Cho f(x) = log 3 x x - 2 ; x ∈ ( 2 ; + ∞ ) . Tính f'(x)
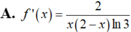
![]()
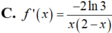
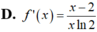
Đề bài
Giải mỗi phương trình sau:
a) \({\left( {0,3} \right)^{x - 3}} = 1\)
b) \({5^{3x - 2}} = 25\)
c) \({9^{x - 2}} = {243^{x + 1}}\)
d) \({\log _{\frac{1}{x}}}(x + 1) = - 3\)
e) \({\log _5}(3x - 5) = {\log _5}(2x + 1)\)
f) \({\log _{\frac{1}{7}}}(x + 9) = {\log _{\frac{1}{7}}}(2x - 1)\)
\(a,\left(0,3\right)^{x-3}=1\\ \Leftrightarrow x-3=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x=3\\ b,5^{3x-2}=25\\ \Leftrightarrow3x-2=2\\ \Leftrightarrow3x=4\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{4}{3}\\ c,9^{x-2}=243^{x+1}\\ \Leftrightarrow3^{2x-4}=3^{5x+5}\\ \Leftrightarrow2x-4=5x+5\\ \Leftrightarrow3x=-9\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-3\)
d, Điều kiện: \(x>-1;x\ne0\)
\(log_{\dfrac{1}{x}}\left(x+1\right)=-3\\ \Leftrightarrow x+1=x^3\\ x\simeq1,325\left(tm\right)\)
e, Điều kiện: \(x>\dfrac{5}{3}\)
\(log_5\left(3x-5\right)=log_5\left(2x+1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow3x-5=2x+1\\ \Leftrightarrow x=6\left(tm\right)\)
f, Điều kiện: \(x>\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(log_{\dfrac{1}{7}}\left(x+9\right)=log_{\dfrac{1}{7}}\left(2x-1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow x+9=2x-1\\ \Leftrightarrow x=10\left(tm\right)\)
Câu 1: Gọi \(F\left(x\right)\) là một nguyên hàm của \(f\left(x\right)\) . Cho \(f’\left(x\right)=2x\ln\left(x\right)+2x\) và \(f\left(1\right)=\frac{1}{2}\), \(F\left(1\right)=\frac{1}{18}\) . Hỏi phương trình \(\frac{f\left(x\right).F\left(x\right)}{F\left(f\left(x\right)\right)+f\left(F\left(x\right)\right)}=0\) có bao nhiêu nghiệm dương.
Câu 2: Cho \(\int\limits^4_1f\left(x\right)dx=\frac{14\sqrt{2}}{3}\) và \(\int\limits^4_1f’\left(x\right)dx=\sqrt{2}\), \(f\left(0\right)=0\). Tính \(f\left(1\right)+f\left(2\right)\) bằng
Câu 3: Cho \(\int\limits^2_1f\left(x\right)\log\left(x\right)dx=\log\left(4\right)-\frac{3}{4\ln\left(10\right)}\), \(\int\limits^2_1f’\left(x\right)\log\left(x\right)dx=\log\left(4\right)-\frac{1}{\ln10}\) . Khi này phương trình \(f\left(x\right)^2+f\left(x\right)-2=0\) có bao nhiêu nghiệm nguyên.
1)Cho X = log\(\dfrac{1}{2}\)+log\(\dfrac{2}{3}\)+...+log\(\dfrac{99}{100}\). Chọn câu trả lời đúng về giá trị của X:
a)X>2 b)X=0 c) X=-2 d)X=\(\dfrac{1}{2}\)
2)Đặt log32 =a ,log35 = b. X=log3\(\dfrac{1}{2}\)+log3\(\dfrac{2}{3}\)+....+log3\(\dfrac{99}{100}\). X được biểu thị qua a,b là:
a) X=-2a-2b b)X =-2a+2b
c)X =2a-2b c)X =2a+2b
1) X=log1-log2+log2-log3+...+log99-log100
=log1-log100
=0-2
=-2
Đáp án C
2)X=-log3100=-log3102=-2log3(2.5)=-2log32-2log35=-2a-2b
Đáp án A
Tìm giá trị lớn nhất và nhỏ nhất của hàm số :
\(f\left(x\right)=\log^2x-4\log x+3\) trên \(\left[10;1000\right]\)
Đặt \(t=\log x\) với \(x\in\left[10;1000\right]\Rightarrow t\in\left[1;3\right]\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)=t^2-4t+3=g\left(t\right)\) với \(t\in\left[1;3\right]\)
Ta có : \(g'\left(t\right)=2t-4=0\Leftrightarrow t=2\in\left[1;3\right]\)
Mà : \(\begin{cases}g\left(1\right)=0\\g\left(2\right)=-1\\g\left(3\right)=0\end{cases}\) \(\Rightarrow\begin{cases}Max_{x\in\left[10;1000\right]}f\left(x\right)=0;x=10;x=1000\\Min_{x\in\left[10;1000\right]}f\left(x\right)=0;x=1000\end{cases}\)
Cho bốn số thực dương a, b, x, y với \(a,b \ne 1\). Khẳng định nào sau đây là sai?
A. \({\log _a}(xy) = {\log _a}x + {\log _b}y\).
B. \({\log _a}\frac{x}{y} = {\log _a}x - {\log _a}y\).
C. \({\log _a}\frac{1}{x} = \frac{1}{{{{\log }_a}x}}\).
D. \({\log _a}b \cdot {\log _b}x = {\log _a}x\).
Tìm tập nghiệm của phương trình l o g ( x + 3 ) + l o g ( x - 1 ) = l o g ( x 2 - 2 x - 3 )
A. ∅
B. {0}
C. R
D. (1; +∞)
Cho hàm số f(x) =log0,5(6x-x2). tập nghiệm của bất phương trình .
Rút gọn biểu thức: \(A = {\log _2}\left( {{x^3} - x} \right) - {\log _2}\left( {x + 1} \right) - {\log _2}\left( {x - 1} \right)\,\,\,\,\left( {x > 1} \right).\)
\(A=log_2\left(x^3-x\right)-log_2\left(x+1\right)-log_2\left(x-1\right)\)
\(=log_2\left(\dfrac{x^3-x}{x+1}\right)-log_2\left(x-1\right)\)
\(=log_2\left(\dfrac{x\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{x+1}\right)-log_2\left(x-1\right)\)
\(=log_2\left(\dfrac{x\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}\right)=log_2x\)
Giải mỗi phương trình sau:
a) \({\log _5}\left( {2x - 4} \right) + {\log _{\frac{1}{5}}}\left( {x - 1} \right) = 0\)
b) \({\log _2}x + {\log _4}x = 3\)
a)
ĐK: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-4>0\\x-1>0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x>1\)
\(\log_5\left(2x-4\right)+\log_{\dfrac{1}{5}}\left(x-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\log_5\left(2x-4\right)-\log_5\left(x-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\log_5\left(\dfrac{2x-4}{x-1}\right)=\log_51\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x-4}{x-1}=1\\ \Leftrightarrow2x-4=x-1\\ \Leftrightarrow x=3\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy x = 3.
b) ĐK: x > 0
\(\log_2x+\log_4x=3\\ \Leftrightarrow\log_2x+\dfrac{1}{2}\log_2x=3\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(1+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\log_2x=3\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3}{2}\log_2x=3\\ \Leftrightarrow\log_2x=2\\ \Leftrightarrow x=4\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy x= 4
Giải phương trình:
a, logx216 + log2x64=3
b, log2(4x+1+4).log2(4x+1)=log1/√2√1/8
c, 5lnx=50-xlg5
d, 2log5(x+3)=x
e, x+log(x2-x-6)=4+lg(x+2)