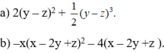cho x-1/3=x-2/4=x-3/5 tính N=2x+y-2z

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử
1/. y(x-2z)2+8xyz+x(y-2z)2-2z(x+y)2
2/. 8x3(y+z)-y3(z+2x)-z3(2x-y)
3/. (x2+x)2-2(x2+x)-15
4/. (4x+1).(12x-1).(3x+2).(x+1)-4
5/. x2(y-z)+y2(z-x)+z2(x-y)
6/. x4-2x3+2x-1
Bài 2 : Phân tích các đa thức thành nhân tử
a, x^4 - 2x^3 + 2x - 1
b, a^6 - a^4 + 2a^3 + 2a^2
c, x^4 + x^3 + 2x^2 + x + 1
d, x^4 + 2x^3 + 2x^2 + 2x + 1
e, x^2y + xy^2 + x^2z + y^2z + 2xyz
f, x^5 + x^4 + x^3 + x^2 + x + 1
Giúp mk vs ạ mk đang cần gấp
Bài 2 : Phân tích các đa thức thành nhân tử :
a, x^4 - 2x^3 + 2x - 1
b, a^6 - a^4 + 2a^3 + 2a^2
c, x^4 + x^3 + 2x^2 + x + 1
d, x^4 + 2x^3 + 2x^2 + 2x + 1
e, x^2y + xy^2 + x^2z + y^2z + 2xyz
f, x^5 + x^4 + x^3 + x^2 + x + 1
Giúp mk vs ạ mk cần gấp ạ
a)
$x^4-2x^3+2x-1=(x^4-2x^3+x^2)-(x^2-2x+1)$
$=(x^2-x)^2-(x-1)^2$
$=x^2(x-1)^2-(x-1)^2=(x-1)^2(x^2-1)=(x-1)^2(x-1)(x+1)$
$=(x-1)^3(x+1)$
b)
$a^6-a^4+2a^3+2a^2$
$=a^4(a^2-1)+2a^2(a+1)$
$=a^4(a-1)(a+1)+2a^2(a+1)$
$=(a+1)[a^4(a-1)+2a^2]$
$=a^2(a+1)[a^2(a-1)+2]$
$=a^2(a+1)(a^3-a^2+2)=a^2(a+1)[a^2(a+1)-2(a^2-1)]$
$=a^2(a+1)[a^2(a+1)-2(a-1)(a+1)]$
$=a^2(a+1)(a+1)(a^2-2a+2)=a^2(a+1)^2(a^2-2a+2)$
c)
$x^4+x^3+2x^2+x+1$
$=(x^4+2x^2+1)+(x^3+x)$
$=(x^2+1)^2+x(x^2+1)=(x^2+1)(x^2+1+x)$
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
d)
$x^4+2x^3+2x^2+2x+1$
$=(x^4+2x^3+x^2)+(x^2+2x+1)$
$=(x^2+x)^2+(x+1)^2=x^2(x+1)^2+(x+1)^2$
$=(x+1)^2(x^2+1)$
e)
$x^2y+xy^2+x^2z+y^2z+2xyz$
$=xy(x+y)+z(x^2+y^2)+2xyz$
$=xy(x+y)+z(x^2+y^2+2xy)$
$=xy(x+y)+z(x+y)^2=(x+y)(xy+zx+zy)$
f)
$x^5+x^4+x^3+x^2+x+1$
$=(x^5+x^4)+(x^3+x^2)+(x+1)=x^4(x+1)+x^2(x+1)+(x+1)$
$=(x+1)(x^4+x^2+1)$
$=(x+1)[(x^4+2x^2+1)-x^2]$
$=(x+1)[(x^2+1)^2-x^2]=(x+1)(x^2+1-x)(x^2+1+x)$
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
BT10: Thực hiện phép tính
\(a,\dfrac{4}{5}y^2x^5-x^3.x^2y^2\)
\(b,-xy^3-\dfrac{2}{7}y^2.xy\)
\(c,\dfrac{5}{6}xy^2z-\dfrac{1}{4}xyz.y\)
\(d,15x^4+7x^4-20x^2.x^2\)
\(e,\dfrac{1}{2}x^5y-\dfrac{3}{4}x^5y+xy.x^4\)
\(f,13x^2y^5-2x^2y^5+x^6\)
a: =-1/5x^5y^2
b: =-9/7xy^3
c: =7/12xy^2z
d: =2x^4
e: =3/4x^5y
f: =11x^2y^5+x^6
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1:
a)So sánh \(\left(\dfrac{3}{4}\right)^{2021}+1với\dfrac{3}{4}+1\)
b)Cho x,y,z khác 0 thỏa mãn
\(\dfrac{2x-3}{5}=\dfrac{5y-2z}{3}=\dfrac{3z-5x}{2}\)
Tính GTBT: B=\(\dfrac{12x-5y-3z}{x-3y+2z}\)
help me ai nhanh nhất mik tích cho
Đúng 0
Bình luận (1)
a) Ta có: \(\left(\dfrac{3}{4}\right)^{2021}>\left(\dfrac{3}{4}\right)^1=\dfrac{3}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\dfrac{3}{4}\right)^{2021}+1>\dfrac{3}{4}+1\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (1)
Cmr.
a)1/2^2+1/3^2+...+1/ n^2 <1
Tìm x,y :
x/3=y/4=z/5 và 2x+y=2z
Tìm x,y
Ta có: \(\frac{x}{3}=\frac{y}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow y=\frac{4x}{3}\) ( 1 )
Ta có: \(\frac{x}{3}=\frac{z}{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow z=\frac{5x}{3}\) ( 2 )
Theo đề bài: 2x + y = 2z ( 3 )
Thay ( 1 ), ( 2 ) vào ( 3 ) ta được một phương trình mới:
\(2x+\frac{4x}{3}=2.\left(\frac{5x}{3}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{6x+4x}{3}=\frac{10x}{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x+4x=10x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow10x=10x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=x\) ( Vô số nghiệm )
\(\Rightarrow x\in R\) ( R là số thực, có nghĩa là tất cả các số trong vũ trụ này nha )
Ta có: \(x\in R\)
\(\Rightarrow y\in R\)
Vậy \(x,y\in R\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
cho x,y,z là 3 cạnh của 1 tam giác , CMR :
2x^2y^2+2^2z^2+2z^2x^2-x^4-y^4-z^4>0
1.Tìm x,y,z biết:
|2x-3y|+|2y-4z|=0 và x+y+z=7
2. a) |x-2|+|x-3|+|x-4|=0
b) |x+1|+|x+2|+|x+3|+|x+4|+|x+5|+|x+6|+|x+7|+|x+8|+|x+9|= x-1
3. Tìm x,y,z biết:
|2x-3y|+|5y-2z|+|2z-6|=0
a)\(\left|2x-3y\right|+\left|2y-4z\right|=0\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left|2x-3y\right|\ge0\forall x;y\\\left|2y-4z\right|\ge0\forall y;z\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left|2x-3y\right|+\left|2y-4z\right|\ge0\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left|2x-3y\right|=0\\\left|2y-4z\right|=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x=3y\\2y=4z\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{x}{3}=\dfrac{y}{2}\\\dfrac{y}{4}=\dfrac{z}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{x}{6}=\dfrac{y}{4}\\\dfrac{y}{4}=\dfrac{z}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{x}{6}=\dfrac{y}{4}=\dfrac{z}{2}\)
Áp dụng tính chất dãy tỉ số bằng nhau ta có:
\(\dfrac{x}{6}=\dfrac{y}{4}=\dfrac{z}{2}=\dfrac{x+y+z}{6+4+2}=\dfrac{7}{12}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{7}{12}.6=\dfrac{7}{2}\\y=\dfrac{7}{12}.4=\dfrac{7}{3}\\z=\dfrac{7}{12}.2=\dfrac{7}{6}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b)\(\left|x-2\right|+\left|x-3\right|+\left|x-4\right|=0\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left|x-2\right|\ge0\\\left|x-3\right|\ge0\\\left|x-4\right|\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left|x-2\right|+\left|x-3\right|+\left|x-4\right|\ge0\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left|x-2\right|=0\\\left|x-3\right|=0\\\left|x-4\right|=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=3\\x=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vì \(2\ne3\ne4\) nên \(x\in\varnothing\)
c)
\(\left|x+1\right|+\left|x+2\right|+...+\left|x+8\right|+\left|x+9\right|\)
Với mọi \(x\ge0\) ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left|x+1\right|=x+1\\\left|x+2\right|=x+2\\\left|x+8\right|=x+8\\\left|x+9\right|=x+9\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow x+1+x+2+...+x+8+x+9=x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x+90=x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x=x-89\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-8x=89\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{89}{-8}\left(KTM\right)\)
Với mọi \(x< 0\) ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+1=-x-1\\x+2=-x-2\\x+8=-x-8\\x+9=-x-9\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left(-x-1\right)+\left(-x-2\right)+...+\left(-x-8\right)+\left(-x-9\right)=x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-9x-90=x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-9x=x+89\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-10x=89\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{89}{-10}\left(TM\right)\)
d)\(\left|2x-3y\right|+\left|5y-2z\right|+\left|2z-6\right|=0\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left|2x-3y\right|\ge0\\ \left|5y-2z\right|\ge0\\ \left|2z-6\right|\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left|2x-3y\right|+\left|5y-2z\right|+\left|2z-6\right|\ge0\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left|2x-3y\right|=0\\\left|5y-2z\right|=0\\\left|2z-6\right|=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}z=3\\y=\dfrac{6}{5}\\x=\dfrac{9}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Làm tính chia:a)
[
12
(
y
-
z
)
4
-
3
(
z
-
y
)
5
]
:
6
(...
Đọc tiếp
Làm tính chia:
a) [ 12 ( y - z ) 4 - 3 ( z - y ) 5 ] : 6 ( y - z ) 2 ;
b) [ 2 ( x - 2 y + z ) 3 + 4 ( 2 y - x - z ) 2 ] : (2z - 4y + 2x).