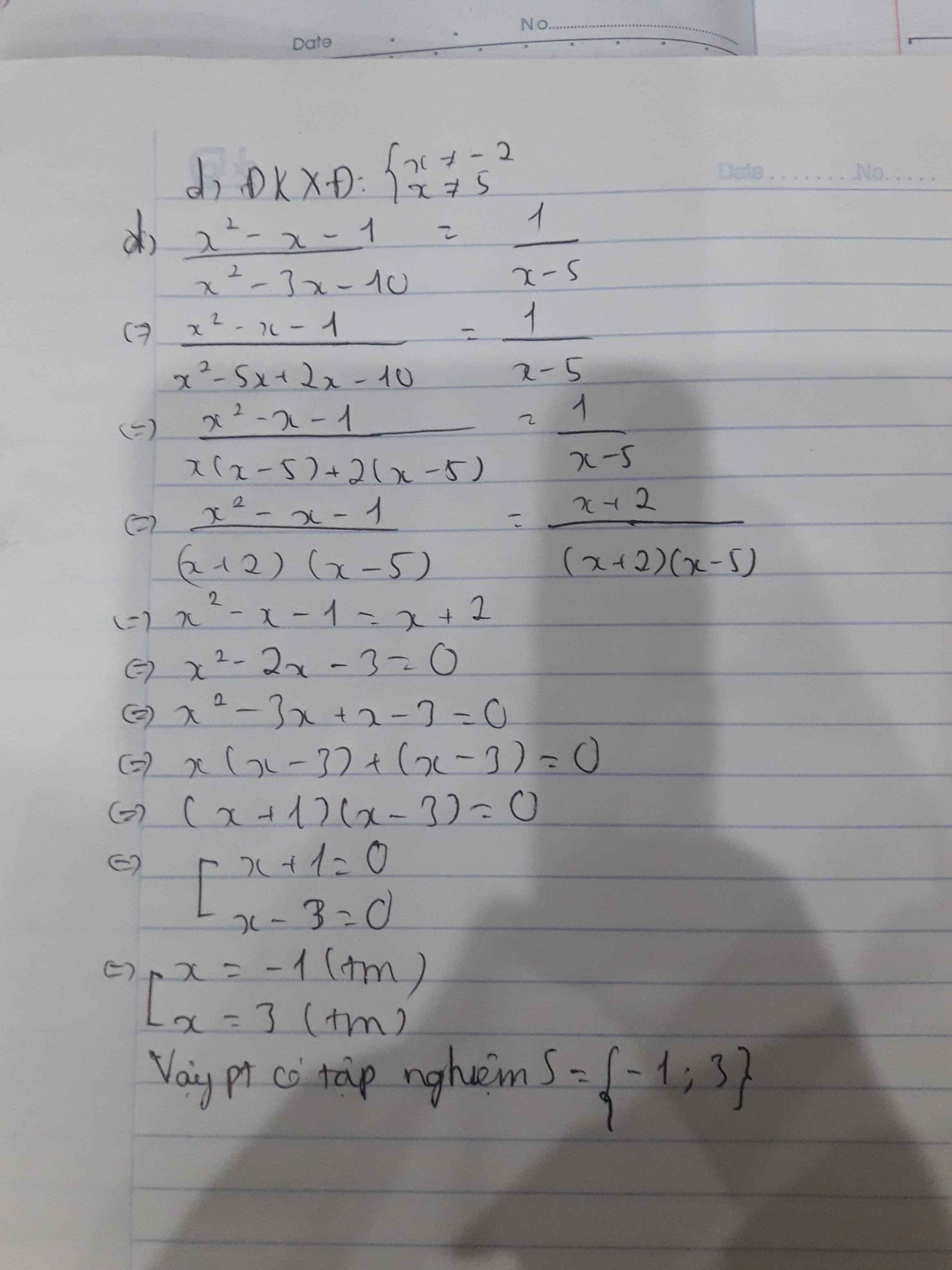câu 4 thôi ha

Những câu hỏi liên quan
câu 3, câu 4 thôi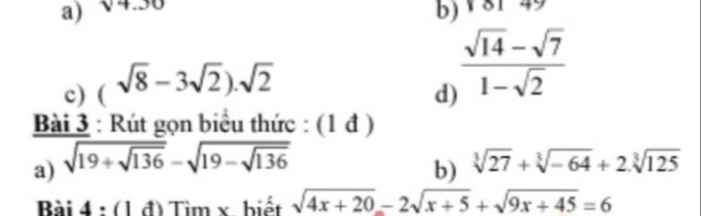
Đặt A=\(\sqrt{19+\sqrt{136}}-\sqrt{19-\sqrt{136}}\)
=> A^2=38-2\(\sqrt{\left(19+\sqrt{136}\right)\left(19-\sqrt{136}\right)}\)
=38-2\(\sqrt{19^2-136}\)
=38-2\(\sqrt{225}\)=38-30=8
B)B=3-4+2.5=9
B4:đặt \(\sqrt{x+5}=t\)
=>\(\sqrt{4t}-2\sqrt{t}+\sqrt{9t}\)=6
=>\(\sqrt{t}\)(2-2+3)=6
=>\(\sqrt{t}\)=6
=>t=36 tmđk
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Câu 3,câu 4 thôi ạ

lm câu 3 câu 4 thôi ạ
c. \(\left(x+2\right)^4-6\left(x+2\right)^2+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)^4-\left(x+2\right)^2-5\left(x+2\right)^2+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)^2\left[\left(x+2\right)^2-1\right]-5\left[\left(x+2\right)^2-1\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[\left(x+2\right)^2-1\right]\left[\left(x+2\right)^2-5\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+3\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2+\sqrt{5}\right)\left(x+2-\sqrt{5}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+3=0\\x+1=0\\x+2+\sqrt{5}=0\\x+2-\sqrt{5}=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=-1\\x=-\sqrt{5}-2\\x=\sqrt{5}-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Phương trình có tập nghiệm \(S=\left\{-3;-1;-\sqrt{5}-2;\sqrt{5}-2\right\}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Cho tam giác ABC vuông tại A có góc ABC=55 độ,lấy M là trung điểm của AC
1)Góc ACB=bao nhêu độ
2)Trên tia đối của MB lấy điểm N sao cho:MN=MBCMR tam giác AMB=tam giá CMN
3)vẽ AH _|_ BC(H thuộc BC),trên tia đối của HA lấy điểm I sao cho HI=HA,CMR BI=CN
4)CMR AN//BC và AN_|_ Ai
(ko cần hình vẽ,giúp câu 3;4 thôi)
4+4=?
còn một câu thôi bạn nào đc điểm thì thôi cho bạn khác nữa nhé
 GIÚP MÌNH CÂU 4,CÂU 5, CÂU 9, CÂU 11, CÂU 12 VÀ CÂU 15 THÔI Ạ!!
GIÚP MÌNH CÂU 4,CÂU 5, CÂU 9, CÂU 11, CÂU 12 VÀ CÂU 15 THÔI Ạ!!
4 If you aren't alert, you computer will be infected with viruses
5 If we use much pesticide on vegetables, they will become poisonous
9 Because Nam needs to improve his social skills, he attends the activity
11 How about using public buses instead of motorbike
12 They enjoy protecting the environment unpolluted
15 Mr Brown was disappointed that his son didn't write to him
Đúng 4
Bình luận (17)

Giúp mình câu 3 với câu 4 thôi nha mn!
 làm câu 4 thôi
làm câu 4 thôi
mỗi câu 4 thôi

Bài 4:
b: Xét ΔAHB vuông tại H có HE là đường cao ứng với cạnh huyền AB
nên \(AE\cdot AB=AH^2\left(1\right)\)
Xét ΔAHC vuông tại H có HF là đường cao ứng với cạnh huyền AC
nên \(AF\cdot AC=AH^2\left(2\right)\)
Từ (1) và (2) suy ra \(AE\cdot AB=AF\cdot AC\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)