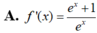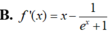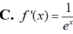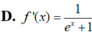Biết F ( x ) = a ln | x - 1 | + b ln | x - 2 | ( a , b ∈ Z ) là một nguyên hàm của hàm số f ( x ) = x + 1 ( x - 1 ) ( x - 2 ) . Giá trị của biểu thức b-a bằng
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Câu 1: Cho \(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow e}\frac{\log_2\left(\ln\left(x\right)\right)}{f\left(x\right)}=\frac{1}{\ln\left(2\right)e}\). Biết \(\ln\left(f\left(0\right)\right)=1\) và \(\int\limits^{5e}_{-e}f\left(2x\right)dx=18e^2\). Tính \(\frac{\ln\left(f\left(1+e\right)\right)}{f\left(1+e\right)^{10}}\) bằng:
a) 0
b) \(\frac{\ln\left(1+e\right)}{\left(1+e\right)^{10}}\)
c) \(1\)
d) \(\frac{\ln\left(1+2e\right)}{\left(1+2e\right)^{10}}\)
Cho hàm số f ( x ) = ln 2019 - ln x + 2 x tính tổng S = f ' ( 1 ) + f ' ( 3 ) + . . . + f ' ( 2019 )
A. 4305 2019
B. 2021
C. 2019 2021
D. 2020 2021
Cho hàm số f ( x ) = ln ( 1 - 4 ( 2 x - 1 ) 2 ) . Biết rằng f ( 2 ) + f ( 3 ) + . . . + f ( 2020 ) = ln a b , trong đó a b là phân số tối giản, a , b ∈ N * . Tính b -3a
A. -2
B. 3
C. -1
D. 1
Cho hàm số y = f ( x ) liên tục trên 0 ; + ∞ .
Biết f ' ( x ) ln ( x ) x v à f ( 1 ) = 3 2 và tính f ( 3 )
![]()
![]()
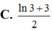
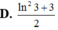
Cho hàm số f ( x ) = ln 1 - 4 ( 2 x - 1 ) 2 . Biết rằng ,f(2) + f(3) + ....+f(2020) = ln a b trong đó a b , là phân số tối giản, a, b ∈ ℕ * . Tính b - 3a
A. -2
B. 3
C. -1
D. 1
Chọn A
Ta có
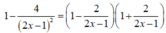
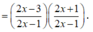
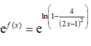
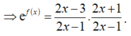
Vì f(2) + f(3) + ....+f(2020) = ln
a
b
nên 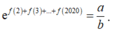
Mà ![]()
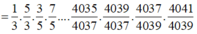
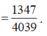
Do đó 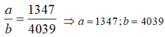
=> b = 3a = -2
Cho hàm số y = f(x) liên tục trên khoảng 0 ; + ∞ . Biết f(1) = 1 và f(x) = xf'(x) + ln (x). Giá trị f(e) bằng
A. e
B. 1
C. 2
D. 1 e
Viết mỗi biểu thức sau thành lôgarit của một biểu thức (giả thiết các biểu thức đều có nghĩa):
a) \(A = \ln \left( {\frac{x}{{x - 1}}} \right) + \ln \left( {\frac{{x + 1}}{x}} \right) - \ln \left( {{x^2} - 1} \right);\)
b) \(B = 21{\log _3}\sqrt[3]{x} + {\log _3}\left( {9{x^2}} \right) - {\log _3}9.\)
\(a,A=ln\left(\dfrac{x}{x-1}\right)+ln\left(\dfrac{x+1}{x}\right)-ln\left(x^2-1\right)\\ =ln\left(\dfrac{x}{x-1}\cdot\dfrac{x+1}{x}\right)-ln\left(x^2-1\right)\\ =ln\left(\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}\right)-ln\left(x^2-1\right)\\ =ln\left(\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}\cdot\dfrac{1}{x^2-1}\right)\\ =ln\left[\dfrac{1}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\right]\\ =2ln\left(\dfrac{1}{x-1}\right)\)
\(b,21log_3\sqrt[3]{x}+log_3\left(9x^2\right)-log_3\left(9\right)\\ =7log_3\left(x\right)+log_3x^2+log_39-log_39\\ =7log_3x+2log_3x\\ =9log_3x\)
Viết mỗi biểu thức sau thành lôgarit của một biểu thức (giả thiết các biểu thức đều có nghĩa):
a) \(A = \ln \left( {\frac{x}{{x - 1}}} \right) + \ln \left( {\frac{{x + 1}}{x}} \right) - \ln \left( {{x^2} - 1} \right);\)
b) \(B = 21{\log _3}\sqrt[3]{x} + {\log _3}\left( {9{x^2}} \right) - {\log _3}9.\)
a)
\(\begin{array}{c}A = {\log _{\frac{1}{3}}}5 + 2{\log _9}25 - {\log _{\sqrt 3 }}\frac{1}{5} = {\log _{{3^{ - 1}}}}5 + 2{\log _{{3^2}}}{5^2} - {\log _{{3^{\frac{1}{2}}}}}{5^{ - 1}}\\ = - {\log _3}5 + 2{\log _3}5 + 2{\log _3}5 = 3{\log _3}5\end{array}\)
b) \(B = {\log _a}{M^2} + {\log _{{a^2}}}{M^4} = 2{\log _a}M + \frac{1}{2}.4{\log _a}M = 4{\log _a}M\)
Tính các nguyên hàm.
a)\(\int\dfrac{2dx}{x^2-5x}=A\ln\left|x\right|+B\ln\left|x-5\right|+C\) . Tìm 2A-3B.
b)\(\int\dfrac{x^3-1}{x+1}\)dx=\(Ax^3-Bx^2+x+E\ln\left|x+1\right|+C\).Tính A-B+E
a) \(\int\dfrac{2dx}{x^2-5x}=\int\left(\dfrac{-2}{5x}+\dfrac{2}{5\left(x-5\right)}\right)dx=-\dfrac{2}{5}ln\left|x\right|+\dfrac{2}{5}ln\left|x-5\right|+C\)
\(\Rightarrow A=-\dfrac{2}{5};B=\dfrac{2}{5}\Rightarrow2A-3B=-2\)
b) \(\int\dfrac{x^3-1}{x+1}dx=\int\dfrac{x^3+1-2}{x+1}dx=\int\left(x^2-x+1-\dfrac{2}{x+1}\right)dx=\dfrac{1}{3}x^3-\dfrac{1}{2}x^2+x-2ln\left|x+1\right|+C\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{1}{3};B=\dfrac{1}{2};E=-2\Rightarrow A-B+E=-\dfrac{13}{6}\)
Cho f(x) =ln e x e x + 1 . Tính f'(x)