Tìm x: x : 2/3 = 1/2
A. x=4/5
B. x=4/3
C. x=2/4
D. x= 1/3

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Cho a\LARGE \!Nhấp chuột và kéo để di chuyển/b = c/d Chứng minh 2a+ 5b / 3a -4b = 2c + 5d / 3c - 4d 2 y+x+1 / x = x+z+2 / y = x+y-3 /z = 1 / x+y+z tính x,y,z
Câu 1:): Tìm X
A) X + 2/3 = 4/5
B) 7/9 - X = 1/3
C) X : 2/3 = 9/8
D) X x 4/7 - X x 3/4 = 10
GIẢI GIÚP MÌNH VỚI Ạ!
A) \(x-\dfrac{2}{3}=\dfrac{4}{5}\\ x=\dfrac{4}{5}+\dfrac{2}{3}\)
\(x=\dfrac{22}{15}\)
b)\(\dfrac{7}{9}-x=\dfrac{1}{3}\\ x=\dfrac{7}{9}-\dfrac{1}{3}\\ x=\dfrac{4}{9}\)
C)\(x:\dfrac{2}{3}=\dfrac{9}{8}\\ x=\dfrac{9}{8}x\dfrac{2}{3}\\ x=\dfrac{3}{4}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (5)
1.tính thuận tiện
a. 2/3 x 4/5 + 1/3 x 4/5
b. 2/3 x 4/5 - 1/3 x 4/5
c. 1/2 : 3/4 + 1/6 : 3/4
d. 1/2 : 3/4 - 1/6 : 3/4
a)\(\dfrac{2}{3}.\dfrac{4}{5}+\dfrac{1}{3}.\dfrac{4}{5}=\left(\dfrac{2}{3}+\dfrac{1}{3}\right).\dfrac{4}{5}=1.\dfrac{4}{5}=\dfrac{4}{5}\)
b)\(\dfrac{2}{3}.\dfrac{4}{5}-\dfrac{1}{3}.\dfrac{4}{5}=\left(\dfrac{2}{3}-\dfrac{1}{3}\right).\dfrac{4}{5}=\dfrac{1}{3}.\dfrac{4}{5}=\dfrac{4}{15}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (4)
a) \(\dfrac{2}{3}\times\dfrac{4}{5}+\dfrac{1}{3}\times\dfrac{4}{5}=\dfrac{4}{5}\times\left(\dfrac{2}{3}+\dfrac{1}{3}\right)=\dfrac{4}{5}\times1=\dfrac{4}{5}\)
b) \(\dfrac{2}{3}\times\dfrac{4}{5}-\dfrac{1}{3}\times\dfrac{4}{5}=\dfrac{4}{5}\times\left(\dfrac{2}{3}-\dfrac{1}{3}\right)=\dfrac{4}{5}\times\dfrac{1}{3}=\dfrac{4}{15}\)
c) \(\dfrac{1}{2}:\dfrac{3}{4}+\dfrac{1}{6}:\dfrac{3}{4}=\dfrac{1}{2}\times\dfrac{4}{3}+\dfrac{1}{6}\times\dfrac{4}{3}=\dfrac{4}{3}\times\left(\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{6}\right)=\dfrac{4}{3}\times\dfrac{2}{3}=\dfrac{8}{9}\)
d) \(\dfrac{1}{2}:\dfrac{3}{4}-\dfrac{1}{6}:\dfrac{3}{4}=\dfrac{1}{2}\times\dfrac{4}{3}-\dfrac{1}{6}\times\dfrac{4}{3}=\dfrac{4}{3}\left(\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{6}\right)=\dfrac{4}{3}\times\dfrac{1}{3}=\dfrac{4}{9}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
c)\(\dfrac{1}{2}:\dfrac{3}{4}+\dfrac{1}{6}:\dfrac{3}{4}=\dfrac{1}{2}.\dfrac{4}{3}+\dfrac{1}{6}.\dfrac{4}{3}=\left(\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{6}\right).\dfrac{4}{3}=\dfrac{2}{3}.\dfrac{4}{3}=\dfrac{8}{9}\)
d)\(\dfrac{1}{2}:\dfrac{3}{4}-\dfrac{1}{6}:\dfrac{3}{4}=\dfrac{1}{2}.\dfrac{4}{3}-\dfrac{1}{6}.\dfrac{4}{3}=\left(\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{6}\right).\dfrac{4}{3}=\dfrac{1}{3}.\dfrac{4}{3}=\dfrac{4}{9}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Dùng định nghĩa 2 phân thức bằng nhau chứng tỏ rằng: 1)1-x/2-y=x-1/y-2 2)2a/-5b=-2a/5b 3)x-2 /-x=2^3-x^3/x (x^2+2x+4)
Viết theo HĐT
a) (x - 1)3
b) (2x + 3y)3
c) x3– 64.
d) 27x3+ 8y3
.
Bài 3. Tìm x, biết:
a) (x – 2)3– x2(x – 6) = 5
b) (x – 1)(x2+ x + 1) – x(x + 2)(x – 2) = 4
c) (x + 2)3– (x + 2) = 0
Bài 4. Tìm x biết (x + 2021)3+ (3x - 2022)3=(4x– 1)3
a) \(\left(x-1\right)^3\)
\(=x^3-3x^2+3x-1\)
b) \(\left(2x-3y\right)^3\)
\(=\left(2x\right)^3-3\left(2x\right)^23y+3.2x\left(3y\right)^3+\left(3y\right)^3\)
\(=8x^3-36x^2y+54xy^2-27y^3\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 3:
a: Ta có: \(\left(x-2\right)^3-x^2\left(x-6\right)=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-6x^2+12x-8-x^3+6x^2=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x=13\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{13}{12}\)
b: Ta có: \(\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)-x\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-1-x^3+4x=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=5\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{5}{4}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
tìm x , biết
a. 4x(x-5)-(x-1)(4x-3)=5
b. (3x-4)(x-2) = 3x(x-9)-3
c.2(x+3)-x2 -3x=0
d. 8x3-50x=0
e. (4x-30)2-3x(3-4x)
\(a,\Rightarrow4x^2-20x-4x^2+3x+4x-3=5\\ \Rightarrow-13x=8\Rightarrow x=-\dfrac{8}{13}\\ b,\Rightarrow3x^2-10x+8-3x^2+27x=-3\\ \Rightarrow17x=-11\Rightarrow x=-\dfrac{11}{17}\\ c,\Rightarrow\left(x+3\right)\left(2-x\right)=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\\ d,\Rightarrow2x\left(4x^2-25\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow2x\left(2x-5\right)\left(2x+5\right)=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\dfrac{2}{5}\\x=-\dfrac{2}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\\ e,Sửa:\left(4x-3\right)^2-3x\left(3-4x\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(4x-3\right)^2+3x\left(4x-3\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(4x-3\right)\left(7x-3\right)=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3}{4}\\x=\dfrac{3}{7}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
a.
4x(x-5) - (x-1)(4x-3)-5=0
4x^2-20x-4x^2+3x+4x+3=0
(4x^2-4x^2)+(-20x+3x+4x)+3=0
13x+3 = 0
13x=-3
x=-3/13
b,
(3x-4)(x-2)-3x(x-9)+3=0
3x^2-6x-4x+8 - 3x^2+27x+3=0
(3x^2-3x^2)+(-6x-4x+27x)+(8+3)=0
17x+11=0
17x=-11
x=-11/17
c, 2(x+3)-x^2-3x=0
2(x+3) - x(x+3)=0
(x+3)(2-x)=0
TH1: x+3 = 0; x=-3
TH2: 2-x=0;x=2
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm x
a) -1/2 . x = 5
b) x-1/9 = 8/3
c) x + 5/6 = 16/42 - -8/56
d) 1 3/4x - 5 = -3 1/3
e) 3 1/3 - 3/4 : x = -1/6
g) 3/x + 5 = 15%
h) 1/2 + 1/2.3 + 1/3.4 +...+1/x(x+1) = 49/50
Tìm x
a) -1/2 . x = 5
b) x-1/9 = 8/3
c) x + 5/6 = 16/42 - -8/56
d) 1 3/4x - 5 = -3 1/3
e) 3 1/3 - 3/4 : x = -1/6
g) 3/x + 5 = 15%
h) 1/2 + 1/2.3 + 1/3.4 +...+1/x(x+1) = 49/50
a: x=5:(-1/2)=-10
b: x=8/3+1/9=25/9
c: =>x+5/6=11/21
=>x=-13/42
d: =>7/4x-5=-10/3
=>7/4x=5/3
=>x=20/21
e: =>10/3-3/4:x=-1/6
=>3/4:x=10/3+1/6=21/6=7/2
=>x=3/4:7/2=3/4*2/7=6/28=3/14
g: =>3/(x+5)=3/20
=>x+5=20
=>x=15
h: =>1-1/2+1/2-1/3+...+1/x-1/x+1=49/50
=>1-1/x+1=49/50
=>x+1=50
=>x=49
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
` P = ( (x)/(2x-2) + ( 3 - x )/(2x^2-2) ) . ( (x+1)/(x^2+x+1) + ( x+2)/(x^3-1) ) `
a) rút gọn
b) Tìm x để P = 3
c) Tìm x để P > 4
d) So sánh P với 2
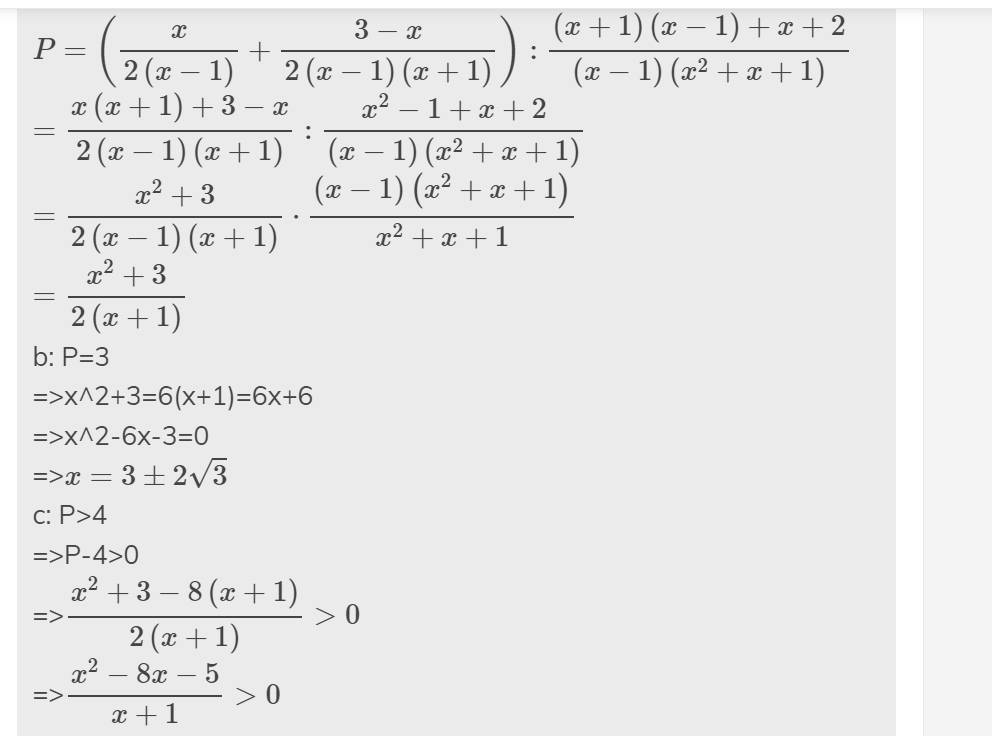
a: Sửa đề: \(P=\left(\dfrac{x}{2x-2}+\dfrac{3-x}{2x^2-2}\right):\left(\dfrac{x+1}{x^2+x+1}+\dfrac{x+2}{x^3-1}\right)\)\(P=\left(\dfrac{x}{2\left(x-1\right)}+\dfrac{3-x}{2\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\right):\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)+x+2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)+3-x}{2\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}:\dfrac{x^2-1+x+2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+3}{2\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}{x^2+x+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+3}{2\left(x+1\right)}\)
b: P=3
=>x^2+3=6(x+1)=6x+6
=>x^2-6x-3=0
=>\(x=3\pm2\sqrt{3}\)
c: P>4
=>P-4>0
=>\(\dfrac{x^2+3-8\left(x+1\right)}{2\left(x+1\right)}>0\)
=>\(\dfrac{x^2-8x-5}{x+1}>0\)
TH1: x^2-8x-5>0 và x+1>0
=>x>-1 và (x<4-căn 21 hoặc x>4+căn 21)
=>-1<x<4-căn 21 hoặc x>4+căn 21
Th2: x^2-8x-5<0 và x+1<0
=>x<-1 và (4-căn 21<x<4+căn 21)
=>Vô lý
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
` P = ( (x)/(2x-2) + ( 3 - x )/(2x^2-2) ) : ( (x+1)/(x^2+x+1) + ( x+2)/(x^3-1) ) `
a) rút gọn
b) Tìm x để P = 3
c) Tìm x để P > 4
d) So sánh P với 2