Tìm x: \(-x^2+16x+6=0\)

Những câu hỏi liên quan
4x ^ 3 - 16x ^ 2 + 19x - 6 = 0 tìm x
\(4x^3-16x^2+19x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^3-8x^2-8x^2+16x+3x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(4x^2-8x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(2x-3\right)\left(2x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{3}{2}\\x=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Tìm x:
4x^2 + 16x + 3= 0
7x^2 + 16x + 2= 1 + 3x^2
4x^2 + 20x + 4 = 0
Xem chi tiết
7x^2 + 16x + 2= 1 + 3x^2
4x^2 + 20x + 4 = 0
a) \(4x^2+16x+3=0\)
\(\Delta'=84-12=72\Rightarrow\sqrt[]{\Delta'}=6\sqrt[]{2}\)
Phương trình có 2 nghiệm
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{-8+6\sqrt[]{2}}{4}\\x=\dfrac{-8-6\sqrt[]{2}}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{-2\left(4-3\sqrt[]{2}\right)}{4}\\x=\dfrac{-2\left(4+3\sqrt[]{2}\right)}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{-\left(4-3\sqrt[]{2}\right)}{2}\\x=\dfrac{-\left(4+3\sqrt[]{2}\right)}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3\sqrt[]{2}-4}{2}\\x=\dfrac{-3\sqrt[]{2}-4}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) \(7x^2+16x+2=1+3x^2\)
\(4x^2+16x+1=0\)
\(\Delta'=84-4=80\Rightarrow\sqrt[]{\Delta'}=4\sqrt[]{5}\)
Phương trình có 2 nghiệm
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{-8+4\sqrt[]{5}}{4}\\x=\dfrac{-8-4\sqrt[]{5}}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{-4\left(2-\sqrt[]{5}\right)}{4}\\x=\dfrac{-4\left(2+\sqrt[]{5}\right)}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\left(2-\sqrt[]{5}\right)\\x=-\left(2+\sqrt[]{5}\right)\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2+\sqrt[]{5}\\x=-2-\sqrt[]{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) \(4x^2+20x+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(x^2+5x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+5x+1=0\)
\(\Delta=25-4=21\Rightarrow\sqrt[]{\Delta}=\sqrt[]{21}\)
Phương trình có 2 nghiệm
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{-5+\sqrt[]{21}}{2}\\x=\dfrac{-5-\sqrt[]{21}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
TÌM X
a)4x^4-16x^2=0
b)3x^3-1/9=0
c)x^2(x-3)=25x-75
d)x^2= -5x-6
e)x^4-5x^2+4=o
Tìm x biết:
a, 16x² – 9(x + 1)²= 0
b, x2 (x – 1) – 4x2 + 8x – 4 = 0
c, x(2x – 3) – 2(3 – 2x) = 0
d, (x – 3)(x² + 3x + 9) – x(x + 2)(x – 2) = 1
e, 4x² + 4x – 6 = 2
f, 2x² + 7x + 3 = 0
e: ta có: \(4x^2+4x-6=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2+4x-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
f: Ta có: \(2x^2+7x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Tìm x:a) 3xleft(3x-8right)-9x^2+80b)6x-15-xleft(5-2xright)0c) x^3-16x0d) 2x^2+3x-50e) 3x^2-xleft(3x-6right)36f) left(x+2right)^2-left(x-5right)left(x+1right)17g) left(x-4right)^2-xleft(x+6right)9h) 4xleft(x-1000right)-x+10000i) x^2-360j) x^2y-2+x+x^2-2y+xy0k) xleft(x+1right)-left(x-1right).left(2x-3right)0l) 3x^3-27x0
Đọc tiếp
Tìm x:
a) \(3x\left(3x-8\right)-9x^2+8=0\)
b)\(6x-15-x\left(5-2x\right)=0\)
c) \(x^3-16x=0\)
d) \(2x^2+3x-5=0\)
e) \(3x^2-x\left(3x-6\right)=36\)
f) \(\left(x+2\right)^2-\left(x-5\right)\left(x+1\right)=17\)
g) \(\left(x-4\right)^2-x\left(x+6\right)=9\)
h) \(4x\left(x-1000\right)-x+1000=0\)
i) \(x^2-36=0\)
j) \(x^2y-2+x+x^2-2y+xy=0\)
k) \(x\left(x+1\right)-\left(x-1\right).\left(2x-3\right)=0\)
l) \(3x^3-27x=0\)
Tìm x:
a) x4-2x2+1=0
b) x4-2x2-8=0
c) x4-4x2-60=0
d) x6-16x2+64=0
a) x^4 - 2x^2 + 1 = 0
=> ( x^2 - 1 )^2 = 0
=> x^2 - 1 = 0
=> x^2 = 1
=> x = 1 hoặc x = -1
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a) x4-2x2+1=0
(thang Tran giải rồi nhé)
b) x4-2x2-8=0
<=> x^4 - 2x^2 +1 -9 =0
<=> (x^2 -1)^2 -9 =0
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x^2-1=-3\\x^2-1=3\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x^2=-2\left(VN\right)\\x=+_-\sqrt{2}\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy x=+- căn 2
c) x4-4x2-60=0
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4-4x^2+4-64=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-2\right)-64=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+62\right)\left(x^2-66\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x^2+62=0\\x^2-66=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x^2=-62\left(VN\right)\\x^2=+_-\sqrt{66}\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy x=+- căn 66
d) x6-16x2+64=0
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm x, biết:
a
)
16
x
8
b
)
4
x
5
c
)
9
x
-
1
21
d
)
4
1
-
x...
Đọc tiếp
Tìm x, biết:
a ) 16 x = 8 b ) 4 x = 5 c ) 9 x - 1 = 21 d ) 4 1 - x 2 - 6 = 0
a) √16x = 8 (điều kiện: x ≥ 0)
⇔ 16x = 82 ⇔ 16x = 64 ⇔ x = 4
(Hoặc: √16x = 8 ⇔ √16.√x = 8
⇔ 4√x = 8 ⇔ √x = 2 ⇔ x = 4)
b) điều kiện: x ≥ 0
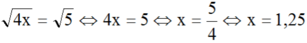
c) điều kiện: x - 1 ≥ 0 ⇔ x ≥ 1 (*)
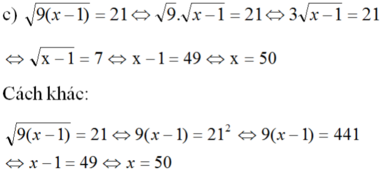
x = 50 thỏa mãn điều kiện (*) nên x = 50 là nghiệm của phương trình.
d) Vì (1 - x)2 ≥ 0 ∀x nên phương trình xác định với mọi giá trị của x.
![]()
- Khi 1 – x ≥ 0 ⇔ x ≤ 1
Ta có: 2|1 – x| = 6 ⇔ 2(1 – x) = 6 ⇔ 2(1 – x) = 6
⇔ –2x = 4 ⇔ x = –2 (nhận)
- Khi 1 – x < 0 ⇔ x > 1
Ta có: 2|1 – x| = 6 ⇔ 2[– (1 – x)] = 6
⇔ x – 1 = 3 ⇔ x = 4 (nhận)
Vậy phương trình có hai nghiệm: x = - 2; x = 4
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
. Bài 1:Tìm x,biết
a; x^3-16x=0
b: 9x^2-4.(3x-2)^2=0
c: (x+2)(x^2-2x+4)+(x+2)^2
. Bài 2: CMR
a; n^3+11n chia hết cho 6 với mọi n thuộc Z
b; n^6-n^2 chia hết cho 60 với mọi n thuộc Z
\(a.\left(x^3-16x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x^2-16\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=0\\x-4=0\\x+4=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=4\\x=-4\end{cases}}}\)
Uầy lười lm waa
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
. Hãy nhiệt tình lên :>> Chúng ta là công dân cùng một nước,phải giúp đỡ nhau a~~~
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm giá trị của x, biết:
a. x3 - 16x = 0 b. (2x + 1)2 - (x - 1)2 = 0
a) \(x^3-16x=0\)
⇔\(x\left(x^2-16\right)=0\)
⇒\(x=0\) hoặc \(x^2-16=0\)
\(TH_1:x=0\)
\(TH_2:x^2-16=0\) ⇔ \(x^2=16\) ⇔ \(x=\pm4\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{0;\pm4\right\}\)
b) \(\left(2x+1\right)^2-\left(x-1\right)^2=0\)
⇒ \(2x+1=x-1\)
⇒ \(2x+2=x\)
⇒ \(2\left(x+1\right)=x\) ⇒ x = -2
Vậy x = -2
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm x biết :
a) \(3x^2+4x=0\)
b) \(25x^2-0,64=0\)
c) \(x^4-16x^2=0\)
d) \(x^2+x=6\)
Bài làm :
\(a\text{)}3x^2+4x=0\Leftrightarrow x\left(3x+4\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\3x+4=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=-\frac{4}{3}\end{cases}}\)
\(b\text{)}25x^2-0,64=0\Leftrightarrow\left(5x-0,8\right)\left(5x+0,8\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}5x-0,8=0\\5x+0,8=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0,16\\-0,16\end{cases}}\)
\(c\text{)}x^4-16x^2=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-4x\right)\left(x^2+4x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x^2-4x=0\\x^2+4x=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x\left(x-4\right)=0\\x\left(x+4\right)=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=\pm4\end{cases}}\)
\(d\text{)}x^2+x=6\Leftrightarrow x^2+x-6=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-2x\right)+\left(3x-6\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-2\right)+3\left(x-2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+3=0\\x-2=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-3\\x=2\end{cases}}\)
Bài làm :
\(a)3x^2+4x=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(3x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\3x+4=0\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=\frac{-4}{3}\end{cases}}\)
Vậy x = 0 hoặc \(x=\frac{-4}{3}\) .
\(b)25x^2-0,64=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(5x\right)^2=\frac{16}{25}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(5x\right)^2=\left(\frac{4}{5}\right)^2\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}5x=\frac{4}{5}\\5x=\frac{-4}{5}\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{4}{25}\\x=\frac{-4}{25}\end{cases}}\)
Vậy \(x=\frac{4}{25}\) hoặc \(x=\frac{-4}{25}\) .
\(c)x^4-16x^2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2\left(x^2-16\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x^2=0\\x^2-16=0\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x^2=4^2\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=\pm4\end{cases}}\)
Vậy x = 0 hoặc \(x=\pm4\) .



























