 làm hộ mik bài 5 ạ,mik cảm ơn ạ
làm hộ mik bài 5 ạ,mik cảm ơn ạ

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Làm hộ mik bài này ạ,mik cảm ơn
Lời giải:
a.
Nếu $m=3$ thì pt trở thành:
$x^2+4x-5=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-1)(x+5)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=1$ hoặc $x=-5$
b.
Để pt có 2 nghiệm pb $x_1,x_2$ thì:
$\Delta'=4+m^2-4>0\Leftrightarrow m^2>0\Leftrightarrow m\neq 0$
PT có 2 nghiệm $(-2+m, -2-m)$
Khi đó:
\(x_2=x_1^3+4x_2^2\Leftrightarrow \left[\begin{matrix} -2+m=(-2-m)^3+4(-2+m)^2\\ -2-m=(-2+m)^3+4(-2-m)^2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \left[\begin{matrix} -m^3+2m^2-29m+10=0\\ m^3-2m^2+29m+10=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Nghiệm khá xấu, cảm giác đề cứ sai sai bạn ạ.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Làm hộ mik bài 2 câu b) và cả bài 3 ạ,mik cảm ơn

Bạn nào biết làm hộ mik được ko ạ! Mik cảm ơn! Bạn nào làm hộ mik, mik tick hết chứ ko phải mỗi bn đầu! Bạn nào biết bài nào thì làm hộ mik bài đó nha!
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
double a,b,c,p,s;
int main()
{
cin>>a>>b>>c;
p=(a+b+c)/2;
s=sqrt(p*(p-a)*(p-b)*(p-c));
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(2)<<p;
return 0;
}
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
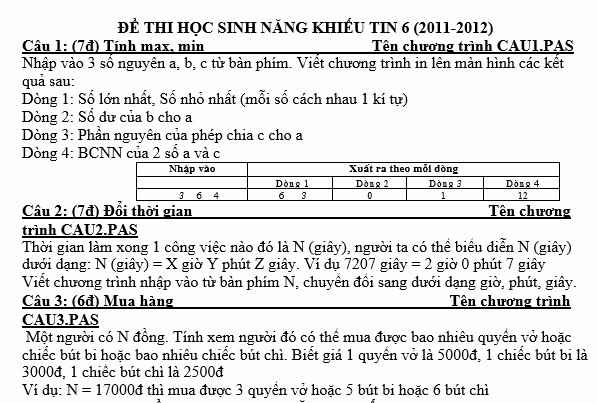
Bạn nào biết làm hộ mik được ko ạ! Mik cảm ơn! Bạn nào làm hộ mik, mik tick hết chứ ko phải mỗi bn đầu! Bạn nào biết bài nào thì làm hộ mik bài đó nha!
1:
uses crt;
var a,b,c,max,min:longint;
begin
clrscr;
readln(a,b,c);
max=a;
if max<b then max:=b;
if max<c then max:=c;
min:=a;
if min>c then min:=c;
if min>b then min:=b;
writeln(max,' ',min);
readln;
end.
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
làm hộ mik bài này ạ.mik cảm ơn ạ
làm hộ mik b1.2, 2.2, 3.2
bài 2.2 lm bằng pp chặn giúp mik ạ
mik cảm ơn
Bài 1.2
\(A=\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}+7}{\sqrt{x}+2}=2+\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{x}+2}\)
C1:Bạn dùng pp chặn như bài 2.2
C2: (Gợi ý)\(\sqrt{x}+2\ge2\) và \(\sqrt{x}+2\inƯ\left(3\right)\)\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{x}+2=3\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
Vậy x=1 thì A nguyên
Bài 2.2
\(A=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+7}{\sqrt{x}+2}=1+\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+2}\)
Do \(\sqrt{x}\ge0;\forall x\)\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{x}+2\ge2\) \(\Rightarrow\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+2}\le\dfrac{5}{2}\)\(\Rightarrow A\le\dfrac{7}{2}\) (1)
mà \(\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+2}>0;\forall x\Rightarrow A>1\) (2)
Từ (1) (2) \(\Rightarrow1< A\le\dfrac{7}{2}\) mà A nguyên
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}A=2\\A=3\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}1+\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+2}=2\\1+\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+2}=3\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x}+2=5\\\sqrt{x}+2=\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x}=3\\\sqrt{x}=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=9\\x=\dfrac{1}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy...
Bài 3.2
\(A=\dfrac{-x-2\sqrt{x}-5}{\sqrt{x}+2}\)\(=\dfrac{-\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)-5}{\sqrt{x}+2}=-\sqrt{x}-\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+2}\)
\(=2-\left(\sqrt{x}+2+\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+2}\right)\)
Áp dụng bđt cosi: \(\sqrt{x}+2+\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+2}\ge2\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right).\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+2}}=2\sqrt{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow A\le2-2\sqrt{5}\)
Dấu = xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}+2=\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+2}\Leftrightarrow x=9-4\sqrt{5}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)

Các bạn giải hộ mik bài này vs ạ, đồng thời cũng lập bảng bài nyaf hộ mik vs! Cảm ơn trc ạ
 làm bài hộ mình voiwas ạ, mik cảm ơn trước! ngày sinh là 20/2/2008
làm bài hộ mình voiwas ạ, mik cảm ơn trước! ngày sinh là 20/2/2008
Làm hộ mik bảng này ạ,mik cảm ơn










