a) 2x(x + 1) – 2x2 = 0
b) 3(x – 7) + 4x(x – 7) = 0
c) x2 – x = 12

Những câu hỏi liên quan
a) 2x2 + 2x(5 - x)12 d) 2(x + 5) - x2 - 5x 0 g) (3x + 1)2 - (x+1) 0b) (5 - 2x)2 - 16 0 e) (2x - 1)2 - 4(x + 7)(x - 7) 0 h) x2 + 7x - 8 0c) 3x2 - 3x(x-2) 36 f) (x + 4)2 - (x + 1)(x - 1) 16 i) -2x2 +13x -15 0mik cần gấp, cảm ơn mọi người.
Đọc tiếp
a) 2x2 + 2x(5 - x)=12 d) 2(x + 5) - x2 - 5x = 0 g) (3x + 1)2 - (x+1) = 0
b) (5 - 2x)2 - 16 = 0 e) (2x - 1)2 - 4(x + 7)(x - 7) = 0 h) x2 + 7x - 8 = 0
c) 3x2 - 3x(x-2) = 36 f) (x + 4)2 - (x + 1)(x - 1) = 16 i) -2x2 +13x -15 = 0
mik cần gấp, cảm ơn mọi người.
\(a,\Leftrightarrow2x^2+10x-2x^2=12\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{12}{10}=\dfrac{6}{5}\\ b,\Leftrightarrow\left(5-2x-4\right)\left(5-2x+4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(1-2x\right)\left(9-2x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=\dfrac{9}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\\ c,\Leftrightarrow3x^2-3x^2+6x=36\Leftrightarrow x=6\\ d,\Leftrightarrow2\left(x+5\right)-x\left(x+5\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2-x\right)\left(x+5\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\\ e,\Leftrightarrow4x^2-4x+1-4x^2+196=0\\ \Leftrightarrow-4x=-197\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{197}{4}\)
\(f,\Leftrightarrow x^2+8x+16-x^2+1=16\Leftrightarrow8x=-1\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{8}\\ g,Sửa:\left(3x+1\right)^2-\left(x+1\right)^2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3x+1-x-1\right)\left(3x+1+x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow2x\left(4x+2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\\ h,\Leftrightarrow x^2+8x-x-8=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+8\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-8\end{matrix}\right.\\ i,\Leftrightarrow2x^2-13x+15=0\\ \Leftrightarrow2x^2+2x-15x-15=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(2x-15\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=\dfrac{15}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Giúp vs ạBài 1 giải các bất phương trình saua.x2 - x - 6 0b.2x2 - 7x + 5 0c.3x2 - 9x + 6 ≥ 0d.2x2 - 5x + 3 0Bài 2 Giải phương trình sauA.√x2 + x + 5 √2x2 - 4x + 1B.√11x2 -14x - 12 √3x2 + 4x - 7
Đọc tiếp
Giúp vs ạ
Bài 1 giải các bất phương trình sau
a.x2 - x - 6 = 0
b.2x2 - 7x + 5 < 0
c.3x2 - 9x + 6 ≥ 0
d.2x2 - 5x + 3 < 0
Bài 2 Giải phương trình sau
A.√x2 + x + 5 = √2x2 - 4x + 1
B.√11x2 -14x - 12 = √3x2 + 4x - 7
Bài 2:
a: =>2x^2-4x+1=x^2+x+5
=>x^2-5x-4=0
=>\(x=\dfrac{5\pm\sqrt{41}}{2}\)
b: =>11x^2-14x-12=3x^2+4x-7
=>8x^2-18x-5=0
=>x=5/2 hoặc x=-1/4
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình bằng cách đặt ẩn phụ:
a
)
3.
x
2
+
x
2
−
2
x
2
+
x...
Đọc tiếp
Giải phương trình bằng cách đặt ẩn phụ:
a ) 3. x 2 + x 2 − 2 x 2 + x − 1 = 0 b ) x 2 − 4 x + 2 2 + x 2 − 4 x − 4 = 0 c ) x − x = 5 x + 7 d ) x x + 1 − 10 ⋅ x + 1 x = 3
a)
3 · x 2 + x 2 - 2 x 2 + x - 1 = 0 ( 1 )
Đặt t = x 2 + x ,
Khi đó (1) trở thành : 3 t 2 – 2 t – 1 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2) : Có a = 3 ; b = -2 ; c = -1
⇒ a + b + c = 0
⇒ (2) có hai nghiệm t 1 = 1 ; t 2 = c / a = - 1 / 3 .
+ Với t = 1 ⇒ x 2 + x = 1 ⇔ x 2 + x – 1 = 0 ( * )
Có a = 1; b = 1; c = -1 ⇒ Δ = 1 2 – 4 . 1 . ( - 1 ) = 5 > 0
(*) có hai nghiệm
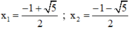
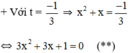
Có a = 3; b = 3; c = 1 ⇒ Δ = 3 2 – 4 . 3 . 1 = - 3 < 0
⇒ (**) vô nghiệm.
Vậy phương trình (1) có tập nghiệm 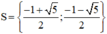
b)
x 2 − 4 x + 2 2 + x 2 − 4 x − 4 = 0 ⇔ x 2 − 4 x + 2 2 + x 2 − 4 x + 2 − 6 = 0 ( 1 )
Đặt x 2 – 4 x + 2 = t ,
Khi đó (1) trở thành: t 2 + t – 6 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2): Có a = 1; b = 1; c = -6
⇒ Δ = 1 2 – 4 . 1 . ( - 6 ) = 25 > 0
⇒ (2) có hai nghiệm
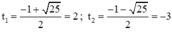
+ Với t = 2 ⇒ x 2 – 4 x + 2 = 2
⇔ x 2 – 4 x = 0
⇔ x(x – 4) = 0
⇔ x = 0 hoặc x = 4.
+ Với t = -3 ⇒ x 2 – 4 x + 2 = - 3
⇔ x2 – 4x + 5 = 0 (*)
Có a = 1; b = -4; c = 5 ⇒ Δ ’ = ( - 2 ) 2 – 1 . 5 = - 1 < 0
⇒ (*) vô nghiệm.
Vậy phương trình ban đầu có tập nghiệm S = {0; 4}.
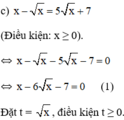
Khi đó (1) trở thành: t 2 – 6 t – 7 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2): Có a = 1; b = -6; c = -7
⇒ a – b + c = 0
⇒ (2) có nghiệm t 1 = - 1 ; t 2 = - c / a = 7 .
Đối chiếu điều kiện chỉ có nghiệm t = 7 thỏa mãn.
+ Với t = 7 ⇒ √x = 7 ⇔ x = 49 (thỏa mãn).
Vậy phương trình đã cho có nghiệm x = 49.
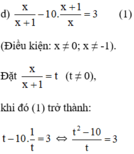
⇔ t 2 – 10 = 3 t ⇔ t 2 – 3 t – 10 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2): Có a = 1; b = -3; c = -10
⇒ Δ = ( - 3 ) 2 - 4 . 1 . ( - 10 ) = 49 > 0
⇒ (2) có hai nghiệm:
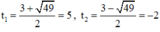
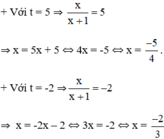
Cả hai nghiệm đều thỏa mãn điều kiện xác định.
Vậy phương trình đã cho có tập nghiệm 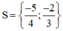
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a)9x2 – 49 = 0
b)(x – 1)(x + 2) – x – 2 = 0
c)(4x + 1)(x - 2) - (2x -3)(2x + 1) = 7
d)x(3x + 2) + (x + 1)2 – (2x – 5)(2x + 5) = 0
e)(x + 3)(x2 – 3x + 9) –x(x – 1)(x + 1) – 27 = 0
f)(4x-3)^2-3x(3-4x)=0
\(a,\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-7\right)\left(3x+7\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{7}{3}\\x=-\dfrac{7}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\\ b,\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\\ c,\Leftrightarrow4x^2-7x-2-4x^2+4x+3=7\\ \Leftrightarrow-3x=6\Leftrightarrow x=-2\\ d,\Leftrightarrow3x^2+2x+x^2+2x+1-4x^2+25=0\\ \Leftrightarrow4x=-26\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{13}{2}\\ e,\Leftrightarrow x^3+27-x^3+x-27=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x=0\\ f,\Leftrightarrow\left(4x-3\right)\left(4x-3+3x\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3}{4}\\x=\dfrac{3}{7}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
a) 9x2-49=0
(3x)2-72=0
<=> (3x-7)(3x+7)=0
th1: 3x-7=0
<=>3x=7
<=>x=\(\dfrac{7}{3}\)
th2: 3x+7=0
<=>3x=-7
<=>x=\(-\dfrac{7}{3}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
a) 4x – 20 = 0
b) 2x + x + 12 = 0
c) x – 5 = 3 – x
d) 7 – 3x = 9 – x
a) 4x – 20 = 0
⇔ 4x = 20
⇔ x = 20 : 4
⇔ x = 5
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất x = 5.
b) 2x + x + 12 = 0
⇔ 3x + 12 = 0
⇔ 3x = -12
⇔ x = -12 : 3
⇔ x = -4
Vậy phương trình đã cho có nghiệm duy nhất x = -4
c) x – 5 = 3 – x
⇔ x + x = 5 + 3
⇔ 2x = 8
⇔ x = 8 : 2
⇔ x = 4
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất x = 4
d) 7 – 3x = 9 – x
⇔ 7 – 9 = 3x – x
⇔ -2 = 2x
⇔ -2 : 2 = x
⇔ -1 = x
⇔ x = -1
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất x = -1.
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Em lớp 6 em chỉ làm dc phần a,b,c
Kết quả như sau:
a,4x-20=0
4x=20+0
4x=20
x=20:4
x=5
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Giải các phương trình sau:
a/ (3x – 2)(4x + 5) = 0
b/ (2,3x – 6,9)(0,1x + 2) = 0
c/ (4x + 2)(x2 + 1) = 0
d/(2x + 7)(x – 5)(5x + 1) = 0
e/ (x – 1)(2x + 7)(x2 + 2) = 0
f/ (3x + 2)(x2 – 1) = (9x2 – 4)(x + 1)
a) \(\left(3x-2\right)\left(4x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x-2=0\\4x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\x=-\dfrac{5}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\dfrac{2}{3};-\dfrac{5}{4}\right\}\)
b) \(\left(2,3x-6,9\right)\left(0,1x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2,3x-6,9=0\\0,1x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-20\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) \(\left(4x+2\right)\left(x^2+1\right)=0\)
Vì \(x^2+1\ge1>0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow4x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)
d) \(\left(2x+7\right)\left(x-5\right)\left(5x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+7=0\\x-5=0\\5x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{7}{2}\\x=5\\x=-\dfrac{1}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{7}{2};5;-\dfrac{1}{5}\right\}\)
e) \(\left(x-1\right)\left(2x+7\right)\left(x^2+2\right)=0\)
Vì \(x^2+2\ge2>0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(2x+7\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\2x+7=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-\dfrac{7}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
f) \(\left(3x+2\right)\left(x^2-1\right)=\left(9x^2-4\right)\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)-\left(3x-2\right)\left(3x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[\left(3x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)\right].\left(x-1-3x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x^2+5x+2\right)\left(-2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x^2+3x+2x+2\right)\left(-2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[3x\left(x+1\right)+2\left(x+1\right)\right]\left(-2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(3x+2\right)\left(-2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+1=0\\3x+2=0\\-2x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=-\dfrac{2}{3}\\x=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-1;-\dfrac{2}{3};\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Khoanh tròn vào đáp án đúng
1 PT nào sau đây là PT bậc hai một ẩn :
A. x2 + 3x = 0
B. 3x + 3 = 0
C. X4 + 2x + 7 = 0
D. 1/x2 + x + 4 = 0
2. PT nào sau đây có nghiệm kép :
A. -x2 - 4x + 4 = 0
B. x2 - 4x - 4 = 0
C. x2 - 4x + 4 = 0
D. Cả 3 đáp án trên đều đúng
1)
a) -2x2+3 ≤ 0
b) -x2- 2x + 3 ≥ 0
c) \(\sqrt{1-3x}\) + x - 2 ≤ 0
a.
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2\ge3\Leftrightarrow x^2\ge\dfrac{3}{2}\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\ge\sqrt{\dfrac{3}{2}}\\x\le-\sqrt{\dfrac{3}{2}}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b.
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(1-x\right)\left(x-3\right)\ge0\Rightarrow1\le x\le3\)
c.
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{1-3x}\le2-x\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}1-3x\ge0\\2-x\ge0\\1-3x\le x^2-4x+4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\le\dfrac{1}{3}\\x\le2\\x^2-x+3\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow x\le\dfrac{1}{3}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
1. Tìm x,y:
a) (x+2)2 + (x-3)2 = 2x ( x+ 7)
b) x3- 3x2 + 3x - 126 = 0
c) x2 + y2 - 2x + 4y + 5 = 0
d) 2x2 - 2xy + y2 + 4x + 4 = 0
\(a.\left(x^2+4x+4\right)+\left(x^2-6x+9\right)=2x^2+14x\)
\(x^2+4x+4+x^2-6x+9-2x^2-14x=0\)
\(-18x+13=0\)
\(x=\dfrac{13}{18}\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{\dfrac{13}{18}\right\}\)
\(b.\left(x-1\right)^3-125=0\)
\(\left(x-1\right)^3=125\)
\(x-1=5\)
\(x=6\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{6\right\}\)
\(c.\left(x-1\right)^2+\left(y +2\right)^2=0\)
\(Do\left(x-1\right)^2\ge0\forall x;\left(y+2\right)^2\ge0\forall y\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2+\left(y+2\right)^2\ge0\forall x,y\)
Mà \(\left(x-1\right)^2+\left(y+2\right)^2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left(x-1\right)^2=0\\\left(y+2\right)^2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\y+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{1;-2\right\}\)
\(d.x^2-4x+4+x^2-2xy+y^2=0\)
\(\left(x-2\right)^2+\left(x-y\right)^2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left(x-2\right)^2=0\\\left(x-y\right)^2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\x-y=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\y=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{2;2\right\}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)

























