a) Vẽ đồ thị các hàm số y=-x+4(d1) và y=x-4(d2) trên cùng một mặt phẳng tọa độ.
b) Gọi A, B lần lượt là giao điểm của các đường thẳng (d1);(d2) với trục tung và giao điểm của 2 đường thẳng là C. Tìm tọa độ giao điểm A,B,C.
c) Tính S tam giác ABC
Cho các đường thẳng d1: y = x+ 1 và d2: y = x căn 3 -3
a) Vẽ d1 và d2 trên cùng một mặt phẳng tọa độ.
b) Gọi A và B lần lượt là giao điểm của d1, d2 với trục hoành và C là giao điểm của d1,d2. Tính số đo các góc của tam giác ABC
mình cần gấp, cảm ơnnhe
a: 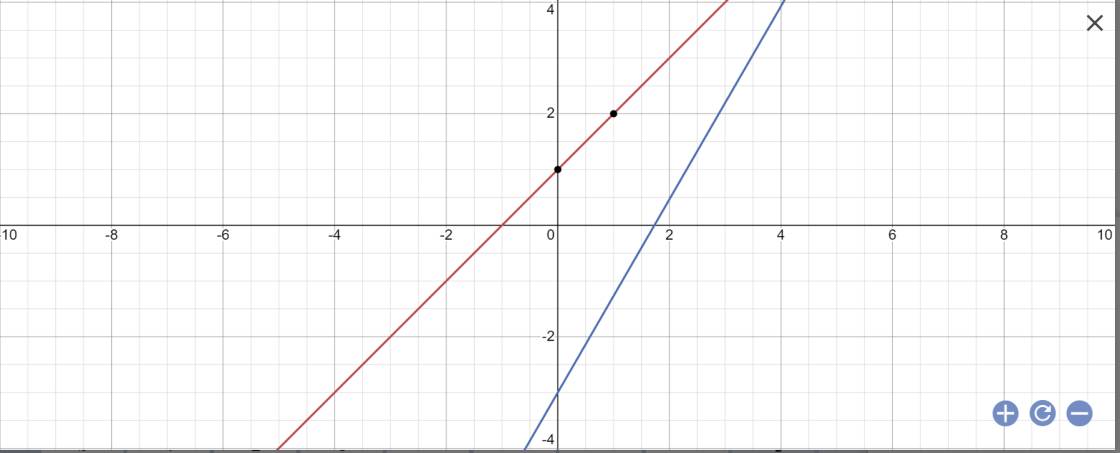
b: Tọa độ A là;
y=0 và x+1=0
=>x=-1 và y=0
Tọa độ B là:
y=0 và x*căn 3-3=0
=>x=căn 3 và y=0
Tọa độ C là:
x+1=xcăn 3-3 và y=x+1
=>\(x=\dfrac{-4}{-\sqrt{3}+1}=2+2\sqrt{3}\) và y=3+3căn 3
A(-1;0); B(căn 3;0); \(C\left(2+2\sqrt{3};3+3\sqrt{3}\right)\)
\(AC=\sqrt{\left(2+2\sqrt{3}+1\right)^2+\left(3\sqrt{3}\right)^2}\simeq8,29\)
\(AB=\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{3}+1\right)^2}\simeq2,73\)
\(BC=\sqrt{\left(2+2\sqrt{3}-\sqrt{3}\right)^2+\left(3+3\sqrt{3}\right)^2}\simeq9,0\left(cm\right)\)
\(cosA=\dfrac{AB^2+AC^2-BC^2}{2\cdot AB\cdot AC}\simeq-\dfrac{245}{2487}\)
=>góc A=96 độ
\(cosB=\dfrac{BA^2+BC^2-AC^2}{2\cdot BA\cdot BC}=\dfrac{271}{675}\)
=>góc B=67 độ
=>góc C=17 độ
Cho hàm số y=3x-1 có đồ thị d1 và hàm số y=-x +3 có đồ thị d2 A. Vẽ đồ thị hs trên cùng hệ trục tọa độ Oxy B. Gọi giao điểm d1, d2 với trục Õ lần lượt là A và B, giao điểm của 2 đường thẳng d1 và d2 là C. Tìm tọa độ các điểm A,B,C C. Tính số đo của góc tạo bởi đường thẳng d1 với tia Ox
a: 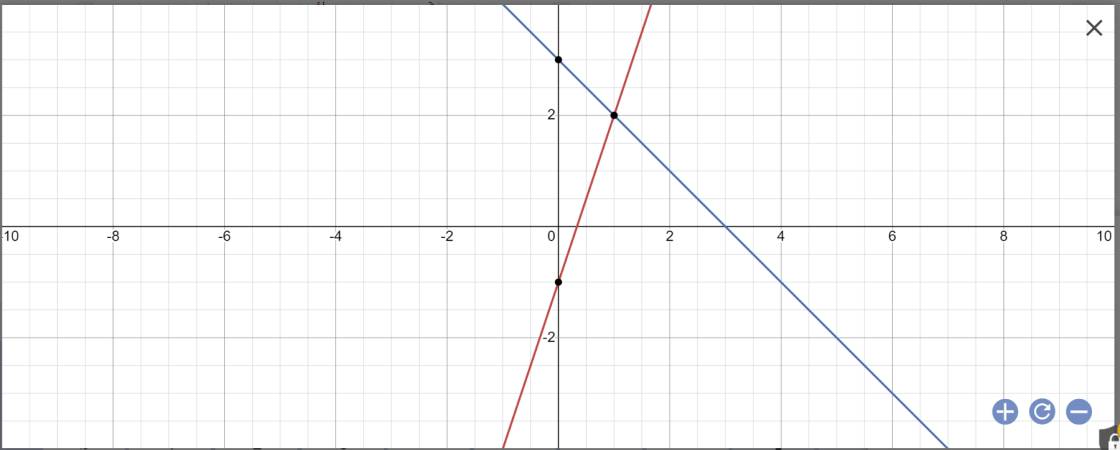
b: Tọa độ A là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\3x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1}{3}\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: A(1/3;0)
Tọa độ B là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\-x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\-x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: B(3;0)
Tọa độ C là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x-1=-x+3\\y=3x-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x=4\\y=3x-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=3\cdot1-1=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: C(1;2)
c: Gọi \(\alpha\) là góc tạo bởi (d1) với trục Ox
\(tan\alpha=a=3\)
=>\(\alpha\simeq71^033'\)
Cho hai hàm số y = 2x + l và y = x – 1 có đồ thị lần lượt là đường thẳng d 1 và d 2
a, Vẽ d 1 và d 2 trên cùng một hệ trục tọa độ Oxy
b, Tìm tọa độ giao điểm C của d 1 và d 2 bằng đồ thị và bằng phép toán
c, Gọi A và B lần lượt là giao điểm của d 1 và d 2 với trục hoàng. Tính diện tích của tam giác ABC
a, HS Tự làm
b, Tìm được C(–2; –3) là tọa độ giao điểm của d 1 và d 2
c, Kẻ OH ⊥ AB (CH ⊥ Ox)
S A B C = 1 2 C H . A B = 9 4 (đvdt)
Cho hai hàm số : y = -2x + 4 (d1)
y = x + 1 (d2)
a. Vẽ đồ thị hai hàm số trên cùng một mặt phẳng tọa độ
b. gọi A là tọa độ giao điểm của 2 đường thẳng.B , C là giao điểm của (d1) và (d2) với trục hoành. Tìm tọa độ A,B,C.
\(b,\) Tọa độ giao điểm 2 đường thẳng là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-2x+4\\y=x+1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+1=-2x+4\\y=x+1\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow A\left(1;2\right)\)
Tọa độ giao điểm 2 đường thẳng với trục hoành là
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}y=-2x+4\\y=x+1\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}4-2x=0\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow B\left(2;0\right),C\left(-1;0\right)\)
Cho hai hàm số: y = 2x – 3 và y = (-1/2)x + 2 có đồ thị lần lượt là các đường thẳng (d1) và (d2). a) Vẽ trên cùng một hệ trục tọa độ các đường thẳng (d1) và (d2). b) Tìm tọa độ giao điểm hai đường thẳng (d1) và (d2) bằng phép toán. c) Tính góc tạo bởi đường thẳng (d1) và trục Ox.
Cho đồ thị hàm số (d1) : y= mx+3 và (d2) : y= \(\dfrac{-1}{m}\)x+3 (m≠0)
a) Với m=1. Vẽ các đồ thị (d1), (d2) trên cùng một mặt phẳng tọa độ và tìm tọa độ giao điểm của (d1) cắt (d2).
b) Gọi A là giao điểm của (d1) và (d2); B và C lần lượt là giao điểm của (d1) và (d2) với trục hoành. Tìm m để diện tích tam giác ABC nhỏ nhất. Tính diện tích nhỏ nhất đó.
Cho đồ thị hàm số (d1) : y= mx+3 và (d2) : y= \(\dfrac{-1}{m}\)x+3 (m≠0)
a) Với m=1. Vẽ các đồ thị (d1), (d2) trên cùng một mặt phẳng tọa độ và tìm tọa độ giao điểm của (d1) cắt (d2).
b) Gọi A là giao điểm của (d1) và (d2); B và C lần lượt là giao điểm của (d1) và (d2) với trục hoành. Tìm m để diện tích tam giác ABC nhỏ nhất. Tính diện tích nhỏ nhất đó.
Cho 2 hàm số bậc nhất y=4x-2 và y=-x + 3 A. Vẽ trên cùng 1 mặt phẳng tọa độ Oxy đồ thị hai hàm số y=4x -2 (d1) và y= -x +3 (d2) B. Gọi M là giao điểm của hai đường thẳng d1 và d2. Tìm tọa độ điểm M C. Tính góc tạo bởi 2 đường thẳng d1, d2 với trục Ox (làm tròn đến phút) D. Tìm đường thẳng d cắt d1 tại điềm A có tung độ là 6 và cắt d2 tại điểm B có hoành độ bằng nửa tung độ A. Tính chu vi và các góc tam giác AMB
a: 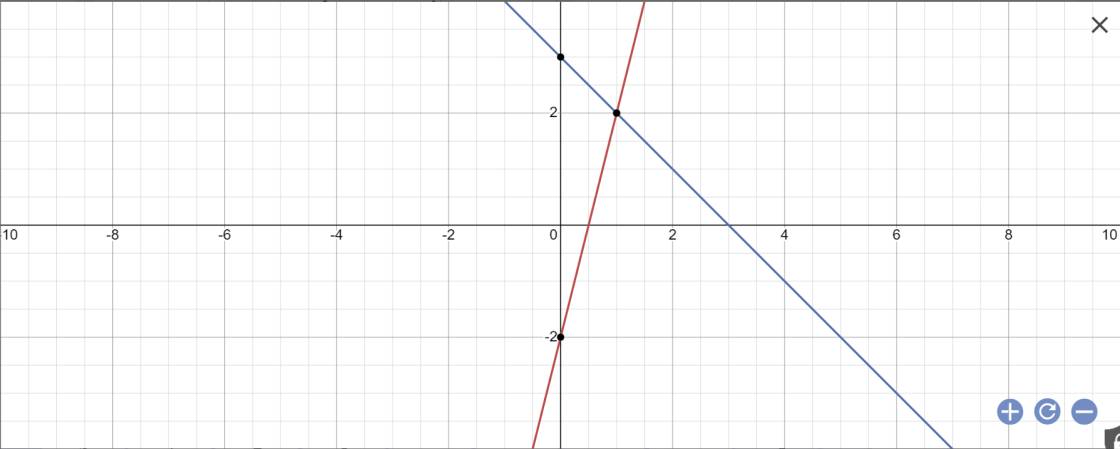
b: Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
4x-2=-x+3
=>4x+x=3+2
=>5x=5
=>x=1
Thay x=1 vào y=-x+3, ta được:
\(y=-1+3=2\)
Vậy: M(1;2)
c: Gọi \(\alpha;\beta\) lần lượt là góc tạo bởi (d1),(d2) với trục Ox
(d1): y=4x-2
=>\(tan\alpha=4\)
=>\(\alpha=76^0\)
(d2): y=-x+3
=>\(tan\beta=-1\)
=>\(\beta=135^0\)
d: Thay y=6 vào (d1), ta được:
4x-2=6
=>4x=8
=>x=2
=>A(2;6)
Thay x=6/2=3 vào (d2), ta được:
\(y=-3+3=0\)
vậy: B(3;0)
Vì (d):y=ax+b đi qua A(2;6) và B(3;0) nên ta có hệ phương trình:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2a+b=6\\3a+b=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2a+b-3a-b=6-0\\3a+b=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-a=6\\b=-3a\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=-6\\b=-3\cdot\left(-6\right)=18\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: (d): y=-6x+18
e: A(2;6); B(3;0); M(1;2)
\(AM=\sqrt{\left(1-2\right)^2+\left(2-6\right)^2}=\sqrt{17}\)
\(BM=\sqrt{\left(1-3\right)^2+\left(2-0\right)^2}=2\sqrt{2}\)
\(AB=\sqrt{\left(3-2\right)^2+\left(0-6\right)^2}=\sqrt{37}\)
Chu vi tam giác AMB là:
\(C_{AMB}=\sqrt{17}+2\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{37}\)
Xét ΔAMB có
\(cosAMB=\dfrac{MA^2+MB^2-AB^2}{2\cdot MA\cdot MB}=\dfrac{17+8-37}{2\cdot2\sqrt{2}\cdot\sqrt{17}}=\dfrac{-3}{\sqrt{34}}\)
=>\(\widehat{AMB}\simeq121^0\) và \(sinAMB=\sqrt{1-\left(-\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{34}}\right)^2}=\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{34}}\)
Xét ΔAMB có
\(\dfrac{AB}{sinAMB}=\dfrac{AM}{sinABM}=\dfrac{BM}{sinBAM}\)
=>\(\dfrac{\sqrt{17}}{sinABM}=\dfrac{2\sqrt{2}}{sinBAM}=\sqrt{37}:\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{34}}\)
=>\(sinABM\simeq0,58;\widehat{BAM}\simeq0,4\)
=>\(\widehat{ABM}\simeq35^0;\widehat{BAM}\simeq24^0\)
Cho hàm số y = − 2x + 3 có đồ thị là đường thẳng (d1) và hàm số y = 0,5x – 2 có đồ thị là đường thẳng (d2). 1. Vẽ đường thẳng (d1) và (d2) cùng trên một mặt phẳng tọa độ2. Tìm tọa độ giao điểm C của hai đường thẳng (d1) và (d2) bằng phép toán3. Gọi A, B thứ tự là giao điểm của đường thẳng (d1) và (d2) với trục Oy. Tính diện tích tam giác ABC (đơn vị đo trên các trục tọa độ là cm)