Giải phương trình:
(x2 + x)2 + 4( x2 + x) = 12
Giải các phương trình sau: ( x 2 + x ) 2 + 4 ( x 2 + x ) - 12 = 0
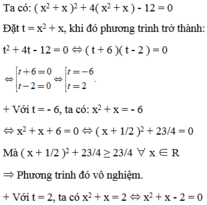
⇔ ( x + 2 )( x - 1 ) = 0 ⇔ 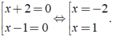
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm là S = { - 2;1 }.
giải phương trình sau:
a) (x2 + x)2 + 4(x2 + x) = 12;
b) x(x-1)(x + 1)(x+2)= 24;
c) (x-7)(x-5)(x-4)(x-2)= 72.
1. Đặt $x^2+x=a$ thì pt trở thành:
$a^2+4a=12$
$\Leftrightarrow a^2+4a-12=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (a-2)(a+6)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow a-2=0$ hoặc $x+6=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x^2+x-2=0$ hoặc $x^2+x+6=0$
Dễ thấy $x^2+x+6=0$ vô nghiệm.
$\Rightarrow x^2+x-2=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-1)(x+2)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=1$ hoặc $x=-2$
2.
$x(x-1)(x+1)(x+2)=24$
$\Leftrightarrow [x(x+1)][(x-1)(x+2)]=24$
$\Leftrightarrow (x^2+x)(x^2+x-2)=24$
$\Leftrightarrow a(a-2)=24$ (đặt $x^2+x=a$)
$\Leftrightarrow a^2-2a-24=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (a+4)(a-6)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow a+4=0$ hoặc $a-6=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x^2+x+4=0$ hoặc $x^2+x-6=0$
Nếu $x^2+x+4=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x+\frac{1}{2})^2=\frac{1}{4}-4<0$ (vô lý - loại)
Nếu $x^2+x-6=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-2)(x+3)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x-2=0$ hoặc $x+3=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=2$ hoặc $x=-3$
3.
$(x-7)(x-5)(x-4)(x-2)=72$
$\Leftrightarrow [(x-7)(x-2)][(x-5)(x-4)]=72$
$\Leftrightarrow (x^2-9x+14)(x^2-9x+20)=72$
$\Leftrightarrow a(a+6)=72$ (đặt $x^2-9x+14=a$)
$\Leftrightarrow a^2+6a-72=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (a-6)(a+12)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow a-6=0$ hoặc $a+12=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x^2-9x+8=0$ hoặc $x^2-9x+26=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x^2-9x+8=0$ (dễ thấy pt $x^2-9x+26=0$ vô nghiệm)
$\Leftrightarrow (x-1)(x-8)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x-1=0$ hoặc $x-8=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=1$ hoặc $x=8$
Giải phương trình
( x2 + x - 2 )(x2 + x - 3 ) = 12
Lời giải:
Đặt $x^2+x=a$ thì pt trở thành:
$(a-2)(a-3)=12$
$\Leftrightarrow a^2-5a+6=12$
$\Leftrightarrow a^2-5a-6=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (a+1)(a-6)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow a+1=0$ hoặc $a-6=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x^2+x+1=0$ hoặc $x^2+x-6=0$
Nếu $x^2+x+1=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x+\frac{1}{2})^2=-\frac{3}{4}<0$ (vô lý - loại)
Nếu $x^2+x-6=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-2)(x+3)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=2$ hoặc $x=-3$
Giải phương trình sau: 1/x+2+5/x-2=2x-12/x2-4
\(\dfrac{1}{x+2}\)+\(\dfrac{5}{x-2}\)=\(\dfrac{2x-12}{x^2-4}\)
(đkxđ: x≠2, x≠-2)
⇔ \(\dfrac{x-2}{x^2-4}\)+\(\dfrac{5\left(x+2\right)}{x^2-4}\)= \(\dfrac{2x-12}{x^2-4}\)
⇔ x-2+5(x+2)=2x-12
⇔ x-2+5x+10=2x-12
⇔ 4x=-20
⇔ x=-5(tm)
Mn ai giỏi Toán giải giúp mik bài này đc ko ạ☺
Bài 1 Giải các phương trình sau:
a) x(4x + 2) = 4x2 – 14;
b) (x2 – 9)(2x – 1) = 0;
c) 3/x-2 + 4/x+2 = X-12/x2-4 ( / là Phần)
a) x(4x + 2) = 4x2 - 14
⇔ 4x2 + 2x = 4x2 - 14
⇔ 4x2 - 4x2 + 2x = -14
⇔ 2x = -14
⇔ x = -7
Vậy tập nghiệm S = ......
b) (x2 - 9)(2x - 1) = 0
⇔ x2 - 9 = 0 hoặc 2x - 1 = 0
⇔ x2 = 9 hoặc 2x = 1
⇔ x = 3 hoặc -3 hoặc x = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Vậy .......
c) \(\dfrac{3}{x-2}\) + \(\dfrac{4}{x+2}\) = \(\dfrac{x-12}{x^2-4}\)
⇔ \(\dfrac{3}{x-2}\) + \(\dfrac{4}{x+2}\) = \(\dfrac{x-12}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
ĐKXĐ: x - 2 ≠ 0 và x + 2 ≠ 0
⇔ x ≠ 2 và x ≠ -2MSC (mẫu số chung): (x - 2)(x + 2)Quy đồng mẫu hai vế và khử mẫu ta được:3x + 6 + 4x - 8 = x - 12⇔ 3x + 4x - x = 8 - 6 - 12⇔ 6x = -10⇔ x = \(-\dfrac{5}{3}\) (nhận)Vậy ........Giải các phương trình sau: (2 x 2 + 1)(4x – 3) = (2 x 2 + 1)(x – 12)
Giải các phương trình: 3 x 2 + 4(x – 1) = x - 1 2 + 3
Ta có: 3 x 2 + 4(x – 1) = x - 1 2 + 3
⇔ 3 x 2 + 4x – 4 = x 2 – 2x + 1 + 3
⇔ 2 x 2 + 6x – 8 = 0 ⇔ x 2 + 3x – 4 = 0
Phương trình x 2 + 3x – 4 = 0 có hệ số a = 1, b = 3, c = -4 nên có dạng a + b + c = 0, suy ra x 1 = 1, x 2 = -4
Vậy phương trình đã cho có hai nghiệm x 1 = 1, x 2 = -4
Giải phương trình ( x + 1 ) 2 ( x 2 + 4 ) = x 2 − x − 2
( x + 1 ) 2 ( x 2 + 4 ) = x 2 − x − 2 (1)
Điều kiện: x2 + 4 ≥ 0 (luôn đùng ∀ x)
( 1 ) ⇔ ( x + 1 ) 2 ( x 2 + 4 ) = ( x − 2 ) ( x + 1 ) ⇔ ( x + 1 ) 2 ( x 2 + 4 ) − ( x − 2 ) = 0 ⇔ x = − 1 2 ( x 2 + 4 ) = x − 2 ( 2 )
Có ( 2 ) ⇔ x ≥ 2 2 ( x 2 + 4 ) = x - 2 2 ⇔ x ≥ 2 x 2 + 4 x + 4 = 0 ⇔ x ≥ 2 x = − 2 (loại)
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình đã cho là {–1}
giải các phương trình sau:
a)(x+2)(x2-2x+4)-x(x2-2)=15
b)x(x-5)(x+5)-(x+2)(x2-2x+4)=3
\(a,=>x^3-2x^2+4x+2x^2-4x+8-x^3+2x-15=0\)
\(< =>2x-7=0< =>x=\dfrac{7}{2}\)
b,\(=>x\left(x^2-25\right)-\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)-3=0\)
\(< =>x^3-25x-x^3+2x^2-4x-2x^2+4x-8-3=0\)
\(< =>-25x-11=0\)
\(< =>x=-0,44\)
Giải các bất phương trình sau
a) (x2+2)2-(x+2)(x-2)(x2+4)-4x(x+1)< hoặc = 20
b) (x+2)(x2-2x+4)-x(x2+2)> hoặc = 15
a) \(\left(x^2+2\right)^2-\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+4\right)-4x\left(x+1\right)\le20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4+4x^2+4-x^4+16-4x^2-4x\le20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^4-x^4\right)+\left(4x^2-4x^2\right)-4x+4+16\le20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4x+20\le20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4x\le20-20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4x\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4x:-4\ge0:-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ge0\)
Vậy nghiệm của bất phương trình là: \(x\ge0\)
b) \(\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)-x\left(x^2+2\right)\ge15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3+8-x^3-2x\ge15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^3-x^3\right)+8-2x\ge15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8-2x\ge15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x\ge15-8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x\ge7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x:-2\le7:-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\le-\dfrac{7}{2}\)
Vậy nghiệm của bất phương trình là \(x\le-\dfrac{7}{2}\)
a: =>x^4+4x^2+4-x^4+16-4x^2-4x<=20
=>-4x+20<=20
=>-4x<=0
=>x>=0
b: =>x^3+8-x^3-2x>=15
=>-2x>=7
=>x<=-7/2