(d1): y = -2x - 2
(d2): y = 2x + 4
a) Vẽ d1 và d2
b) Tìm tọa độ giao điểm (d1) và (d2)
Vẽ và tìm tọa độ giao điểm : a) (d2):y=x+1 và (d1):y=2x+5 c) (d1): y=2x-1 và (d2):y=-2x+3 b) (d1):y=5-3x và (d2):y=3-x d) (d1):y=x+2 và (d2):y=3x-4
a, PTHDGD: \(x+1=2x+5\Leftrightarrow x=-4\Leftrightarrow y=-3\Leftrightarrow A\left(-4;-3\right)\)
Vậy \(A\left(-4;-3\right)\) là giao 2 đths
b, PTHDGD: \(5-3x=3-x\Leftrightarrow x=1\Leftrightarrow y=2\Leftrightarrow B\left(1;2\right)\)
Vậy \(B\left(1;2\right)\) là giao 2 đths
c, PTHDGD: \(2x-1=-2x+3\Leftrightarrow x=1\Leftrightarrow y=1\Leftrightarrow C\left(1;1\right)\)
Vậy \(C\left(1;1\right)\) là giao 2 đths
d, PTHDGD: \(x+2=3x-4\Leftrightarrow x=3\Leftrightarrow y=5\Leftrightarrow D\left(3;5\right)\)
Vậy \(D\left(3;5\right)\) là giao 2 đths
(d1) : y = 2x - 1
(d2) : y = x + 2
a) Vẽ (d1) và (d2).
b) Tìm tọa độ giao điểm của (d1) và (d2).
c) Tìm m để (d3) : y = 2x - m đồng quy với (d1) và (d2).
Cho 2 đường thẳng d1:y=2x-3,d2:y=3-x
a,vẽ d1 và d2 trên cùng 1 hệ trục tọa độ
b,tìm tọa độ giao điểm của d1 và d2
a: 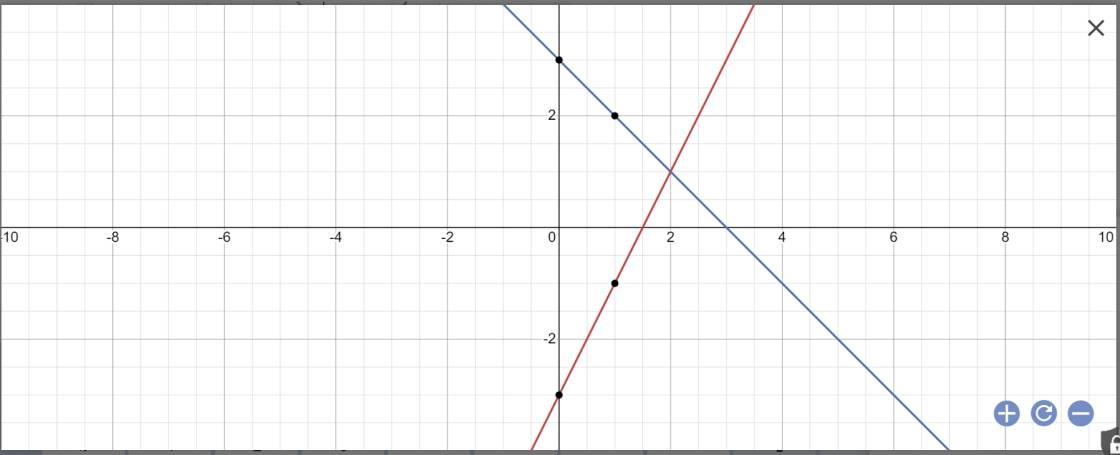
b: Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
2x-3=3-x
=>3x=6
=>x=6/3=2
Thay x=2 vào y=3-x, ta được:
\(y=3-2=1\)
cho hàm số:y=2x(d1) và y=x+3(d2).a) vẽ (d1)và(d2) trên cùng hệ trục tọa độ.
b) tìm tọa độ giao điểm A của (d1) và (d2)
Câu 4: a, Vẽ y = 2/3x + 2 (d1) y = 2x+2 trên cùng mặt phẳng tọa độ b, Gọi A,B là giao điểm d1 và d2 với trục Ox và giao d1 với d2 là C : Tìm toạ độ giao điểm A,B,C
a:
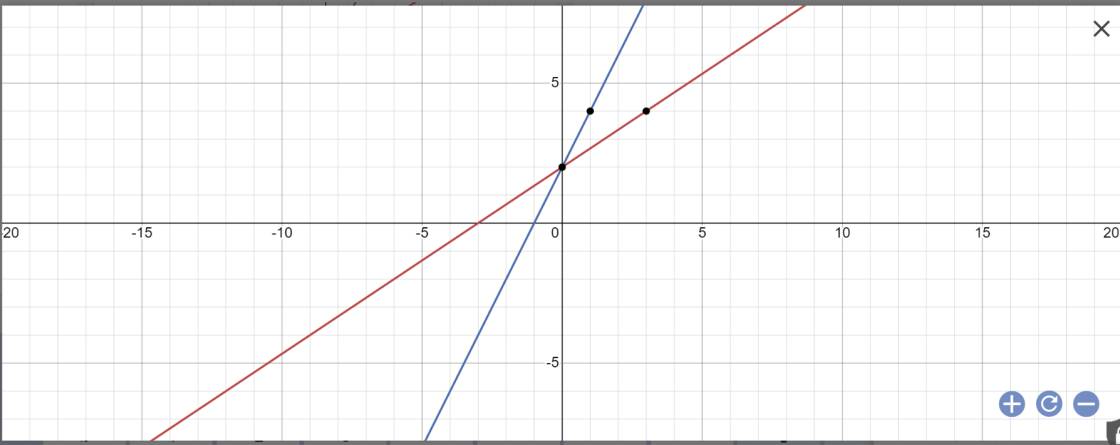
b: Tọa độ A là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\\dfrac{2}{3}x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\\dfrac{2}{3}x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\x=-2:\dfrac{2}{3}=-2\cdot\dfrac{3}{2}=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tọa độ B là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\2x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\2x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tọa độ C là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2}{3}x+2=2x+2\\y=2x+2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-\dfrac{4}{3}x=0\\y=2x+2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=2\cdot0+2=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: A(-3;0); B(-1;0); C(0;2)
Bài 1: Cho (d1): y = 3x + 2 (d2): y = x – 2 a) Tìm tọa độ giao điểm của (d1) và (d2) với trục hoành b) Tìm tọa độ giao điểm của (d1) và (d2) với trục tung c) Vẽ (d1) và (d2) trên cùng một hệ trục tọa độ Oxy d) Tìm tọa độ giao điểm của (d1) và (d2)
\(b,\) PT hoành độ giao điểm: \(3x+2=x-2\Leftrightarrow x=-2\Leftrightarrow y=-4\Leftrightarrow A\left(-2;-4\right)\)
Vậy \(A\left(-2;-4\right)\) là tọa độ giao điểm
Cho (d1): y=2x và (d2):y= -1/2x + 5 1/ vẽ d1 và d2 trên cùng mặt phẳng tọa độ 2/ xác định tọa độ giao điểm A của d1 và d2 3/ gọi giao điểm của d2 với Ox là B. Tính các góc của tam giác AOB 4/ tính chu vi và diện tích của tam giác AOB
1) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(d_1\right):y=2x\\\left(d_2\right):y=-\dfrac{1}{2}x+5\end{matrix}\right.\)
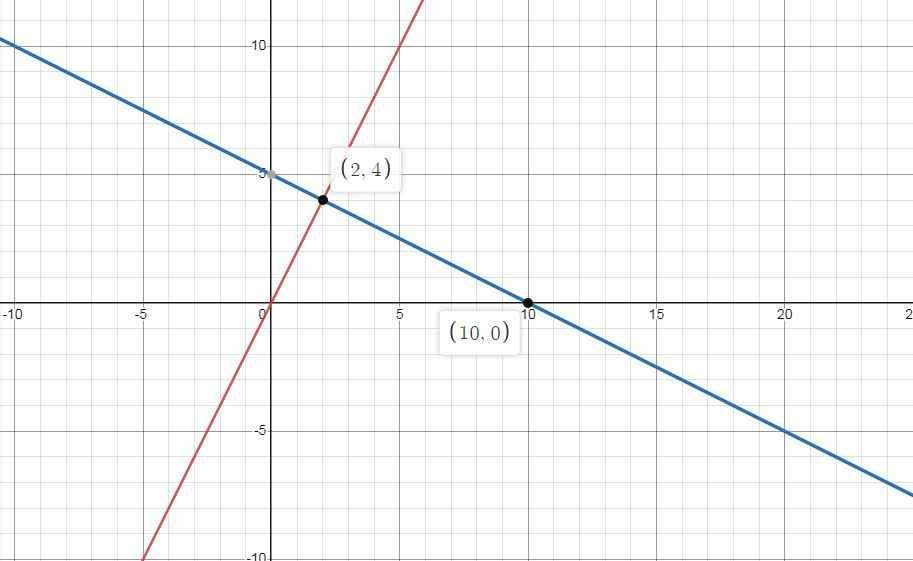
2) Theo đồ thi ta có :
\(\left(d_1\right)\cap\left(d_2\right)=A\left(2;4\right)\)
3) \(\left(d_2\right)\cap Ox=B\left(a;0\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{1}{2}a+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}a=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a=10\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(d_2\right)\cap Ox=B\left(10;0\right)\)
4) \(OA=\sqrt[]{\left(2-0\right)^2+\left(4-0\right)^2}=\sqrt[]{20}=2\sqrt[]{5}\)
\(OB=\sqrt[]{\left(10-0\right)^2+\left(0-0\right)^2}=\sqrt[]{10^2}=10\)
\(AB=\sqrt[]{\left(10-2\right)^2+\left(0-4\right)^2}=\sqrt[]{80}=4\sqrt[]{5}\)
Ta thấy :
\(OA^2+AB^2=20+80=OB^2=100\)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta OAB\) vuông tại A
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{OAB}=90^o\)
\(sin\widehat{AOB}=\dfrac{AB}{OB}=\dfrac{4\sqrt[]{5}}{10}=\dfrac{2\sqrt[]{5}}{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{AOB}\sim63,43^o\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{OBA}=90^o-63,43^o=26,57^o\)
5) Chu vi \(\Delta OAB\) :
\(AB+OA+OB=4\sqrt[]{5}+2\sqrt[]{5}+10=10\sqrt[]{5}+10=10\left(\sqrt[]{5}+1\right)\left(đvmd\right)\)
Diện tích \(\Delta OAB\) :
\(\dfrac{1}{2}AB.OA=\dfrac{1}{2}.4\sqrt[]{5}.2\sqrt[]{5}=20\left(đvdt\right)\)
Cho hai đường thẳng d1: y=2x-3 và d2: y=-3x+7
a, vẽ d1, d2 trên cùng 1 hệ trục tọa độ
b, tìm tọa độ giao điểm của d1 và d2
a, bạn tự vẽ nhé
b, Hoành độ giao điểm thỏa mãn phương trình
\(2x-3=-3x+7\Leftrightarrow5x=10\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
Thay vào ptđt d1 ta được : \(y=4-3=1\)
Vậy d1 cắt d2 tại A(2;1)
Hàm số y = 3/2 x - 2 có đồ thị (D1) và hàm số y = -2x + 5 có đồ thị (D2)
a) Vẽ (D1) và (D2) trên cùng một hệ mặt phẳng tọa độ.
b) Tìm tọa độ giao điểm của (D1) và (D2) bằng phép tính toán.
b, PT hoành độ giao điểm là \(\dfrac{3}{2}x-2=-2x+5\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{7}{2}x=7\Leftrightarrow x=2\Leftrightarrow y=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A\left(2;1\right)\)
Vậy A(2;1) là tọa độ giao điểm 2 đths
a,vẽ y=1/2x-2(d1)
y=2x+2(d2)
b,tìm tọa độ giao điểm A của (d1),(d2)
c,gọi B và C lần lượt là giao điểm của (d1) và (d2) với trục Oy.tính chu vi và diện tích tam giác ABC