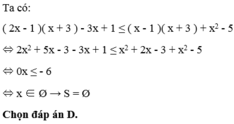Giải bất phương trình sau: (2x - 1)(x + 3) - 3x + 1 ≤ (x - 1)(x + 3) + x2 - 5

Những câu hỏi liên quan
giải các bất phương trình sau và biểu diễn tập nghiệp trên trục số
1, 6+2x ≥ 3-x
2, 2x+7 > 16-x
3, x-5<3x+1
1.
\(6+2x\ge3-x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\ge-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ge-1\)
2.
\(2x+7>16-x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x>23\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>\dfrac{23}{3}\)
3.
\(x-5< 3x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x>-6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>-3\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (2)
Mik chưa học đến lớp 8 nên ko bt biểu diễn trên trục số nên chỉ tìm dc x thôi nha:
1. 6 + 2x \(\ge\) 3 - x
<=> 6 - 3 \(\ge\) -x - 2x
<=> 3 \(\ge\) -3x
<=> 3 : (-3) \(\ge\) -3x : (-3)
<=> -1 \(\le\) x
<=> x \(\ge\) -1
2. 2x + 7 > 16 - x
<=> 2x + x > 16 - 7
<=> 3x > 9
<=> 3x : 3 > 9 : 3
<=> x > 3
3. x - 5 < 3x + 1
<=> -5 - 1 < 3x - x
<=> -6 < 2x
<=> -6 : 2 < 2x : 2
<=> -3 < x
<=> x > (-3)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1: Ta có: \(2x+6\ge3-x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\ge-3\)
hay \(x\ge-1\)
2: ta có: \(2x+7>16-x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x>9\)
hay x>3
3: Ta có: \(x-5< 3x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x< 6\)
hay x>-3
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1) Giải các phương trình sau : a) x-3/x=2-x-3/x+3 b) 3x^2-2x-16=0 2) Giải bất phương trình sau: 4x-3/4>3x-5/3-2x-7/12
\(a,\dfrac{x-3}{x}=\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}\)\(\left(đk:x\ne0,-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-3}{x}-\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)-x\left(x-3\right)}{x\left(x+3\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-9-x^2+3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\left(n\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{3\right\}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
\(b,\dfrac{4x-3}{4}>\dfrac{3x-5}{3}-\dfrac{2x-7}{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4x-3}{4}-\dfrac{3x-5}{3}+\dfrac{2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3\left(4x-3\right)-4\left(3x-5\right)+2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x-9-12x+20+2x-7>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+4>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x>-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>-2\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Kiểm tra xem -2 là nghiệm của bất phương trình nào trong các bất phương trình sau:
a) -3x + 2 > -5 ; b) 10 - 2x < 2
c) x2 - 5 < 1 ; d) |x| < 3
e) |x| > 2 ; f) x + 1 > 7 - 2x
Lần lượt thay x = -2 vào từng bất phương trình:
a) -3x + 2 = -3.(-2) + 2 = 8
Vì 8 > -5 nên x = -2 là nghiệm của bất phương trình -3x + 2 > -5.
b) 10 – 2x = 10 – 2.(-2) = 10 + 4 = 14
Vì 14 > 2 nên x = -2 không phải nghiệm của bất phương trình 10 – 2x < 2.
c) x2 – 5 = (-2)2 – 5 = 4 – 5 = -1
Vì -1 < 1 nên x = -2 là nghiệm của bất phương trình x2 – 5 < 1.
d) |x| = |-2| = 2
Vì 2 < 3 nên x = -2 là nghiệm của bất phương trình |x| < 3.
e) |x| = |-2| = 2
Vì 2 = 2 nên x = -2 không phải nghiệm của bất phương trình |x| > 2.
f) x + 1 = -2 + 1 = -1.
7 – 2x = 7 – 2.(-2) = 7 + 4 = 11
Vì -1 < 11 nên x = -2 không phải nghiệm của bất phương trình x + 1 > 7 – 2x.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
giải các bất phương trình sau
a, <x-3>*<x2+x-20>≥0
b, x2-4x-5 /2x+4 ≥0
c, -1/x2-6x+8≤1
a, \(\left(x-3\right)\left(x^2+x-20\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left(x-3\right)\left(x-4\right)\left(x+5\right)\ge0\)
+) \(x-3=0\Leftrightarrow x=3\); \(x-4=0\Leftrightarrow x=4\); \(x+5=0\Leftrightarrow x=-5\)
+) Lập trục xét dấu f(x) (Bạn tự kẻ trục nha)
\(\Rightarrow\) Bpt có tập nghiệm S = \(\left[-5;3\right]\cup\) [4; \(+\infty\))
b, \(\dfrac{x^2-4x-5}{2x+4}\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\dfrac{\left(x-5\right)\left(x+1\right)}{2x+4}\ge0\)
+) \(x-5=0\Leftrightarrow x=5\); \(x+1=0\Leftrightarrow x=-1\); \(2x+4=0\Leftrightarrow x=-2\)
+) Lập trục xét dấu f(x)
\(\Rightarrow\) Bpt có tập nghiệm S = (-2; -1] \(\cup\) [5; \(+\infty\))
c, \(\dfrac{-1}{x^2-6x+8}\le1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\dfrac{\left(x-3\right)^2}{\left(x-4\right)\left(x-2\right)}\ge0\)
+) \(x-3=0\Leftrightarrow x=3\); \(x-4=0\Leftrightarrow x=4\); \(x-2=0\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
+) Lập trục xét dấu f(x)
\(\Rightarrow\) Bpt có tập nghiệm S = (\(-\infty\); 2) \(\cup\) (4; \(+\infty\))
Chúc bn học tốt!
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Bất phương trình
(
2
x
-
1
)
(
x
+
3
)
-
3
x
+
1
≤
(
x
-
1
)
(
x
+
3
)
+
x
2
-
5
có tập nghiệm là? A.
x
-
2
3
B.
x
≥
-
...
Đọc tiếp
Bất phương trình ( 2 x - 1 ) ( x + 3 ) - 3 x + 1 ≤ ( x - 1 ) ( x + 3 ) + x 2 - 5 có tập nghiệm là?
A. x < - 2 3
B. x ≥ - 2 3
C. S = R
D. S = Ø
Bất phương trình
(
2
x
-
1
)
(
x
+
3
)
-
3
x
+
1
≤
(
x
-
1
)
(
x
+
3
)
+
x
2
-
5
có tập nghiệm là? A.
x
-
2
3
B.
x
≥
-
...
Đọc tiếp
Bất phương trình ( 2 x - 1 ) ( x + 3 ) - 3 x + 1 ≤ ( x - 1 ) ( x + 3 ) + x 2 - 5 có tập nghiệm là?
A. x < - 2 3
B. x ≥ - 2 3
C. S = R
D. S = Ø
giải bất phương trình sau f(x)=(3x-4)(2x-3)/(x2-5x+6)(5-x)>0
\(f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{\left(3x-4\right)\left(2x-3\right)}{\left(x^2-5x+6\right)\left(5-x\right)}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(3x-4\right)\left(2x-3\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(5-x\right)}>0\)
Bảng xét dấu:
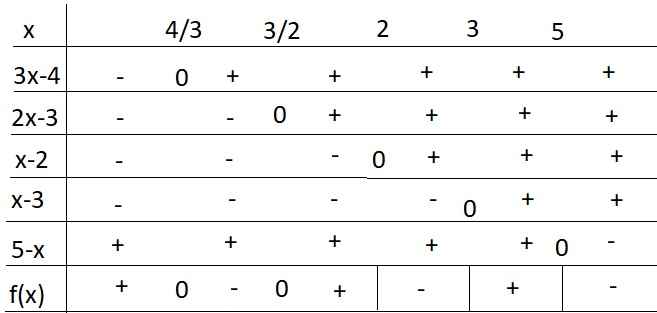
Từ bảng xét dấu ta thấy nghiệm của BPT là: \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< 5\\\dfrac{3}{2}< x< 2\\3< x< 5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các bất phương trình sau
a) 4(x-3)2-(2x-1)2<10
b) x(x-5)(x+5)-(x+2)(x2-2x+4)< hoặc = 3
\(a,4\left(x-3\right)^2-\left(2x-1\right)^2< 10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(x^2-6x+9\right)-\left(4x^2-4x+1\right)-10< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-24x+36-4x^2+4x-1-10< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-20x< -25\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>\dfrac{5}{4}\)
\(b,x\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)-\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)\le3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x^2-25\right)-\left(x^3-2x^2+4x+2x^2-4x+8\right)\le3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-25x-\left(x^3+8\right)\le3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-25x-x^3-8-3\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-25x\le11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ge-\dfrac{11}{25}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
giải các bất phương trình sau
a, 3x-5 ≥ 2(x-6) -12
b, 2 (5-2x) ≥ 3-x
c, 2 ( -2x+1) ≤ -x+3
d, 2( x+1) ≤ -x+3
a: Ta có: \(3x-5\ge2\left(x-6\right)-12\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-5\ge2x-24\)
hay \(x\ge-19\)
b: Ta có: \(2\left(5-2x\right)\ge3-x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow10-4x-3+x\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3x\ge-7\)
hay \(x\le\dfrac{7}{3}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)