2xX+3=9x2/3

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Phương trình
2
x
x
-
2
-
5
x
-
3
-
9
x
2
-
5
x
+
6
có số nghiệm là: A. 2 B. 1 C. 0 D. 3
Đọc tiếp
Phương trình 2 x x - 2 - 5 x - 3 = - 9 x 2 - 5 x + 6 có số nghiệm là:
A. 2
B. 1
C. 0
D. 3
Đáp án C

Suy ra phương trình đã cho vô nghiệm.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Phương trình
2
x
x
-
2
-
5
x
-
3
-
9
x
2
-
5
x
+
6
có số nghiệm là: A....
Đọc tiếp
Phương trình 2 x x - 2 - 5 x - 3 = - 9 x 2 - 5 x + 6 có số nghiệm là:
A. 2
B. 1
C. 0
D. 3
Phương trình
2
x
x
-
2
-
5
x
-
3
-
9
x
2
-
5
x
+
6
có số nghiệm là: A. 2 B. 1 C. 0 D. 3
Đọc tiếp
Phương trình 2 x x - 2 - 5 x - 3 = - 9 x 2 - 5 x + 6 có số nghiệm là:
A. 2
B. 1
C. 0
D. 3
Đáp án C

Suy ra phương trình đã cho vô nghiệm.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a)1/2xX+3/2=7
b)3/2xX-2/7x(X-7/2)=18
`1/2 xx x +3/2 =7`
`=> 1/2 xx x = 7-3/2`
`=> 1/2 xx x = 14/2 -3/2`
`=> 1/2 xx x = 11/2`
`=> x= 11/2 :1/2`
`=> x=11/2 xx2`
`=> x= 22/2`
`=>x=11`
Vậy `x=11`
__
`3/2 xx x -2/7 xx(x-7/2)=18`
`=> 3/2 xx x -2/7x + 1=18`
`=> (3/2 -2/7 )x+ 1 =18`
`=> 17/14 x=18-1`
`=> 17/14x=17`
`=>x=17:17/14`
`=> x=17 xx 14/17`
`=>x=14`
Đúng 4
Bình luận (0)
a) \(\dfrac{1}{2}\times x+\dfrac{3}{2}=7\)
\(\dfrac{1}{2}\times x=7-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{2}\times x=\dfrac{11}{2}\)
\(x=\dfrac{11}{2}\div\dfrac{1}{2}\\ x=\dfrac{11}{2}\times2\\ x=\dfrac{22}{2}=11\)
b) \(\dfrac{3}{2}\times x-\dfrac{2}{7}\times\left(x-\dfrac{7}{2}\right)=18\)
\(\dfrac{3}{2}\times x-\left(\dfrac{2}{7}x-1\right)=18\)
\(\dfrac{3}{2}\times x-\dfrac{2}{7}x+1=18\)
\(\dfrac{3}{2}x-\dfrac{2}{7}x+1=18\)
\(\dfrac{17}{14}x+1=18\)
\(\dfrac{17}{14}x=18-1\)
\(\dfrac{17}{14}x=17\)
\(x=17\div\dfrac{17}{14}\)
\(x=17\times\dfrac{14}{17}\)
\(x=14\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a) \(\dfrac{1}{2}\times x+\dfrac{3}{2}=7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}\times x=7-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}\times x=\dfrac{11}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{11}{2}:\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{11}{2}\times\dfrac{2}{1}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=11\)
b) \(\dfrac{3}{2}\times x-\dfrac{2}{7}\times\left(x-\dfrac{7}{2}\right)=18\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3}{2}\times x-\dfrac{7}{2}\times x+1=18\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\dfrac{3}{2}-\dfrac{7}{2}\right)\times x+1=18\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{17}{14}\times x=18-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{17}{14}\times x=17\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=17:\dfrac{17}{14}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=17\times\dfrac{14}{17}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=14\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
tìm x biết 2xX+108 chia hết cho 2xX+3
(2xX-15)5=(2xX-15)3
(2x-15)5=(2x-15)3
=> 2x-15=0 hoặc 2x-15=1 (vì 05=03)
=> 2x=0+15 hoặc 2x=1+15
=> 2x=15 hoặc 2x=16
=> x=15:2 hoặc x=16:2
=> x=7,5 hoặc x=8
Vậy x = 7,5 hoặc x = 8
Giải các hệ phương trình sau:
a
)
x
5
−
(
1
+
3
)
y
1...
Đọc tiếp
Giải các hệ phương trình sau:
a ) x 5 − ( 1 + 3 ) y = 1 ( 1 − 3 ) x + y 5 = 1 b ) 2 x x + 1 + y y + 1 = 2 x x + 1 + 3 y y + 1 = − 1
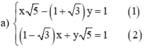
Từ (1) rút ra được: 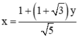 (*)
(*)
Thay (*) vào phương trình (2) ta được:
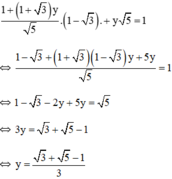
Thay 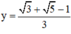 vào (*) ta được:
vào (*) ta được:
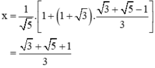
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm 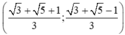
b) Điều kiện xác định: x ≠ -1; y ≠ -1.
Đặt 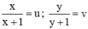 , hệ phương trình trở thành:
, hệ phương trình trở thành:
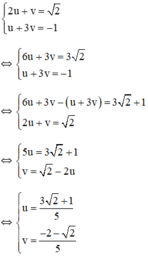
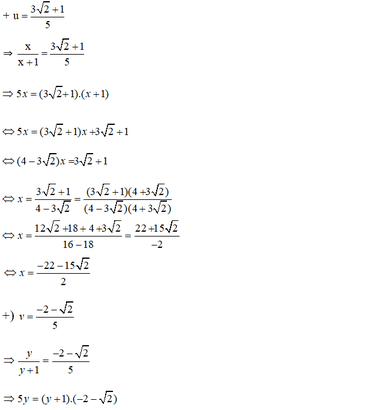
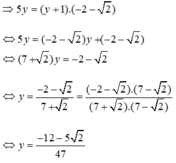
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm 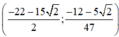 a
a
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(\dfrac{1+3+6+10+...+45+55}{1x10+9x2+3x8+...9x2+10x1}\)
5/4:X-3/2=3/2+1/2xX
\(\dfrac{5}{4x}-\dfrac{3}{2}=\dfrac{3}{2}+\dfrac{x}{2}\\ \Leftrightarrow5-6x=6x+2x^2\\ \Leftrightarrow2x^2+12x-5=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{-6+\sqrt{46}}{2}\\x=\dfrac{-6-\sqrt{46}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)


















