Tính giá trị biểu thức
1/8x³ - 3/2x²+ 6x- 8x tại x=24
Tính giá trị biểu thức
A=(3x2-bx+1/3)/(2x-1/3) tại giá trị tuyệt đối x=1/3
C=8x2-2|x|+3/2 ttại |x-1|=1/2
Tính giá trị của biểu thức sau: A=4x-5y/8x-7y. a) Tại x=-2, y=3; b) Biết x/y=5/4
a, Thay x = -2 ; y = 3 ta được
\(A=\dfrac{4\left(-2\right)-5.3}{8\left(-2\right)-7.3}=\dfrac{-8-15}{-16-21}=\dfrac{23}{37}\)
b, Ta có \(\dfrac{x}{y}=\dfrac{5}{4}\Rightarrow\dfrac{x}{5}=\dfrac{y}{4}=k\Rightarrow x=5k;y=4k\)
Thay vào ta được \(A=\dfrac{4.5k-5.4k}{8.5k-7.4k}=\dfrac{0}{40k-28k}=0\)
Với mọi giá trị của x thì giá trị của biểu thức 2x(3x−1)−6x(x+1)+(3+8x) là: *
AMột đáp số khác
B2
C3
D4
cho x-y=9
tính giá trị biểu thức B= 7x-9/6x+y +7x+9/8x-y ta đượ B=.........
từ x-y=9=>x=y+9
thay x=y+9 vào B ta được:
\(\frac{7x-9}{6x+y}=\frac{7\left(y+9\right)-9}{6\left(y+9\right)+y}=\frac{7y+63-9}{6y+54+y}=\frac{7y+54}{\left(6y+y\right)+54}=\frac{7y+54}{7y+54}=1\) (1)
\(\frac{7x+9}{8x-y}=\frac{7\left(y+9\right)+9}{8\left(y+9\right)-y}=\frac{7y+63+9}{8y+72-y}=\frac{7y+72}{\left(8y-y\right)+72}=\frac{7y+72}{7y+72}=1\) (2)
từ (1);(2)
=>B=1-1=0
Vậy B=0
tính giá trị biểu thức A=x^15-8x^14+8x^13-8x^12+...-8x^2+8x-5 với x=7
Ta có x =7
=>x+1=8
\(\Rightarrow\)\(A=x^{15}-8x^{14}+8x^{13}-8x^{12}+.......8x^2+8x-5\)
\(\Rightarrow x^{15}-\left(x+1\right)x^{14}+\left(x+1\right)x^{13}-\left(x+1\right)x^{12}+...\left(x+1\right)x^2\)
\(+\left(x+1\right)x^5\)
\(\Rightarrow x^{15}-x^{15}-x^{14}+x^{14}+x^{13}-x^{13}-x^{12}+...-x^3-x^2+x-5\)
\(\Rightarrow x-5\Leftrightarrow A=7-5=2\Rightarrow A=2\)
Vậy A=2 khi x=7
Vì x=7 nên 8 = x + 1
Thay 8 = x + 1 vào biểu thức A ta có
\(A=x^{15}-x^{14}\left(x+1\right)+x^{13}\left(x+1\right)-x^{12}\left(x+1\right)+....-x^2\left(x+1\right)+x\left(x+1\right)-5\)
\(=x^{15}-x^{15}-x^{14}+x^{14}+x^{13}-x^{13}-x^{12}+....-x^3-x^2+x^2+x-5\)
\(=x-5\)
Mà x = 7
Nên \(A=7-5\)
\(=2\)
Vậy A = 2 tại x=7
rút gọn rồi tính giá trị biểu thức tại x=1; y=2
A= \(\dfrac{6x^3-4x^2y+2x^2}{x\left(3x+y\right)\left(3x-y\right)}\)
\(A=\dfrac{2x^2\left(3x-4y+2\right)}{x\left(3x+y\right)\left(3x-y\right)}=\dfrac{2x\left(3x-4y+2\right)}{\left(3x+y\right)\left(3x-y\right)}\\ A=\dfrac{2\left(3-8+2\right)}{\left(3+2\right)\left(3-2\right)}=\dfrac{2\left(-3\right)}{5}=\dfrac{-6}{5}\)
Cho biểu thức : A=\(\left(\dfrac{3-x}{x+3}.\dfrac{x^2+6x+9}{x^2-9}+\dfrac{x}{x+3}\right):\dfrac{3x^2}{x+3}\)
a, Rút gọn biểu thức A
b, Tính giá trị biểu thức A tại x, biết \(x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
c, Tính giá trị của x để A<0
a, ĐKXĐ: x≠±3
A=\(\left(\dfrac{3-x}{x+3}.\dfrac{x^2+6x+9}{x^2-9}+\dfrac{x}{x+3}\right):\dfrac{3x^2}{x+3}\)
A=\(\left(\dfrac{3-x}{x+3}.\dfrac{\left(x+3\right)^2}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}+\dfrac{x}{x+3}\right):\dfrac{3x^2}{x+3}\)
A=\(\left(\dfrac{3-x}{x-3}+\dfrac{x}{x+3}\right):\dfrac{3x^2}{x+3}\)
A=\(\left(\dfrac{9-x^2}{x^2-9}+\dfrac{x^2-3x}{x^2-9}\right):\dfrac{3x^2}{x+3}\)
A=\(\left(\dfrac{-3}{x+3}\right):\dfrac{3x^2}{x+3}\)
A=\(\dfrac{-1}{x^2}\)
b, Thay x=\(-\dfrac{1}{2}\) (TMĐKXĐ) vào A ta có:
\(\dfrac{-1}{\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2}\)=-4
c, A<0 ⇔ \(\dfrac{-1}{x^2}< 0\) ⇔ x2>0 (Đúng với mọi x)
Vậy để A<0 thì x đúng với mọi giá trị (trừ ±3)
Cho z = x + y i với x, y ∈ R là số phức thỏa mãn điều kiện z ¯ + 2 - 3 i ≤ | z + i - 2 | ≤ 5 . Gọi M, m lần lượt là giá trị lớn nhất và giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức P = x 2 + y 2 + 8 x + 6 x . Tính M+m.
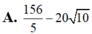
![]()
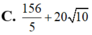
![]()
BT1: Tính giá trị của biểu thức sau
a, A=5x(4x2-2x+1)-2x.(10x2-5x-2) Tại x=15
b, B= 6xy (xy-y2)-8x2(x-y2)+5y2(x2-xy) Tại x=-1;y=2
c, C= (x-3).(x+7)-(2x-5).(x-1) Tại x=-1
d, D=(3x+5).(2x-1)+(4x-1).(3x+2)-(x-2).(2x+5) Tại x=-2