Giải các phương trình: |-2,5x| = 5 + 1,5x

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Giải các phương trình :
a) \(\left|0,5x\right|=3-2x\)
b) \(\left|-2x\right|=3x+4\)
c) \(\left|5x\right|=x-12\)
d) \(\left|-2,5x\right|=5+1,5x\)
a: \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< =\dfrac{3}{2}\\\left(\dfrac{1}{2}x\right)^2-\left(2x-3\right)^2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< =\dfrac{3}{2}\\\left(\dfrac{1}{2}x-2x+3\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{2}x+2x-3\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< =\dfrac{3}{2}\\\left(3-\dfrac{3}{2}x\right)\left(\dfrac{5}{2}x-3\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{\dfrac{6}{5}\right\}\)
b: \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=-\dfrac{4}{3}\\\left(3x+4\right)^2-\left(2x\right)^2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=-\dfrac{4}{3}\\\left(5x+4\right)\left(x+4\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{4}{5}\)
c: \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=12\\\left(5x-x+12\right)\left(5x+x-12\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=12\\\left(4x+12\right)\left(6x-12\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
hay \(x\in\varnothing\)
d: \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=-\dfrac{10}{3}\\\left(2,5x-1,5x-5\right)\left(2,5x+1,5x+5\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=-\dfrac{10}{3}\\\left(x-5\right)\left(4x+5\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{-\dfrac{5}{4};5\right\}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình: |-3,5x| = 1,5x + 5
Giải các phương trình: -2,5x = 10
-2,5x = 10
⇔ x = 10/(-2,5)
⇔ x = -4
Vậy phương trình có một nghiệm duy nhất x = - 4
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các bất phương trình: 0 , 4 x - 2 , 5 x + 1 > 1 , 5
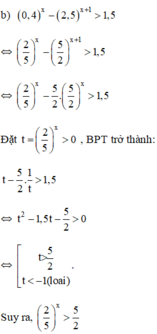
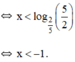
Vậy bất phương trình có tập nghiệm (-∞; -1)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các bất phương trình sau
a) 0.5x(3x-4)+1,5x(0.8-x) > hoặc = 0,32
b) 5x(12x+7)-3x(20x-5)< hoặc = -100
a: =>1,5x^2-2x+1,2x-1,5x^2>=0,32
=>-0,8x>=0,32
=>x<=4
b: =>60x^2+35x-60x^2+15x<=-100
=>50x<=-100
=>x<=-2
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các bất phương trình sau
a) 0.5x(3x-4)+1,5x(0.8-x) > hoặc = 0,32
b) 5x(12x+7)-3x(20x-5)< hoặc = -100
a)\(0,5x\left(3x-4\right)+1,5x\left(0,7-x\right)\ge0,32\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1,5x^2-2+1,05-1,5x^2\ge0,32\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1,5x^2-1,5x^2-2+1,05\ge0,32\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-0,95\ge0,32\)(vô lí)
Vậy bất phương trình vô nghiệm
b)\(5x\left(12x+7\right)-3x\left(20x-5\right)\le-100\)
\(\Leftrightarrow60x^2+35x-60x^2+15x\le-100\)
\(\Leftrightarrow50x\le-100\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\le-2\)
Vậy bất phương trình có nghiệm là \(S=\left\{xIx\le-2\right\}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Vẽ đths sau a) y=1,5x b) y=2,5x c) y=-2,5x d) y=4x e) y=-4x
Vẽ đths sau a) y=1,5x b) y=2,5x c) y=-2,5x d) y=4x e) y=-4x
Giải các phương trình :
a) x(2x - 9) = 3x(x - 5)
b) 0,5x(x - 3) = (x - 3)(1,5x - 1)
c) 3x - 15 = 2x(x - 5)
a) \(x\left(2x-9\right)=3x\left(x-5\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x.\left(2x-9\right)-x.3\left(x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x.\left[\left(2x-9\right)-3\left(x-5\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x.\left(2x-9-3x+15\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x.\left(6-x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow S=\left\{0;6\right\}\)
b) \(0,5x\left(x-3\right)=\left(x-3\right)\left(1,5x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0,5x\left(x-3\right)-\left(x-3\right)\left(1,5x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right).\left[0,5x-\left(1,5x-1\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(0,5x-1,5x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(1-x\right)=0\)
\(+x-3=0\Rightarrow x=3\)
\(+1-x=0\Rightarrow x=1\)
\(\Rightarrow S=\left\{1;3\right\}\)
c) \(3x-15=2x\left(x-5\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-15\right)-2x\left(x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\left(x-5\right)-2x\left(x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3-2x\right)\left(x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow3-2x=\frac{3}{2}\Rightarrow x-5\Rightarrow x=5\)
\(\Rightarrow S=\left\{5;\frac{3}{2}\right\}\)
a)
\(x\left(2\times-9\right)=3\times\left(\times-5\right)\)
\(\text{⇔}x.\left(2\times-9\right)-x.3\left(x-5\right)=0\)
\(\text{⇔}x.[\left(2\times-9\right)-3\left(x-5\right)]=0\)
\(\text{⇔}x.\left(2x-9-3x+15\right)=0\)
\(\text{⇔}x.\left(6-x\right)=0\)
\(\text{⇔}x=0\) hoặc \(6-x=0+6-x=0\)
\(\text{⇔}x=6\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là \(S=\left\{0;6\right\}\) BIẾT MỖI CÂU A :))
a) x(2x - 9) = 3x(x - 5)
x(2x – 9) = 3x(x – 5)
⇔ x.(2x – 9) – x.3(x – 5) = 0
⇔ x.[(2x – 9) – 3(x – 5)] = 0
⇔ x.(2x – 9 – 3x + 15) = 0
⇔ x.(6 – x) = 0
⇔ x = 0 hoặc 6 – x = 0
+ 6 – x = 0 ⇔ x = 6
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là S = {0; 6}.
b) 0,5x(x - 3) = (x - 3)(1,5x - 1)
0,5x(x – 3) = (x – 3)(1,5x – 1)
⇔ 0,5x(x – 3) – (x – 3)(1,5x – 1) = 0
⇔ (x – 3).[0,5x – (1,5x – 1)] = 0
⇔ (x – 3)(0,5x – 1,5x + 1) = 0
⇔ (x – 3)(1 – x) = 0
⇔ x – 3 = 0 hoặc 1 – x = 0
+ x – 3 = 0 ⇔ x = 3.
+ 1 – x = 0 ⇔ x = 1.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = {1; 3}.
c) 3x - 15 = 2x(x - 5)
3x – 15 = 2x(x – 5)
⇔ (3x – 15) – 2x(x – 5) = 0
⇔3(x – 5) – 2x(x – 5) = 0
⇔ (3 – 2x)(x – 5) = 0
⇔ 3 – 2x = 0 hoặc x – 5 = 0
+ 3 – 2x = 0 ⇔ 2x = 3 ⇔ x = 3/2.
+ x – 5 = 0 ⇔ x = 5.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S={5;3/2}
CHO TÔI XIN TCK
Xem thêm câu trả lời













