30+5x-12=0 giải phương trình

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Giải hệ phương trình có các phương trình sau : 5x+5y=30; y+5z=12; 5z+3x= 22
\(\hept{\begin{cases}5x+5y=30\\y+5z=12\\3x+5z=22\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=6-y\\y+5z=12\\3x+5z=22\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}y+5z=12\\3\left(6-y\right)+5z=22\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}y+5z=12\\-3y+5z=4\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}y+5z=12\\3y-5z=-4\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow4y=8\Rightarrow y=2\)
Thay giá trị của y vào phương trình: -3y + 5z = 4
\(-3\times2+5z=4\)
\(\Rightarrow z=2\)
Thế giá trị của y vào phương trình: x = 6 - y
\(\Rightarrow x=4\)
\(12x^4-5x^2+30=0\)
giải phương trình
Đặt t=x^2>=0(1)
(1)<=>12t^2-5t+30=0
∆=(-5)^2-4.12.30=-1415<0
Vậy phương trình vô nghiệm
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
giải phương trình sau
\(\dfrac{5x-150}{50}+\dfrac{5x-102}{49}+\dfrac{5x-56}{48}+\dfrac{5x-12}{47}+\dfrac{5x-660}{46}=0\)
Ta có : \(\dfrac{5x-150}{50}+\dfrac{5x-102}{49}+\dfrac{5x-56}{48}+\dfrac{5x-12}{47}+\dfrac{5x-660}{46}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5x-150}{50}-1+\dfrac{5x-102}{49}-2+\dfrac{5x-56}{48}-3+\dfrac{5x-12}{47}-4+\dfrac{5x-660}{46}+10=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5x-200}{50}+\dfrac{5x-200}{49}+\dfrac{5x-200}{48}+\dfrac{5x-200}{47}+\dfrac{5x-200}{46}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(5x-200\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{50}+\dfrac{1}{49}+\dfrac{1}{48}+\dfrac{1}{47}+\dfrac{1}{46}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x-200=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=40\)
Vậy ...
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{5x-150}{50}+\dfrac{5x-102}{49}+\dfrac{5x-56}{48}+\dfrac{5x-12}{47}+\dfrac{5x-660}{46}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5x-150}{50}-1+\dfrac{5x-102}{49}-2+\dfrac{5x-56}{48}-3+\dfrac{5x-12}{47}-4+\dfrac{5x-660}{46}+10=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5x-200}{50}+\dfrac{5x-200}{49}+\dfrac{5x-200}{48}+\dfrac{5x-200}{47}+\dfrac{5x-200}{46}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(5x-200\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{50}+\dfrac{1}{49}+\dfrac{1}{48}+\dfrac{1}{47}+\dfrac{1}{46}\right)=0\)
mà \(\dfrac{1}{50}+\dfrac{1}{49}+\dfrac{1}{48}+\dfrac{1}{47}+\dfrac{1}{46}>0\)
nên 5x-200=0
\(\Leftrightarrow5x=200\)
hay x=40
Vậy: S={40}
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
giải phương trình x^4+2x^3+5x^2+4x-12=0
\(x^4+2x^3+5x^2+4x-12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(x^4-x^3+3x^3-3x^2+8x^2-8x+12x-12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(x^3\left(x-1\right)+3x^2\left(x-1\right)+8x\left(x-1\right)+12\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left(x^3+3x^2+8x+12\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\orbr{\begin{cases}x-1=0\\x^3+3x^2+8x+12=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x^3+2x^2+x^2+2x+6x+12=0\end{cases}}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2+x+6\right)=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=-2\\x^2+x+6=0\left(1\right)\end{cases}}\)
Giải pt ( 1 ) \(x^2+\frac{1}{2}x.2+\frac{1}{4}+\frac{23}{4}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{23}{4}=0\)suy ra pt ( 1 ) vô nghiệm
Vậy pt có 2 nghiệm là x = 1 ; x = -2
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
x4 + 2x3 + 5x2 + 4x - 10 = 0
x4 - x3 + 3x3 - 3x2 + 8x2 - 8x + 12x - 12 = 0
<=> x3(x - 1) + 3x2(x - 1) + 8x(x - 1) + 12(x - 1) = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-1=0\\x^3+3x^2+8x+12=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x^3+2x^2+x^2+2x+6x+10=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\\left(x+2\right)+\left(x^2+x+6\right)=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=-2\\x^2+x+6=0\left(1\right)\end{cases}}\)
Giải (1) \(x^2+\frac{1}{2}x.2+\frac{1}{4}+\frac{23}{4}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{23}{4}>0\Rightarrow\text{PT}\left(1\right)\)Vô nghiệm
=> PT có 2 nghiệm: \(\hept{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=-2\end{cases}}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình
x2-5x-2căn3x+12=0
x2-2x+1-3x-2căn3x-1+12=0
giải phương trình
\(\frac{5x-150}{50}+\frac{5x-102}{49}+\frac{5x-56}{48}+\frac{5x-12}{47}+\frac{5x-660}{46}=0\) =0
\(pt\Leftrightarrow\frac{5x-150}{50}+\frac{5x-102}{49}+\frac{5x-56}{48}+\frac{5x-12}{47}+\frac{5x-16}{46}-14=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{5x-150}{50}-1+\frac{5x-102}{49}-2+\frac{5x-56}{48}-3+\frac{5x-12}{47}-4+\frac{5x-16}{46}-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{5x-200}{50}+\frac{5x-200}{49}+\frac{5x-200}{48}+\frac{5x-200}{47}+\frac{5x-200}{46}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(5x-200\right)\left(\frac{1}{50}+\frac{1}{49}+\frac{1}{48}+\frac{1}{47}+\frac{1}{46}\right)=0\)
Do \(\frac{1}{50}+\frac{1}{49}+\frac{1}{48}+\frac{1}{47}+\frac{1}{46}\ne0\) nên \(5x-200=0\Rightarrow x=\frac{200}{5}=40\)
Vậy x= 40
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(\frac{5x-150}{50}+\frac{5x-102}{49}+\frac{5x-56}{48}+\frac{5x-12}{47}+\frac{5x-660}{46}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left(\frac{5x-150}{50}-1\right)+\left(\frac{5x-102}{49}-2\right)+\left(\frac{5x-56}{48}-3\right)+\left(\frac{5x-12}{47}-4\right)+\left(\frac{5x-660}{46}+10\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\frac{5x-200}{50}+\frac{5x-200}{49}+\frac{5x-200}{48}+\frac{5x-200}{47}+\frac{5x-200}{46}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left(5x-200\right)\left(\frac{1}{50}+\frac{1}{49}+\frac{1}{48}+\frac{1}{47}+\frac{1}{46}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(5x-200=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(5x=200\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(x=40\)
Vậy x = 40
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
canh thiu các bạn nhìu(thank you)
bài này mk hỏi cô nhưng cô chưa trả lời
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình:
a
)
3
x
2
−
5
x
+
1
x
2
−
4...
Đọc tiếp
Giải các phương trình:
a ) 3 x 2 − 5 x + 1 x 2 − 4 = 0 b ) 2 x 2 + x − 4 2 − 2 x - 1 2 = 0
a)
3 x 2 − 5 x + 1 x 2 − 4 = 0 ⇔ 3 x 2 − 5 x + 1 = 0
hoặc x 2 – 4 = 0 ( 2 )
+ Giải (1): 3 x 2 – 5 x + 1 = 0
Có a = 3; b = -5; c = 1 ⇒ Δ = ( - 5 ) 2 – 4 . 3 = 13 > 0
Phương trình có hai nghiệm: 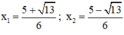
+ Giải (2): x 2 – 4 = 0 ⇔ x 2 = 4 ⇔ x = 2 hoặc x = -2.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 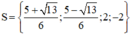
b)
2 x 2 + x − 4 2 − ( 2 x − 1 ) 2 = 0 ⇔ 2 x 2 + x − 4 − 2 x + 1 2 x 2 + x − 4 + 2 x − 1 = 0 ⇔ 2 x 2 − x − 3 2 x 2 + 3 x − 5 = 0 ⇔ 2 x 2 − x − 3 = 0 ( 1 )
hoặc 2 x 2 + 3 x – 5 = 0 ( 2 )
+ Giải (1): 2 x 2 – x – 3 = 0
Có a = 2; b = -1; c = -3 ⇒ a – b + c = 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm x = -1 và x = -c/a = 3/2.
+ Giải (2): 2 x 2 + 3 x – 5 = 0
Có a = 2; b = 3; c = -5 ⇒ a + b + c = 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm x = 1 và x = c/a = -5/2.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 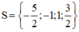
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau:
1/x2+5x+6 + 1/x2+7x+12 + 1/x2+9x+20 + 1/x2+11x+30 = 1/8
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}+\dfrac{1}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x+4\right)}+...+\dfrac{1}{\left(x+5\right)\left(x+6\right)}=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
=>\(\dfrac{1}{x+2}-\dfrac{1}{x+3}+\dfrac{1}{x+3}-\dfrac{1}{x+4}+...+\dfrac{1}{x+5}-\dfrac{1}{x+6}=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
=>1/x+2-1/x+6=1/8
=>\(\dfrac{x+6-x-2}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+6\right)}=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
=>x^2+8x+12=32
=>x^2+8x-20=0
=>(x+10)(x-2)=0
=>x=-10 hoặc x=2
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau:
a. \(5x^2+10x=0\)
b. \(3x^2-12=0\)
c. \(3x^2+7=0\)
d. \(12x^2-3x=0\)
























