Bài 1: Cho x3+4x2+5x+2=(x+1)(x^2+ax+b). Tìm a,b

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Bài 1: Thực hiện phép tính: a) 2x.(3x2 – 5x + 3) b) (-2x-1).( x2 + 5x – 3 ) – (x-1)3c) (2x – y).(4x2 + 2xy + y2) d) (6x5y2 – 9x4y3 + 15x3y4) : 3x3y2 e) (x3 – 3x2 + x – 3) : (x – 3)Bài 2: Tìm x, biết:a) 5x(x – 1) 10 (x – 1); b) 2(x + 5) – x2 – 5x 0; c) x3 - x 0; d) (2x – 1)2 – (4x – 3)2 0 e) (5x + 3)(x – 4) – (x – 5)x (2x – 5)(5+2x )Bài 3: Chứng minh r...
Đọc tiếp
Bài 1: Thực hiện phép tính:
a) 2x.(3x2 – 5x + 3) b) (-2x-1).( x2 + 5x – 3 ) – (x-1)3
c) (2x – y).(4x2 + 2xy + y2) d) (6x5y2 – 9x4y3 + 15x3y4) : 3x3y2
e) (x3 – 3x2 + x – 3) : (x – 3)
Bài 2: Tìm x, biết:
a) 5x(x – 1) = 10 (x – 1); b) 2(x + 5) – x2 – 5x = 0;
c) x3 - x = 0; d) (2x – 1)2 – (4x – 3)2 = 0
e) (5x + 3)(x – 4) – (x – 5)x = (2x – 5)(5+2x )
Bài 3: Chứng minh rằng giá trị của biểu thức không phụ thuộc vào giá trị của biến.
a) x(3x + 12) – (7x – 20) + x2(2x – 3) – x(2x2 + 5).
b) 3(2x – 1) – 5(x – 3) + 6(3x – 4) – 19x.
Bài 4: Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử.
a) 10x(x – y) – 8(y – x) b) (3x + 1)2 – (2x + 1)2
c) - 5x2 + 10xy – 5y2 + 20z2 d) 4x2 – 4x +4 – y2
e) 2x2 - 9xy – 5y2 f) x3 – 4x2 + 4 x – xy2
Bài 5: Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức
a) A = 9x2 – 6x + 11 b) B = 4x2 – 20x + 101
Bài 6: Tìm giá trị lớn nhất của biểu thức
a) A = x – x2 b) B = – x2 + 6x – 11
a) 2x.(3x2 – 5x + 3)
=2x3-10x2+6x
b(-2x-1).( x2 + 5x – 3 ) – (x-1)3
=-2x3 - 10x2 + 6x - x2 - 5x + 3 - x3 + 3x2 - 3x + 1
= -3x3 - 8x2 - 2x + 4
d) (6x5y2 – 9x4y3 + 15x3y4) : 3x3y2
=2x2-3xy+5y2
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1: Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử
a. 1 - 4x2
b. 8 - 27x3
c. 27 + 27x + 9x 2 + x3
d. 2x3 + 4x2 + 2x
e. x2 - 5x - y2 + 5y
f. x2 - 6x + 9 - y2
g. 10x (x - y) - 6y(y - x)
h. x2 - 4x - 5
i. x4 - y4
Bài 2: Tìm x, biết
a. 5(x - 2) x - 2
b. 3(x - 5) 5 - x
c. (x +2)2 - (x+ 2) (x - 2) 0
Bài 3: Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức
a. A x2 - 6x + 11
b. B 4x2 - 20x + 101
c. C -x2 - 4xy + 5y2 + 10x - 22y + 28
Đọc tiếp
Bài 1: Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử
a. 1 - 4x2
b. 8 - 27x3
c. 27 + 27x + 9x 2 + x3
d. 2x3 + 4x2 + 2x
e. x2 - 5x - y2 + 5y
f. x2 - 6x + 9 - y2
g. 10x (x - y) - 6y(y - x)
h. x2 - 4x - 5
i. x4 - y4
Bài 2: Tìm x, biết
a. 5(x - 2) = x - 2
b. 3(x - 5) = 5 - x
c. (x +2)2 - (x+ 2) (x - 2) = 0
Bài 3: Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức
a. A = x2 - 6x + 11
b. B = 4x2 - 20x + 101
c. C = -x2 - 4xy + 5y2 + 10x - 22y + 28
a.
\(1-4x^2=\left(1-2x\right)\left(1+2x\right)\)
b.
\(8-27x^3=\left(2\right)^3-\left(3x\right)^3=\left(2-3x\right)\left(4+6x+9x^2\right)\)
c.
\(27+27x+9x^2+x^3=x^3+3.x^2.3+3.3^2.x+3^3\)
\(=\left(x+3\right)^3\)
d.
\(2x^3+4x^2+2x=2x\left(x^2+2x+1\right)=2x\left(x+1\right)^2\)
e.
\(x^2-y^2-5x+5y=\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)-5\left(x-y\right)\)
\(=\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y-5\right)\)
f.
\(x^2-6x+9-y^2=\left(x-3\right)^2-y^2=\left(x-3-y\right)\left(x-3+y\right)\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
g. 10x(x-y)-6y(y-x)
=10x(x-y)+6y(x-y)
=(x-y)(10x+6y)
h.x2-4x-5
=(x-5)(x+1)
i.x4-y4 = (x2-y2)(x2+y2)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
B2.
a.5(x-2)=x-2
⇔5(x-2)-(x-2)=0
⇔4(x-2)=0
⇔x=2
b.3(x-5)=5-x
⇔3(x-5)+(x-5)=0
⇔4(x-5)=0
⇔x=5
c.(x+2)2-(x+2)(x-2)=0
⇔(x+2)[(x+2)-(x-2)]=0
⇔4(x+2)=0
⇔x=-2
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1. Làm tính nhân:a) 3x2 (2 - 5xy) b) -dfrac{2}{3} xy (xy2 - x3 + 4) c) ( x - 7 y )( xy + 1)Bài 2. Rút gọn các biểu thức sau:a) 5x(4x2 - 2x +1) - 2x(10x2 - 5x - 2)b) 3x( x - 2) - 5x(1- x) - 8(x2 - 3)d) (x3 - 2x)(x2 +1)
Đọc tiếp
Bài 1. Làm tính nhân:
a) 3x2 (2 - 5xy)
b) -\(\dfrac{2}{3}\) xy (xy2 - x3 + 4)
c) ( x - 7 y )( xy + 1)
Bài 2. Rút gọn các biểu thức sau:
a) 5x(4x2 - 2x +1) - 2x(10x2 - 5x - 2)
b) 3x( x - 2) - 5x(1- x) - 8(x2 - 3)
d) (x3 - 2x)(x2 +1)
Bài 1:
\(a,6x^2-15x^3y\\ b,=-\dfrac{2}{3}x^2y^3+\dfrac{2}{3}x^4y-\dfrac{8}{3}xy\)
Bài 2:
\(a,=20x^3-10x^2+5x-20x^3+10x^2+4x=9x\\ b,=3x^2-6x-5x+5x^2-8x^2+24=24-11x\\ c,=x^5+x^3-2x^3-2x=x^5-x^3-2x\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
câu d của bài 2 là của bài 1 nha mình để nhầm chỗ huhu
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1:Thực hiện các phép tính
a. (x5 +4x3 - 6x2):4x2
b. (x3 +x2-12) : (x-2)
c. (-2x5+3x2-4x3):2x2
d. (x3 - 64):(x2 + 4x + 16)
Bài 2:Rút gọn biểu thức
a. 3x (x - 2)- 5x (1 - x) - 8(x2 - 3)
b.(x - y) (x2 + xy + y2)+2y3
c. (x - y)2 + (x+y)2 - 2(x-y) (x+y)
Đọc tiếp
Bài 1:Thực hiện các phép tính
a. (x5 +4x3 - 6x2):4x2
b. (x3 +x2-12) : (x-2)
c. (-2x5+3x2-4x3):2x2
d. (x3 - 64):(x2 + 4x + 16)
Bài 2:Rút gọn biểu thức
a. 3x (x - 2)- 5x (1 - x) - 8(x2 - 3)
b.(x - y) (x2 + xy + y2)+2y3
c. (x - y)2 + (x+y)2 - 2(x-y) (x+y)
a) \(\left(x^5+4x^3-6x^2\right):4x^2\)
\(=\left(x^5:4x^2\right)+\left(4x^3:4x^2\right)+\left(-6x^2:4x^2\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{4}x^3+x-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
b)
Vậy \(\left(x^3+x^2-12\right):\left(x-2\right)=x^2+3x+6\)
c) (-2x5 : 2x2) + (3x2 : 2x2) + (-4x^3 : 2x^2)
= \(-x^3+\dfrac{3}{2}-2x\)
d) \(\left(x^3-64\right):\left(x^2+4x+16\right)\)
\(=\left(x-4\right)\left(x^2+4x+16\right):\left(x^2+4x+16\right)\)
\(=x-4\)
(dùng hẳng đẳng thức thứ 7)
Bài 2 :
a) 3x(x - 2) - 5x(1 - x) - 8(x2 - 3)
= 3x2 - 6x - 5x + 5x2 - 8x2 + 24
= (3x2 + 5x2 - 8x2) + (-6x - 5x) + 24
= -11x + 24
b) (x - y)(x2 + xy + y2) + 2y3
= x3 - y3 + 2y3
= x3 + y3
c) (x - y)2 + (x + y)2 - 2(x - y)(x + y)
= (x - y)2 - 2(x - y)(x + y) + (x + y)2
= [(x - y) + x + y)2 = [x - y + x + y] = (2x)2 = 4x2
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1 :
a]= \(\frac{1}{4}\)x3 + x - \(\frac{3}{2}\).
b] => [x3 + x2 -12 ] = [ x2 +3 ][x-2] + [-6]
c]= -x3 -2x +\(\frac{3}{2}\).
d] = [ x3 - 64 ] = [ x2 + 4x + 16][ x- 4].
Bài 1: Giải các phương trình dưới đây1) x2 - 9 (x - 3)(5x +2)2) x3 - 1 (x - 1)(x2 - 2x +16)3) 4x2 (x - 1) - x + 1 04) x3 + 4x2 - 9x - 36 05) (3x + 5)2 (x - 1)26) 9 (2x + 1)2 4 (x - 5)27) x2 + 2x 158) x4 + 5x3 + 4x2 09) (x2 - 4) - (x - 2)(3 - 2x) 010) (3x + 2)(x2 - 1) (9x2 - 4) (x + 1)11) (3x - 1)(x2 + 2) (3x - 1)(7x - 10)12) (2x2 + 1) (4x - 3) (x - 12)(2x2 + 1)
Đọc tiếp
Bài 1: Giải các phương trình dưới đây
1) x2 - 9 = (x - 3)(5x +2)
2) x3 - 1 = (x - 1)(x2 - 2x +16)
3) 4x2 (x - 1) - x + 1 = 0
4) x3 + 4x2 - 9x - 36 = 0
5) (3x + 5)2 = (x - 1)2
6) 9 (2x + 1)2 = 4 (x - 5)2
7) x2 + 2x = 15
8) x4 + 5x3 + 4x2 = 0
9) (x2 - 4) - (x - 2)(3 - 2x) = 0
10) (3x + 2)(x2 - 1) = (9x2 - 4) (x + 1)
11) (3x - 1)(x2 + 2) = (3x - 1)(7x - 10)
12) (2x2 + 1) (4x - 3) = (x - 12)(2x2 + 1)
1: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)-\left(x-3\right)\left(5x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(-4x+1\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{3;\dfrac{1}{4}\right\}\)
2: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)-\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-2x+16\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1-x^2+2x-16\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(3x-15\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{1;5\right\}\)
3: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(4x^2-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{1;\dfrac{1}{2};-\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)
4: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x+4\right)-9\left(x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+4\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{-4;3;-3\right\}\)
5: \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x+5=x-1\\3x+5=1-x\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=-6\\4x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
6: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(6x+3\right)^2-\left(2x-10\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(6x+3-2x+10\right)\left(6x+3+2x-10\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x+13\right)\left(8x-7\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{-\dfrac{13}{4};\dfrac{7}{8}\right\}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
1.
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=\left(x-3\right)\left(5x-2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+3=5x-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=5\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{4}\)
2.
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)=\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-2x+16\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x+1=x^2-2x+16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=15\Leftrightarrow x=5\)
3.
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2\left(x-1\right)-\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(4x^2-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=\dfrac{1}{2};x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
7.
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x-15=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
8.\(\Leftrightarrow x^4+x^3+4x^3+4x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3\left(x+1\right)+4x^2\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x^3+4x^2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=0;x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
9.\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)=\left(x-2\right)\left(3-2x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+2=3-2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=1\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Bài 1: Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử: a) 4y3 + 16y2 + 16y b) 8x2-48x+6xy-36y c) 8x2-48x-6xy+36y d) a2 –2ab+b2 –4 e) 4–x2 –4xy–4y2 f) 8a2 –16a+8ax–16x g) 16–4x2 +8xy–4y2 h) –4x2 –16xy–16y2 Bài 2: Tìm x, biết: a) x3 – 6x2 + 9x = 0 b) 5x(x–6)+3x–18=0 c) 5x(x – 6) – 18 + 3x = 0 d) 5x(x – 6) – 3x + 18 = 0 e) (2x – 3)2 = (5 – x)2 f) (2x + 1)2 = (3x – 2)2 g) 16(2x–3)=-25x2 (3–2x)
b: \(8x^2-48x+6xy-36y\)
\(=8x\left(x-6\right)+6y\left(x-6\right)\)
\(=2\left(x-6\right)\left(4x+3y\right)\)
d: \(a^2-2ab+b^2-4\)
\(=\left(a-b\right)^2-4\)
\(=\left(a-b-2\right)\left(a-b+2\right)\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho hai phân thức
1
x
2
+
a
x
-
2
và
2
x
2
+
5
x
+
b
. Hãy xác định a và b biết rằng khi quy đồng mẫu thức chúng trở thành những phâ...
Đọc tiếp
Cho hai phân thức 1 x 2 + a x - 2 và 2 x 2 + 5 x + b . Hãy xác định a và b biết rằng khi quy đồng mẫu thức chúng trở thành những phân thức có mẫu thức chung là x 3 + 4 x 2 + x - 6 . Viết tường minh hai phân thức đã cho và hai phân thức thu được sau khi quy đồng với mẫu thức chung là x 3 + 4 x 2 + x - 6
Ta có mẫu thức chung phải chia hết cho từng mẫu thức riêng.
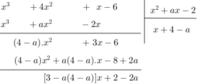
Vì phép chia này là phép chia hết nên số dư phải bằng 0, tức là:
3 – a(4 – a) = 0 và 2 – 2a = 0 ⇒ a = 1.
Vậy phân thức thứ nhất là 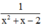
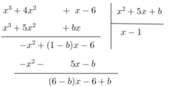
Vì phép chia này là phép chia hết nên số dư phải bằng 0, tức là:
6 – b = 0 và -6 + b = 0 ⇒ b = 6.
Vậy phân thức thứ hai là 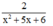
* Quy đồng:
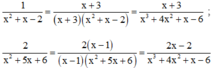
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1. Cho f(x)= x3 - 2x2 + 3x + 1; g(x)+ x3 + x - 1; h(x)= 2x2 -1
a) Tính f(x) - g(x) + h(x)
b) Tìm x sao cho f(x) - g(x) + h(x) = 0
2. Tìm nghiệm của
a) 5x + 3 (3x + 7) - 35
b) x2 + 8x - (x2 + 7x + 8) - 9
3. Tìm f(x) = x3 + 4x2 - 3x + 2; g(x) = x2 (x+4) + x - 5
Tìm x sao cho f(x) = g(x)
4. Tìm m sao cho k(x)= mx2 - 2x + 4 có nghiệm là -2
Thực hiện phép tính:a) (
2
x
3
+
4
x
2
+ 5x +10): (2
x
2
+ 5);b) (
x
3
+ 2
x
2
- 1): (2
x
2
+ x +1).
Đọc tiếp
Thực hiện phép tính:
a) ( 2 x 3 + 4 x 2 + 5x +10): (2 x 2 + 5);
b) ( x 3 + 2 x 2 - 1): (2 x 2 + x +1).























