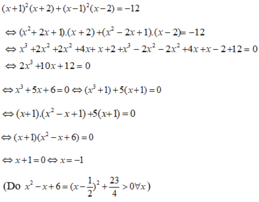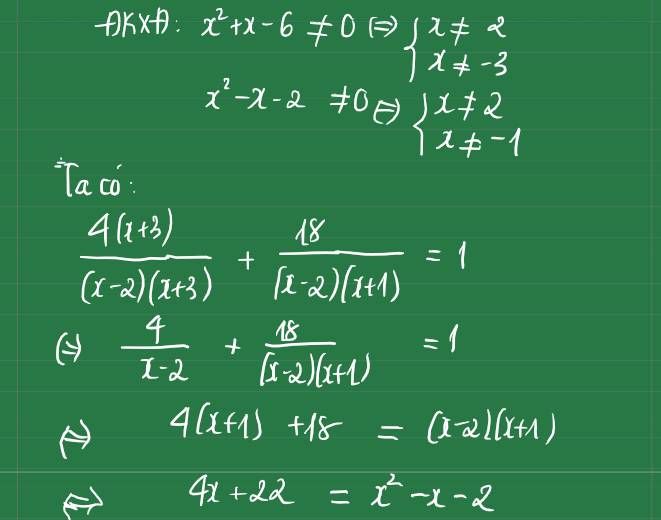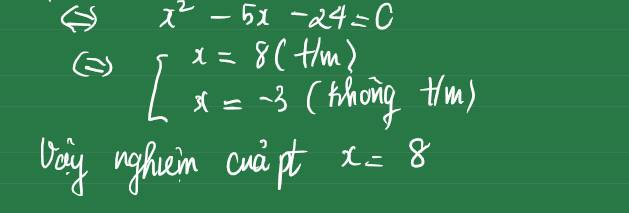giải phương trình (x+1)^2(x+2)+(x-1)^2(x-2)=12

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Giải phương trình: ( x + 1 ) 2 ( x + 2 ) + ( x - 1 ) 2 ( x - 2 ) = - 12
giải phương trình |x+1|+|x-1|=1+|x^2-1|giải phương trình |x+1|+|x-1|=1+|x^2-1|giải phương trình |x+1|+|x-1|=1+|x^2-1|giải phương trình |x+1|+|x-1|=1+|x^2-1|giải phương trình |x+1|+|x-1|=1+|x^2-1|
ta có :
\(\left|x+1\right|+\left|x-1\right|=1+\left|\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\right|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|x-1\right|\left|x+1\right|-\left|x-1\right|-\left|x+1\right|+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\left|x-1\right|-1\right)\left(\left|x+1\right|-1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\left|x-1\right|=1\\\left|x+1\right|=1\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{-2,0,2\right\}\)
giải phương trình (x+1/x-2)^2x+1/x-3=12(X+1/x-3)^2
Giải phương trình:
\(\dfrac{x+1}{x-2}-\dfrac{5}{x+2}=\dfrac{12}{x^2-4}+1\)
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne\pm2\)
\(\dfrac{x+1}{x-2}-\dfrac{5}{x+2}=\dfrac{12}{x^2-4}+1\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\dfrac{5\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{12}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}+\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)-5\left(x-2\right)=12+\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2+x+2x+2-5x+10=12+x^2-4\\ \Leftrightarrow-2x=-4\\ \Leftrightarrow x=2\left(ktm\right)\)
Vậy \(S\in\left\{\varnothing\right\}\)
Đúng 4
Bình luận (0)
ĐKXĐ: \(\begin{cases}x-2\ne 0\\x+2\ne 0\end{cases}\leftrightarrow x\ne 2\\x\ne -2\end{cases}\)
\(\dfrac{x+1}{x-2}-\dfrac{5}{x+2}=\dfrac{12}{x^2-4}+1\)
\(\leftrightarrow \dfrac{(x+1)(x+2)}{(x-2)(x+2)}-\dfrac{5(x-2)}{(x+2)(x-2)}=\dfrac{12}{(x-2)(x+2)}+\dfrac{(x-2)(x+2)}{(x-2)(x+2)}\)
\(\to x^2+3x+2-5x+10=12+x^2-4\)
\(\leftrightarrow x^2-2x-x^2=12-12-4\)
\(\leftrightarrow -2x=-4\)
\(\leftrightarrow x=2(\rm KTM)\)
Vậy pt đã cho vô nghiệm \(S=\varnothing\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
giải phương trình
1)\(\sqrt{x+4}-\sqrt{1-x}=1\)
2)\(\left(x+3\right)\sqrt{10-x^2}=x^2-x-12\)
1/\(\sqrt{x-4}-\sqrt{1-x}=1\)
Để Pt dc xác định
Thì\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-4\ge0\\1-x\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge4\\x\le1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vì xét trên trục số ta thấy nó loại nhau
Nên Pt này vô nghiệm
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1)ĐKXĐ: \(-4\le x\le1\)
\(\sqrt{x+4}-\sqrt{1-x}=1\\ \Rightarrow\sqrt{x+4}=\sqrt{1-x}+1\\ \Rightarrow x+4=1-x+2\sqrt{1-x}+1\\ \Rightarrow2x+2=2\sqrt{1-x}\\ \Rightarrow x+1=\sqrt{1-x}\\ \Rightarrow x^2+2x+1=1-x\\ \Rightarrow x^2+3x=0\\ \Rightarrow x\left(x+3\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow x=-3\)
Vậy x = -3
2)ĐKXĐ: \(-\sqrt{10}\le x\le\sqrt{10}\)
Với x = -3 thì:
0=0(luôn đúng)
Với x khác -3 thì:
\(\left(x+3\right)\sqrt{10-x^2}=x^2-x+12\\ \Rightarrow\left(x+3\right)\sqrt{10-x^2}=\left(x+3\right)\left(x-4\right)\\ \Rightarrow\sqrt{10-x^2}=x-4\\ \Rightarrow10-x^2=x^2-8x+16\\ \Rightarrow2x^2-8x+6=0\\ \Rightarrow x^2-4x+3=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow x\in\left\{1;3\right\}\)
Vậy x\(\in\left\{-3;1;3\right\}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
giải phương trình sau
(x^2+x+1)(x^2+x+2)=12
khó ệ!thằng nào ngu người có khi làm được
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Giải phương trình \(\dfrac{4x+12}{x^2+x-6}+\dfrac{18}{x^2-x-2} = 1 \)
giải phương trình: 12-2(x-1)2 = 4(x-2)-(x-3)(2x-5)
<=> 12 - 2(x^2-2x+1) = 4x-8 - 2x^2 +11x-15
<=> 10 - 2x^2 + 4x = -2x^2 + 15x -23
<=> -11x + 33 =0 <=> x = 3
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
\(\Leftrightarrow12-2\left(x^2-2x+1\right)-4x+8+\left(x-3\right)\left(2x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4x+20-2x^2+4x-2+2x^2-5x-6x+15=0\)
=>-11x+33=0
hay x=3
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)12-2(x2-2x+1)=2x-8-(2x2-5x-6x+15)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)12-2x2+2x-1=2x-8-2x2+5x+6x-15
\(\Leftrightarrow\)-2x2+2x2+2x-2x-5x-6x=-12+1-8-15
\(\Leftrightarrow\)-11x=-34
\(\Leftrightarrow\)x=\(\dfrac{34}{11}\)
Vậy ...
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình A) (x-1)²+2=x²+3x B) x-3/x+3 - 2/2-3=-3(x-1)/x²-9 C) 12x+1/12
a) Ta có: \(\left(x-1\right)^2+2=x^2+3x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+1+2-x^2-3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-5x=-3\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{3}{5}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Giải phương trình ( x-2 ) ^2 /12 - ( x+1 ) ^2 /21 = ( x-4 ) (x-6) /28
\(\frac{\left(x-2\right)^2}{12}-\frac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{21}=\frac{\left(x-4\right)\left(x-6\right)}{28}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{7\left(x-2\right)^2}{84}-\frac{4\left(x+1\right)^2}{84}=\frac{3\left(x-4\right)\left(x-6\right)}{84}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow7\left(x-2\right)^2-4\left(x+1\right)^2=3\left(x-4\right)\left(x-6\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow7\left(x^2-4x+4\right)-4\left(x^2+2x+1\right)=3\left(x^2-10x+24\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow7x^2-28x+28-4x^2-8x-4=3x^2-30x+72\)
\(\Leftrightarrow7x^2-4x^2-3x^2-28x-8x+30+28-4-72=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x-48=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x=48\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-8\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của PT là : \(S=\left\{-8\right\}\)
Chúc bạn học tốt !!!
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
\(\(\frac{\left(x-2\right)^2}{12}-\frac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{21}=\frac{\left(x-4\right)\left(x-6\right)}{28}\)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{7\left(x^2-4x+4\right)}{84}-\frac{4\left(x^2+2x+1\right)}{84}=\frac{3\left(x^2-6x-4x+24\right)}{84}\)
\(\Rightarrow7x^2-28x+28-4x^2-8x-4=3x^2-30x+\frac{72}{ }\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-36x+24=3x^2-30x+72\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x=48\Leftrightarrow x=-8\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)