Giải phương trình sau: 8cos2x + 2sinx – 7 = 0

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Giải phương trình sau: 2 sin x + 2 cos x - 2 = 0
Giải các phương trình sau 3 cos 2 x - 2 sin x + 2 = 0
3 cos 2 x - 2 sin x + 2 = 0 ⇔ 3 ( 1 - sin 2 x ) - 2 sin x + 2 = 0 ⇔ 3 sin 2 x + 2 sin x - 5 = 0 ⇔ ( sin x - 1 ) ( 3 sin x + 5 ) = 0 ⇔ sin x = 1 ⇔ x = π / 2 + k 2 π , k ∈ Z
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
giải phương trình sau: 2sinx-1=0 biết xϵ(-π/2: π)
\(2sinx-1=0\Leftrightarrow sinx=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k2\pi\\x=\dfrac{5\pi}{6}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
Do \(x\in\left(-\dfrac{\pi}{2};\pi\right)\Rightarrow x=\left\{\dfrac{\pi}{6};\dfrac{5\pi}{6}\right\}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình : 2sinx+cscx=0
`2sin x+cosx=0`
`<=> sinx + 1/2 cosx=0`
Có: `a^2+b^2=1^2+(1/2)^2=5/4 \ne 1`
`=>` PTVN.
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
\(2sinx+cosx=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{5}}.sinx+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}}cosx=0\)
Đặt \(cos\alpha=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{5}}\) và \(sin\alpha=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}}\) (vì \(\left(\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{5}}\right)^2+\left(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}}\right)^2=1\))
pttt: \(sinx.cos\alpha+cosx.sin\alpha=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin\left(x+\alpha\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x=-arc.sin\alpha+k\pi\left(k\in Z\right)\)
(phải không?)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (1)
Giải phương trình 2sinx – 3 = 0 là phương trình bậc nhất đối với sinx.
2sinx – 3 = 0 ⇔ sin x = 3/2 , vô nghiệm vì |sinx| ≤ 1
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình sin2x + 2sinx – 30
Đọc tiếp
Giải phương trình sin2x + 2sinx – 3=0
![]()
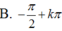
![]()
![]()
Giải phương trình sau: 2sinx + cosx = 1
2.sin x + cos x = 1
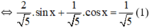
Vì 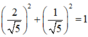 nên tồn tại α thỏa mãn
nên tồn tại α thỏa mãn 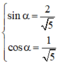
(1) trở thành:
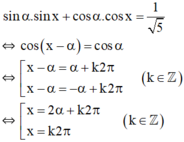
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm {k2π; 2α+k2π/k ∈ Z }
với α thỏa mãn 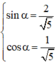
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
giải phương trình sau:
\(\dfrac{\left(1-2sinx\right)cosx}{\left(1+2sinx\right)\left(1-sinx\right)}=\sqrt{3}\)
ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\\x\ne-\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k2\pi\\x\ne\dfrac{7\pi}{6}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\dfrac{cosx-2sinx.cosx}{1-2sin^2x+sinx}=\sqrt{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{cosx-sin2x}{cos2x+sinx}=\sqrt{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow cosx-sin2x=\sqrt{3}cos2x+\sqrt{3}sinx\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx-\sqrt{3}sinx=\sqrt{3}cos2x+sin2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}cosx-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}sinx=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}cos2x+\dfrac{1}{2}sin2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=cos\left(2x-\dfrac{\pi}{6}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-\dfrac{\pi}{6}=x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\\2x-\dfrac{\pi}{6}=-x-\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\left(loại\right)\\x=-\dfrac{\pi}{18}+\dfrac{k2\pi}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
ĐKXĐ : \(sinx\ne1;-\dfrac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{2}+2k\pi\\x\ne\dfrac{-\pi}{6}+2k\pi;\dfrac{7\pi}{6}+2k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ne\dfrac{-\pi}{6}+\dfrac{2}{3}k\pi\)( k thuộc Z )
P/t đã cho \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{cosx-sin2x}{1-2sin^2x+sinx}=\sqrt{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx-sin2x=\sqrt{3}\left(cos2x+sinx\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx-\sqrt{3}sinx=\sqrt{3}cos2x+sin2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}cosx-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}sinx=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}cos2x+\dfrac{1}{2}sin2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=cos\left(2x+\dfrac{\pi}{6}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+\dfrac{\pi}{6}=x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}+2k\pi\\2x+\dfrac{\pi}{6}=-x-\dfrac{\pi}{3}+2k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\) ( k thuộc Z )
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{6}+2k\pi\\x=\dfrac{-\pi}{6}+\dfrac{2}{3}k\pi\left(L\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ...
Đúng 0
Bình luận (1)
Phương trình nào sau đây có nghiệm duy nhất trên R?A.
x
2
- 7x + 12 0 B.
x
3
+ 5x + 6 0C.
x
4
- 3
x
2
+ 1 0 D. 2sinx.
cos
2
x
- 2sinx - ...
Đọc tiếp
Phương trình nào sau đây có nghiệm duy nhất trên R?
A. x 2 - 7x + 12 = 0 B. x 3 + 5x + 6 = 0
C. x 4 - 3 x 2 + 1 = 0 D. 2sinx. cos 2 x - 2sinx - cos 2 x + 1 = 0
Đáp án:B.
Với f(x) = x 3 + 5x + 6 thì vì f'(x) = 3 x 2 + 5 > 0, ∀ x ∈ R nên hàm số f(x) luôn đồng biến trên R. Mặt khác f(-1) = 0. Vậy phương trình f(x) = 0 có nghiệm duy nhất trên R.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)



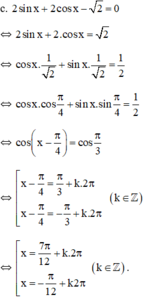
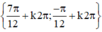 (k ∈ Z)
(k ∈ Z)












