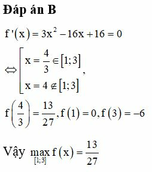x3-16x=0

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Tìm giá trị của x, biết:
a. x3 - 16x = 0 b. (2x + 1)2 - (x - 1)2 = 0
a) \(x^3-16x=0\)
⇔\(x\left(x^2-16\right)=0\)
⇒\(x=0\) hoặc \(x^2-16=0\)
\(TH_1:x=0\)
\(TH_2:x^2-16=0\) ⇔ \(x^2=16\) ⇔ \(x=\pm4\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{0;\pm4\right\}\)
b) \(\left(2x+1\right)^2-\left(x-1\right)^2=0\)
⇒ \(2x+1=x-1\)
⇒ \(2x+2=x\)
⇒ \(2\left(x+1\right)=x\) ⇒ x = -2
Vậy x = -2
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm x:
a) x2+9x=0
b) (x+4)2-16=0
c) x3-16x=0
d) x2-10x+25=0
\(a,\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+9\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-9\end{matrix}\right.\\ b,\Leftrightarrow\left(x+4-4\right)\left(x+4+4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(x+8\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-8\end{matrix}\right.\\ c,\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=4\\x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\\ d,\Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=5\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
a) \(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+9\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-9\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) \(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+8\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-8\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) \(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=4\\x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
d) \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)^2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x=5\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (1)
phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử , tìm x
1, x^3-x=0
2,x3-16x=0
1) \(x^3-x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x.\left(x^2-1\right)=0\)
\(\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x^2-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=1\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy :.....
2) \(x^3-16x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x.\left(x^2-16\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x^2-16=0\Rightarrow x^2=16\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=8\\x=-8\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy :....
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1) x2 - 11x + 3
2) 1+7x3
3) x3 + 3x2 - 16x - 48
4) x3 - x2 – x - 1
5) x3 + 2x2 - 2x - 1
6) 4x(x - 3y )+ 12y(3y - x)
3: \(x^3+3x^2-16x-48\)
\(=x^2\left(x+3\right)-16\left(x+3\right)\)
\(=\left(x+3\right)\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
Tìm x
a, 3/4x*(x2-9)=0
b, x3-16x=0
c, (x-1)(x+2)-x-2=0
d, 3x3-27x=0
e, x2(x+1)+2x(x+1)=0
f, x(2x-3)-2(3-2x)=0
c: =>(x-1)(x+1)=0
hay \(x\in\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a,
\(=\dfrac{3}{4x}.\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)\)=0
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3}{4x}=0\\x-3=0\\x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(x=\left\{3,-3\right\}\)
b,
\(x^3-16x=0\\x\left(x^2-16\right)\\ x\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x-4=0\\x+4=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(x=\left\{-4,0,4\right\}\)
d,
\(3x^3-27x=0\\ 3x\left(x^2-9\right)=0\\ 3x\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x=0\\x-3=0\\x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(x=\left\{-3,0,3\right\}\)
e,
\(x^2+\left(x+1\right)+2x\left(x+1\right)=0\\ x\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x+1=0\\x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(x=\left\{-2,-1,0\right\}\)
f,
\(x\left(2x-3\right)-2\left(3-2x\right)=0\\ \left(2x-3\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-3=0\\x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3}{2}\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Phân thức đa thức thành nhân tử:
x2y-x3-16y+16x
\(x^2y-x^3-16y+16x=\left(x^2y-x^3\right)-\left(16y-16x\right)=x^2\left(y-x\right)-16\left(y-x\right)=\left(x^2-16\right)\left(y-x\right)=\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)\left(y-x\right)\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
\(x^2y-x^3-16y+16x=-x^2\left(x-y\right)+16\left(x-y\right)=\left(x-y\right)\left(16-x^2\right)=\left(x-y\right)\left(4-x\right)\left(4+x\right)\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (2)
Ta có: \(x^2y-x^3+16x-16y\)
\(=x^2\left(y-x\right)-\left(y-x\right)\)
\(=\left(y-x\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử :
a.x4 - 4x3 + 11x2 - 16x + 16
b.x4 + 6x3 + 13x2 + 12x + 4
c.x4 + x3 - 4x2 + x + 1
d.x4 + x3 - 4x2 + x + 1
c: \(x^4+x^3-4x^2+x+1\)
\(=x^4-x^3+2x^3-2x^2-2x^2+2x-x+1\)
\(=\left(x-1\right)\left(x^3+2x^2-2x-1\right)\)
\(=\left(x-1\right)\left[\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)+2x\left(x-1\right)\right]\)
\(=\left(x-1\right)^2\cdot\left(x^2+3x+1\right)\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Xét sự đồng biến, nghịch biến của các hàm số:a) y 3
x
2
− 8
x
3
b) y 16x + 2
x
2
− 16
x
3
/3 −
x
4
c) y
x
3
− 6
x
2
+ 9xd) y
x
4
+ 8...
Đọc tiếp
Xét sự đồng biến, nghịch biến của các hàm số:
a) y = 3 x 2 − 8 x 3
b) y = 16x + 2 x 2 − 16 x 3 /3 − x 4
c) y = x 3 − 6 x 2 + 9x
d) y = x 4 + 8 x 2 + 5
a) TXĐ: R
y′ = 6x − 24 x 2 = 6x(1 − 4x)
y' = 0 ⇔ 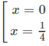
y' > 0 trên khoảng (0; 1/4) , suy ra y đồng biến trên khoảng (0; 1/4)
y' < 0 trên các khoảng ( - ∞ ; 0 ); (14; + ∞ ), suy ra y nghịch biến trên các khoảng ( - ∞ ;0 ); (14; + ∞ )
b) TXĐ: R
y′ = 16 + 4x − 16 x 2 − 4 x 3 = −4(x + 4)( x 2 − 1)
y' = 0 ⇔ 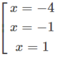
Bảng biến thiên:
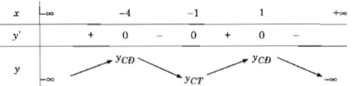
Vậy hàm số y đã cho đồng biến trên các khoảng ( - ∞ ; -4) và (-1; 1), nghịch biến trên các khoảng (-4; -1) và (1; + ∞ )
c) TXĐ: R
y′ = 3 x 2 − 12x + 9
y' = 0
y' > 0 trên các khoảng ( - ∞ ; 1), (3; + ∞ ) nên y đồng biến trên các khoảng ( - ∞ ; 1), (3; + ∞ )
y'< 0 trên khoảng (1; 3) nên y nghịch biến trên khoảng (1; 3)
d) TXĐ: R
y′ = 4 x 3 + 16 = 4x( x 2 + 4)
y' = 0 ⇔ 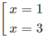
y' > 0 trên khoảng (0; + ∞ ) ⇒ y đồng biến trên khoảng (0; + ∞ )
y' < 0 trên khoảng ( - ∞ ; 0) ⇒ y nghịch biến trên khoảng ( - ∞ ; 0)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giá trị lớn nhất của hàm số f x = x 3 - 8 x 2 + 16 x - 9 trên đoạn 1 ; 3 là:
A. -6
B. 13 27
C. 0
D. 5
Giá trị lớn nhất của hàm số
f
x
x
3
-
8
x
2
+
16
x
-
9
trên đoạn
1
;
3
là A.
m
a
x
[
1
;
3...
Đọc tiếp
Giá trị lớn nhất của hàm số f x = x 3 - 8 x 2 + 16 x - 9 trên đoạn 1 ; 3 là
A. m a x [ 1 ; 3 ] f x = - 6
B. m a x [ 1 ; 3 ] f x = 13 27
C. m a x [ 1 ; 3 ] f x = 0
D. m a x [ 1 ; 3 ] f x = 5