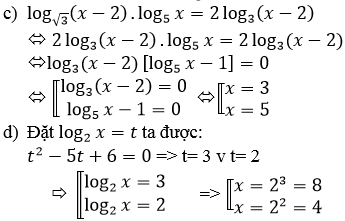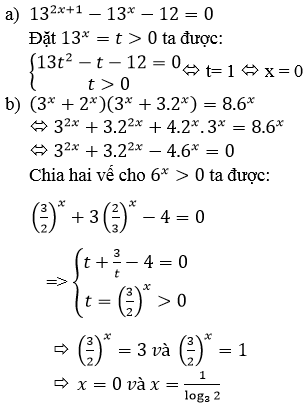↑\(\log_2X+\log_3\left(X+1\right)< \log_4\left(X+2\right)+\log_5\left(X+3\right)\)

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Giải phương trình
\(\log_2x+\log_3\left(x+1\right)=\log_4\left(x+2\right)+\log_5\left(x+3\right)\)
Điều kiện x>0. Nhận thấy x=2 là nghiệm.
Nếu x>2 thì
\(\frac{x}{2}>\frac{x+2}{4}>1\); \(\frac{x+1}{3}>\frac{x+3}{5}>1\)
Suy ra
\(\log_2\frac{x}{2}>\log_2\frac{x+2}{4}>\log_4\frac{x+2}{4}\)hay :\(\log_2x>\log_2\left(x+2\right)\)
\(\log_3\frac{x+1}{3}>\log_3\frac{x+3}{5}>\log_5\frac{x+3}{5}\) hay \(\log_3\left(x+1\right)>\log_5\left(x+3\right)\)
Suy ra vế trái < vế phải, phương trình vô nghiệm.
Đáp số x=2
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
giải các phương trình sau
a) \(\log_5\left(4x-3\right)=2\)
b) \(\log_2x^2=2\)
c) \(\log_5\left(2x+1\right)=\log_5\left(-2x+3\right)\)
d) \(\ln\left(x^2-6x+7\right)=\ln\left(x-3\right)\)
e) \(\log\left(5x-1\right)=log\left(4-2x\right)\)
a: ĐKXĐ: \(4x-3>0\)
=>x>3/4
\(log_5\left(4x-3\right)=2\)
=>\(log_5\left(4x-3\right)=log_525\)
=>4x-3=25
=>4x=28
=>x=7(nhận)
b: ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne0\)
\(log_2x^2=2\)
=>\(log_2x^2=log_24\)
=>\(x^2=4\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\left(nhận\right)\\x=-2\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
c: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{-\dfrac{1}{2};\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\)
\(\log_52x+1=\log_5-2x+3\)
=>2x+1=-2x+3
=>4x=2
=>\(x=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(nhận\right)\)
d: ĐKXD: \(x\notin\left\{3\right\}\)
\(ln\left(x^2-6x+7\right)=ln\left(x-3\right)\)
=>\(x^2-6x+7=x-3\)
=>\(x^2-7x+10=0\)
=>(x-2)(x-5)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\left(nhận\right)\\x=5\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
e: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{\dfrac{1}{5};2\right\}\)
\(log\left(5x-1\right)=log\left(4-2x\right)\)
=>5x-1=4-2x
=>7x=5
=>\(x=\dfrac{5}{7}\left(nhận\right)\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình: \(\log_3\left(4^x-1\right)=\log_4\left(3^x+1\right)\)
giải các bất phương trình sau
a) \(log\left(x-5\right)< 2\)
b) \(log_2\left(2x-3\right)>4\)
c) \(log_3\left(2x+5\right)\le3\)
d) \(log_4\left(4x-5\right)\ge2\)
e) \(log_3\left(1-3x\right)>3\)
a: \(log\left(x-5\right)< 2\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-5>0\\log\left(x-5\right)< log4\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-5>0\\x-5< 4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow5< x< 9\)
b: \(log_2\left(2x-3\right)>4\)
=>\(log_2\left(2x-3\right)>log_216\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-3>0\\2x-3>16\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>2x-3>16
=>2x>19
=>\(x>\dfrac{19}{2}\)
c: \(log_3\left(2x+5\right)< =3\)
=>\(log_3\left(2x+5\right)< =log_327\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+5>0\\2x+5< =27\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>-\dfrac{5}{2}\\x< =11\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(-\dfrac{5}{2}< x< =11\)
d: \(log_4\left(4x-5\right)>=2\)
=>\(log_4\left(4x-5\right)>=log_416\)
=>4x-5>=16 và 4x-5>0
=>4x>=21 và 4x>5
=>4x>=21
=>\(x>=\dfrac{21}{4}\)
e: \(log_3\left(1-3x\right)>3\)
=>\(log_3\left(1-3x\right)>log_327\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}1-3x>0\\1-3x>27\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>1-3x>27
=>\(-3x>26\)
=>\(x< -\dfrac{26}{3}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Cho phương trình log_5left(log_4left(log_3left(log_2left(x^3right)right)right)right)log_2left(log_3left(log_4left(log_5left(x^2right)right)right)right)
giả sử tập xác định của phương tringf trên có dạng left(-infty;aright)cupleft(b;+inftyright). Chọn khẳng đinh định đúng
a) a+b0 và nghiệm của phương trình là số chia hết cho 3.
b) a-b0 và nghiệm của phương trình là số chia hết cho 3.
c) a+b0 và nghiệm của phương trình là một số lập phương.
d) a+b0 và nghiệm của phương trình là một số bình ph...
Đọc tiếp
Cho phương trình \(\log_5\left(\log_4\left(\log_3\left(\log_2\left(x^3\right)\right)\right)\right)=\log_2\left(\log_3\left(\log_4\left(\log_5\left(x^2\right)\right)\right)\right)\)
giả sử tập xác định của phương tringf trên có dạng \(\left(-\infty;a\right)\cup\left(b;+\infty\right)\). Chọn khẳng đinh định đúng
a) \(a+b=0\) và nghiệm của phương trình là số chia hết cho 3.
b) \(a-b=0\) và nghiệm của phương trình là số chia hết cho 3.
c) \(a+b=0\) và nghiệm của phương trình là một số lập phương.
d) \(a+b=0\) và nghiệm của phương trình là một số bình phương.
\(\log_5\left(\log_3x\right)=\log_3\left(\log_5x\right)\)
ĐKXĐ: \(x>1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\log_5\left(\dfrac{\ln x}{\ln3}\right)=\log_3\left(\dfrac{\ln x}{\ln5}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\log_5\left(\ln x\right)-\log_5\left(\ln3\right)=\log_3\left(\ln x\right)-\log_3\left(\ln5\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\ln\left(\ln x\right)}{\ln5}-\log_5\left(\ln3\right)=\dfrac{\ln\left(\ln x\right)}{\ln3}-\log_3\left(\ln5\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\ln\left(\ln x\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{\ln5}-\dfrac{1}{\ln3}\right)=\log_5\left(\ln3\right)-\log_3\left(\ln5\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\ln\left(\ln x\right)=\dfrac{\log_5\left(\ln3\right)-\log_3\left(\ln5\right)}{\dfrac{1}{\ln5}-\dfrac{1}{\ln3}}=\dfrac{\ln3.\ln5\left[\log_5\left(\ln3\right)-\log_3\left(\ln5\right)\right]}{\ln3-\ln5}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=e^{e^{\frac{\ln{3}.\ln{5}[\log_{5}(\ln{3})-\log_{3}(\ln{5})]}{\ln{3}-\ln{5}}}}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm pass Wifi: biết \(\begin{cases}\log_4\left(x^2+y^2\right)-\log_4\left(2x\right)+1=\log_4\left(x+3y\right)\\\log_4\left(xy+1\right)-\log_4\left(4y^2+2y-2x+4\right)=\log_4\left(\frac{x}{y}\right)-1\end{cases}\)
Giải hệ phương trình trên tìm nghiệm x;y sau đó ghép thành số \(\overline{xyxyxy}\) để biết pas Wifi
Giải các phương trình sau :
a) \(13^{2x+1}-13^x-12=0\)
b) \(\left(3^x+2^x\right)\left(3^x+3.2^x\right)=8.6^x\)
c) \(\log_{\sqrt{3}}\left(x-2\right).\log_5x=2.\log_3\left(x-2\right)\)
d) \(\log^2_2x-5\log_2x+6=0\)
a) Đặt t = 13x > 0 ta được phương trình:
13t2 – t – 12 = 0 ⇔ (t – 1)(13t + 12) = 0
⇔ t = 1 ⇔ 13x = 1 ⇔ x = 0
b)
Chia cả hai vế phương trình cho 9x ta được phương trình tương đương
(1+(23)x)(1+3.(23)x)=8.(23)x(1+(23)x)(1+3.(23)x)=8.(23)x
Đặt t=(23)xt=(23)x (t > 0) , ta được phương trình:
(1 + t)(1 + 3t) = 8t ⇔ 3t2 – 4t + 1 = 0 ⇔ t∈{13,1}t∈{13,1}
Với t=13t=13 ta được nghiệm x=log2313x=log2313
Với t = 1 ta được nghiệm x = 0
c) Điều kiện: x > 2
Vì nên phương trình đã cho tương đương với:
[log3(x−2)=0log5x=1⇔[x=3x=5[log3(x−2)=0log5x=1⇔[x=3x=5
d) Điều kiện: x > 0
log22x – 5log2x + 6 = 0
⇔(log2x – 2)(log2x – 3) = 0
⇔ x ∈ {4, 8}
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
giải các bất phương trình sau
a) \(log\left(x-2\right)< 3\)
b) \(log_2\left(2x-1\right)>3\)
c) \(log_3\left(-x-1\right)\le2\)
d) \(log_2\left(2x-3\right)\ge2\)
e) \(log_3\left(2x-7\right)>2\)
a: \(log\left(x-2\right)< 3\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-2>0\\log\left(x-2\right)< log9\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-2>0\\x-2< 9\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow2< x< 11\)
b: \(log_2\left(2x-1\right)>3\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-1>0\\log_2\left(2x-1\right)>log_29\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-1>0\\2x-1>9\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow2x-1>9\)
=>2x>10
=>x>5
c: \(log_3\left(-x-1\right)< =2\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-x-1>0\\log_3\left(-x-1\right)< =log_39\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-x-1>0\\-x-1< =9\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-x>1\\-x< =10\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< -1\\x>=-10\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow-10< =x< -1\)
d: \(log_2\left(2x-3\right)>=2\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-3>0\\log_2\left(2x-3\right)>=log_24\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-3>0\\2x-3>=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>2x-3>=4
=>2x>=7
=>\(x>=\dfrac{7}{2}\)
e: \(log_3\left(2x-7\right)>2\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-7>0\\log_3\left(2x-7\right)>log_39\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>\dfrac{7}{2}\\2x-7>9\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>2x-7>9
=>2x>16
=>x>8
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
a.
\(log\left(x-2\right)< 3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-2>0\\x-2< 10^3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>2\\x< 1002\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow2< x< 1002\)
b.
\(log_2\left(2x-1\right)>3\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-1>0\\2x-1>2^3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>\dfrac{1}{2}\\x>\dfrac{9}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow x>\dfrac{9}{2}\)
c.
\(log_3\left(-x-1\right)\le2\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-x-1>0\\-x-1\le3^2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< -1\\x\ge-10\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow-10\le x< -1\)
d.
\(log_2\left(2x-3\right)\ge2\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-3>0\\2x-3\ge2^2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge\dfrac{3}{2}\\x>\dfrac{7}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow x>\dfrac{7}{2}\)
e,
\(log_3\left(2x-7\right)>2\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-7>0\\2x-7>3^2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>\dfrac{7}{2}\\x>8\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow x>8\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Lời giải:
a. ĐK: $x>2$
$\log(x-2)<3$
$\Leftrightarrow x-2< 10^3$
$\Leftrightarrow x< 1002$
Vậy $2< x< 1002$
b. ĐK: $x> \frac{1}{2}$
$\log_2(2x-1)>3$
$\Leftrightarrow 2x-1> 2^3$
$\Leftrightarrow 2x> 9$
$\Leftrightarrow x> \frac{9}{2}$
Vậy $x> \frac{9}{2}$
c. ĐK: $x< -1$
$\log_3(-x-1)\leq 2$
$\Leftrightarrow -x-1\leq 3^2=9$
$\Leftrightarrow x+1\geq -9$
$\Leftrightarrow x\geq -10$
Vậy $-10\leq x< -1$
d. ĐK: $x> \frac{3}{2}$
$\log_2(2x-3)\geq 2$
$\Leftrightarrow 2x-3\geq 2^2=4$
$\Leftrightarrow x\geq \frac{7}{2}$
Vậy $x\geq \frac{7}{2}$
e. ĐK: $x> \frac{7}{2}$
$\log_3(2x-7)>2$
$\Leftrightarrow 2x-7> 3^2=9$
$\Leftrightarrow x> 8$
Vậy $x>8$
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)