not living things, so they need to enter our bodies to become active. Then, they start to grow and cause the infected cell to make millions of copies of the virus. Vaccines are often used to prevent the spread of diseases caused by viruses.
| Bacteria | Viruses |
1. Living or not when entering the human body? | living | not living |
2. Which is smaller? | bigger
| smaller |
3. Examples of diseases they can cause | tuberculosis or food poisoning | common cold or the flu to more serious diseases such as AIDS and Covid-19 |
4. How to treat/prevent diseases caused by them? | antibiotics | vaccines |
| Bacteria | Viruses |
1. Living or not when entering the human body? | living | not living |
2. Which is smaller? | bigger | smaller |
3. Examples of diseases they can cause | tuberculosis or food poisoning | common cold or the flu to more serious diseases such as AIDS and Covid-19 |
4. How to treat/prevent diseases caused by them? | antibiotics | vaccines |
Read the text and complete the table below with information from the text. Use no more than TWO words or a number in each gap.
UK EDUCATION AFTER SECONDARY SCHOOL
In the UK, students can choose to end their formal education at 16, but in England they must stay in full-time education or do a training course until the age of 18.
Many 16-year-old students go on to study at different vocational colleges. Vocational education usually lasts up to three years. During this time, students learn job-specific skills. That is why vocational education is often referred to as career education or technical education. Many students still go on to higher education after receiving their vocational qualifications.
Alternatively, students can go toa sixth-form college or stay at their secondary school if it offers a sixth form for two more years. Students usually focus on three or four subjects that they are interested in or related to the degree they want to study at university. Exams are taken at the end of the two-year course, and the grades are used to apply for university courses. Not all students leaving sixth form go to university. Some prefer to get into a vocational course or find a job.
At university, students study for at least three years in order to get a bachelor’s degree. After the first degree, they can study for one to two years to get a master’s degree, and three to five years to get a doctorate.
UK education after secondary school | |
Age at end of formal education | - 16 in the UK - stay until the age of (1) ________ in full-time education or do training in England |
Vocational education | - lats up to three years - also called career education or (2) _________ - some students still go on to (3) _________ |
Sixth form | - lasts two years - students study subjects they are interested in or subjects related to higher education. - grades are used to apply for (4) _________ |
University education | Students study to get a (5) ________, a master’s degree, or a doctorate |
1 - 18 | 2 - technical education | 3 - higher education |
4 - university courses | 5 - bachelor’s degree |
1. 18
Thông tin: but in England they must stay in full-time education or do a training course until the age of 18.
(nhưng ở Anh, học sinh phải tiếp tục học toàn thời gian hoặc tham gia một khóa đào tạo cho đến năm 18 tuổi.)
2. technical education
Thông tin: That is why vocational education is often referred to as career education or technical education.
(Đó là lý do tại sao giáo dục nghề nghiệp thường được gọi là giáo dục nghề nghiệp hoặc giáo dục kỹ thuật.)
3. higher education
Thông tin: Many students still go on to higher education after receiving their vocational qualifications.
(Nhiều sinh viên vẫn tiếp tục học cao hơn sau khi nhận được bằng cấp nghề.)
4. university courses
Thông tin: Exams are taken at the end of the two-year course, and the grades are used to apply for university courses.
(Các kỳ thi được thực hiện vào cuối khóa học hai năm và điểm số được sử dụng để nộp đơn vào các khóa học đại học.)
5. bachelor’s degree
Thông tin: At university, students study for at least three years in order to get a bachelor’s degree.
(Tại trường đại học, sinh viên học ít nhất ba năm để lấy bằng cử nhân.)