x-1⋮52 ; x-1⋮35 và 1000 < x < 2000

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Bài 1: tìm x
c) | x | 3,5
d) | x | -2,7
e) | 1 - x | + 0,73 3
f) 52 . 73 . 11x + 52 . 72 .11 0
g) (3 . 5 + 5 . 7)x + ( 3 . 5 + 5 . 7) + (3 . 5 + 5 . 7) 0
h) 52 . 72 . 112x - 52 . 72 . 114 0
l) | x + dfrac{3}{4} | - 5 -2
Đọc tiếp
Bài 1: tìm x
c) \(|\) x \(|\) = 3,5
d) \(|\) x \(|\) = -2,7
e) \(|\) 1 - x \(|\) + 0,73 = 3
f) 52 . 73 . 11x + 52 . 72 .11 = 0
g) (3 . 5 + 5 . 7)x + ( 3 . 5 + 5 . 7) + (3 . 5 + 5 . 7) = 0
h) 52 . 72 . 112x - 52 . 72 . 114 = 0
l) \(|\) x + \(\dfrac{3}{4}\) \(|\) - 5 = -2
c) \(\left|x\right|=3,5\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3,5\\x=-3,5\end{matrix}\right.\)
d) \(\left|x\right|=-2,7\Rightarrow x\in\varnothing\)
l) \(\left|x+\dfrac{3}{4}\right|-5=-2\Rightarrow\left|x+\dfrac{3}{4}\right|=3\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+\dfrac{3}{4}=3\\x+\dfrac{3}{4}=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3-\dfrac{3}{4}\\x=-3-\dfrac{3}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{9}{4}\\x=\dfrac{15}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Đính chính câu l \(x=-\dfrac{15}{4}\) không phải \(x=\dfrac{15}{4}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
c) x = 3,5 hoặc -3,5
d) x = -2,7
e) x = -1,27
f) x = 0
g) x = -2
h) x = 0
l) x = 9/4
x = -15/4
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho hệ phương trình sau:
{x+y√5=0x√5+3y=1−√5{x+y5=0x5+3y=1−5
Ta tìm được nghiệm của hệ là :
A x=√5−52;y=−√5−12x=5−52;y=−5−12
B x=√5−52;y=√5−12x=5−52;y=5−12
C x=1−√52,y=−√5+52x=1−52,y=−5+52
D x=−√5+52;y=√5−12x=−5+52;y=5−12
Tìm x biết:
1. 52x - 3 - 2 . 52 = 52 . 3
2. 41 - 2x+1 = 9
3. 65 - 4x+2 = 20140
1: =>\(5^{2x-3}=5^2\cdot3+5^2\cdot2=5^2\cdot5=5^3\)
=>2x-3=3
=>2x=6
=>x=3
2: \(41-2^{x+1}=9\)
=>\(2^{x+1}=32\)
=>x+1=5
=>x=4
3: =>\(4^{x+2}=65-1=64\)
=>x+2=3
=>x=1
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
\(5^{2x-3}-2.5^2=5^2.3\\ 5^{2x-3}=5^2.3+5^2.2\\ 5^{2x-3}=5^2.\left(3+2\right)\\ 5^{2x-3}=5^2.5\\ 5^{2x-3}=5^3\\ \Rightarrow2x-3=3\\ 2x=3+3\\ 2x=6\\ x=\dfrac{6}{2}\\ Vậy:x=3\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
\(41-2^{x+1}=9\\ 2^{x+1}=41-9\\ 2^{x+1}=32=2^5\\ \Rightarrow x+1=5\\ \Leftrightarrow x=5-1=4\\ ---\\ 65-4^{x+2}=2014^0\\ 65-4^{x+2}=1\\ 4^{x+2}=65-1\\ 4^{x+2}=64=4^3\\ \Rightarrow x+2=3\\ Vậy:x=1\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
tính bằng cách thuận tiện: 52 x 44 + 84 x 52 + 52 - 52 x 29=?
52 x 44 + 84 x 52 + 52 - 52 x 29
= 52 x ( 44 + 84 + 1 - 29 )
= 52 x 100
= 5200
nkớ k nhoa =33
Tính bằng cách thuận tiện: 52 x 44 + 84 x 52 + 52 - 52 x 29=?
52x44+84x52+52-52x29
=52x(44+84+1+29)
=52x100
=52 000
HT
( 1 + 1/51 ) X ( 1 + 1/52) X ( 1 + 1/53 )
(1 + (1 / 51)) X (1 + (1 / 52)) X (1 + (1 / 53)) =
1.05882352941
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
( 1+ 1/51 ) x ( 1 + 1/52 ) x ( 1 + 1/53 )
= ( 51/51 + 1/51 ) x ( 52/52 + 1/52 ) x ( 53/53 + 1/53 )
= 52/51 x 53/52 x 54/53
= 52 x 53 x 54/51 x 52 x 53
= 54/51 = 1 3/51 ( hỗn số )
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Xin phép viết lại bài này 1 lần nữa
Tính bằng cách thuận tiện nhất
19 x ( 52 + 38 ) - 9 x ( 52 + 38 )
2/5 : 3/7 x 3/7 : 2/5 + 2019
19 x ( 52 + 38 ) - 9 x ( 52 + 38 )
= 19 x 90 - 9 x 90
= ( 19 - 9 ) x 90
= 10 x 90
= 900
\(\dfrac{2}{5}:\dfrac{3}{7}\times\dfrac{3}{7}:\dfrac{2}{5}+2019=\left(\dfrac{2}{5}:\dfrac{2}{5}\right)\times\left(\dfrac{3}{7}:\dfrac{3}{7}\right)+2019=1\times1+2019=1+2019=2020\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
(1+1/49)x(1+1/50)x(1+1/51)x(1+1/52)x..............x(1+1/60)
(1 + \(\dfrac{1}{49}\))\(\times\)(1 + \(\dfrac{1}{50}\))\(\times\)(1 + \(\dfrac{1}{51}\))\(\times\)(1 + \(\dfrac{1}{52}\))\(\times\)...\(\times\)(1 + \(\dfrac{1}{60}\))
= \(\dfrac{49+1}{49}\) \(\times\) \(\dfrac{50+1}{50}\)\(\times\) \(\dfrac{51+1}{51}\)\(\times\)\(\dfrac{52+1}{52}\)\(\times\)...\(\times\)\(\dfrac{61}{60}\)
= \(\dfrac{50}{49}\)\(\times\)\(\dfrac{51}{50}\)\(\times\)\(\dfrac{52}{51}\)\(\times\)...\(\times\)\(\dfrac{61}{60}\)
= \(\dfrac{50\times51\times52\times53\times...\times60}{50\times51\times52\times53\times...\times60}\)\(\times\)\(\dfrac{61}{49}\)
= \(\dfrac{61}{49}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình bằng cách đưa về phương trình tích:
a
)
3
x
2
−
7
x
−
10
⋅
2
x
2...
Đọc tiếp
Giải phương trình bằng cách đưa về phương trình tích:
a ) 3 x 2 − 7 x − 10 ⋅ 2 x 2 + ( 1 − 5 ) x + 5 − 3 = 0 b ) x 3 + 3 x 2 − 2 x − 6 = 0 c ) x 2 − 1 ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) = 0 , 6 x 2 + x d ) x 2 + 2 x − 5 2 = x 2 − x + 5 2
a) 3 x 2 − 7 x − 10 ⋅ 2 x 2 + ( 1 − 5 ) x + 5 − 3 = 0
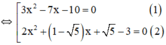
+ Giải (1):
3 x 2 – 7 x – 10 = 0
Có a = 3; b = -7; c = -10
⇒ a – b + c = 0
⇒ (1) có hai nghiệm x 1 = - 1 v à x 2 = - c / a = 10 / 3 .
+ Giải (2):
2 x 2 + ( 1 - √ 5 ) x + √ 5 - 3 = 0
Có a = 2; b = 1 - √5; c = √5 - 3
⇒ a + b + c = 0
⇒ (2) có hai nghiệm:
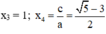
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 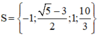
b)
x 3 + 3 x 2 - 2 x - 6 = 0 ⇔ x 3 + 3 x 2 - ( 2 x + 6 ) = 0 ⇔ x 2 ( x + 3 ) - 2 ( x + 3 ) = 0 ⇔ x 2 - 2 ( x + 3 ) = 0
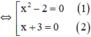
+ Giải (1): x 2 – 2 = 0 ⇔ x 2 = 2 ⇔ x = √2 hoặc x = -√2.
+ Giải (2): x + 3 = 0 ⇔ x = -3.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = {-3; -√2; √2}
c)
x 2 − 1 ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) = 0 , 6 x 2 + x ⇔ x 2 − 1 ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) = x ⋅ ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) ⇔ x 2 − 1 ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) − x ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) = 0 ⇔ ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) x 2 − 1 − x = 0
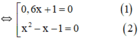
+ Giải (1): 0,6x + 1 = 0 ⇔ 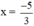
+ Giải (2):
x 2 – x – 1 = 0
Có a = 1; b = -1; c = -1
⇒ Δ = ( - 1 ) 2 – 4 . 1 . ( - 1 ) = 5 > 0
⇒ (2) có hai nghiệm 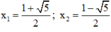
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 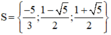
d)
x 2 + 2 x − 5 2 = x 2 − x + 5 2 ⇔ x 2 + 2 x − 5 2 − x 2 − x + 5 2 = 0 ⇔ x 2 + 2 x − 5 − x 2 − x + 5 ⋅ x 2 + 2 x − 5 + x 2 − x + 5 = 0 ⇔ ( 3 x − 10 ) 2 x 2 + x = 0
⇔ (3x-10).x.(2x+1)=0
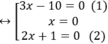
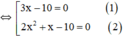
+ Giải (1): 3x – 10 = 0 ⇔ 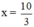
+ Giải (2):
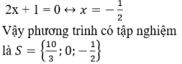
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)

























