Tìm x biết:2x+1/9=11/2x-1

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Tìm 2 phân số có tử =9,biết giá trị của mỗi phân số ấy lớn hơn -11/3 và nhỏ hơn -11/5tìm các số nguyên x để các phân số sau có giá trị là một số nguyên và tính giá trị ấy:
Xem chi tiết
a=x+5/x+1 b=2x+4/x+3 c=3x+8/x-1 d=2x-3/x-1 e=5x+9/x+5 g=4x+9/2x+1 h=6x+5/2x-1 i=4x-6/2x+1 k=4x+4/2x+4 n=4x+6/2x+2
Tìm x biết:
a) 11/15 - (7/9 + x) × 3/8 = 61/90 + x/3
b) (4x + 1)(-2x + 1/3) = 0
c) 5x(2x - 1/2) + 2(2x - 1/2) = 0
Tìm x biết
a) (x+2).(x+3) - (x-2).(x+5)=10
b) (3x+2). (2x+9) - (x+2). (8x+11)=(x+1).(3-2x)
c) 3.(2x-1).(3x-1)-(2x-3).(9x-1)=0
d) (5x-8).(4x-5)-(3x-4).(2x+12)=12
a)(x+2).(x+3)-(x-2).(x+5)=10
( x^2 +3x+2x+6)-(x^2 +5x-2x-10)=10
x^2 +3x+2x+6-x^2 -5x+2x+10-10=0
2x+6=0
2x=-6
x=-3
Tính a) 1/7 × (4/3)^2 - 1/7 : 9/11 b) tìm x biết 2x + 1/4 = 3/5
a, \(\dfrac{1}{7}\) x ( \(\dfrac{4}{3}\))2 - \(\dfrac{1}{7}\) : \(\dfrac{9}{11}\)
= \(\dfrac{1}{7}\) x \(\dfrac{16}{9}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{7}\) x \(\dfrac{11}{9}\)
= \(\dfrac{1}{7}\) x ( \(\dfrac{16}{9}-\dfrac{11}{9}\))
= \(\dfrac{1}{7}\) x \(\dfrac{5}{9}\)
= \(\dfrac{5}{63}\)
b, 2x + \(\dfrac{1}{4}\) = \(\dfrac{3}{5}\)
2x = \(\dfrac{3}{5}-\dfrac{1}{4}\)
2x = \(\dfrac{7}{20}\)
x = \(\dfrac{7}{20}:2\)
x = \(\dfrac{7}{40}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Tìm x biết:
a,x-5/7=1/9
b,2x/5=6/2x+1
c,11/8+13/6=85/x
d,2x-2/11=1.1/5
e,x/15=3/5+-2/3
f,x/182=-6/14.35/91
a, \(x\) - \(\dfrac{5}{7}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{9}\)
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{1}{9}\) + \(\dfrac{5}{7}\)
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{52}{63}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
b, \(\dfrac{2x}{5}\) = \(\dfrac{6}{2x+1}\)
2\(x\).(2\(x\) + 1) = 30
4\(x^2\)+ 2\(x\) - 30 = 0
4\(x^2\) + 12\(x\) - 10\(x\) - 30 = 0
(4\(x^2\) + 12\(x\)) - (10\(x\) + 30) =0
4\(x\).(\(x\) + 3) - 10.(\(x\) +3) = 0
2 (\(x\) + 3).(2\(x\) - 5) = 0
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+3=0\\2x-5=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\) \(\in\) {-3; \(\dfrac{5}{2}\)}
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
c, \(\dfrac{11}{8}\) + \(\dfrac{13}{6}\) = \(\dfrac{85}{x}\)
\(\dfrac{85}{x}\) = \(\dfrac{85}{24}\)
\(x\) = 24
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Tìm x :
a) | x + 12x | = 2x
b) 3x − |x + 1| = 1
c) |2x + 3| = x + 1
d) ||x + 9| + 11| = 2x + 11
Tìm x :
a) | x + 12x | = 2x
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}13x=2x\\13x=-2x\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}11x=0\\15x=0\end{cases}}\)
=> \(x=0\)
b) 3x − |x + 1| = 1
=> |x + 1| = 3x -1
=>\(\orbr{\begin{cases}x+1=3x-1\\x+1=1-3x\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}2x=2\\4x=0\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=0\end{cases}}\)
c) |2x + 3| = x + 1
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}2x+3=x+1\\2x+3=-x-1\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-2\\3x=-4\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-2\\x=-\frac{4}{3}\end{cases}}\)
b) 3x - |x + 1| = 1
<=> |x + 1| = 3x - 1 (1)
ĐK : \(x\ge\frac{1}{3}\)
Khi đó (1) <=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x+1=3x-1\\x+1=-3x+1\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x=2\\4x=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\left(\text{loại}\right)\\x=1\end{cases}}\)
Vậy x = 1
c) ĐK : x + 1\(\ge0\Rightarrow x\ge-1\)
Khi đó |2x + 3| = x + 1
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}2x+3=x+1\\2x+3=-x-1\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-2\\x=-\frac{4}{3}\end{cases}}\left(\text{loại}\right)\)
Vậy \(x\in\varnothing\)
d) ||x + 9| + 11| = 2x + 11 (1)
ĐK : \(2x+11\ge0\Rightarrow x\ge-\frac{5}{2}\)
Khi đó (1) <=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}\left|x+9\right|+11=2x+11\\\left|x+9\right|+11=-2x-11\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\left|x+9\right|=2x\\\left|x+9\right|=-2x-22\end{cases}}\)
Khi |x + 9| = 2x (x \(\ge0\))
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x+9=2x\\x+9=-2x\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=9\left(tm\right)\\x=-3\left(\text{loại}\right)\end{cases}}\)
Khi |x + 9| = -2x - 22 ( \(-\frac{5}{2}\le x\le-11\))
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x+9=-2x-22\\x+9=2x+22\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-\frac{31}{3}\\x=-13\end{cases}}\left(\text{loại}\right)}\)
Vậy x = 9
đúng. Mik học qua lớp anh rồi lên mik biết
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Tìm x từ phương trình (2x + 1) + (2x + 6) + (2x + 11) + ... + (2x + 96) = 1010 biết 1, 6, 11, ... là cấp số cộng.
Xét cấp số cộng 1, 6, 11, ..., 96.
Ta có: 96 = 1 + 5(n − 1) ⇒ n = 20
Suy ra
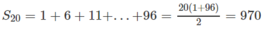
Và 2x.20 + 970 = 1010
Từ đó x = 1
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm x ∈ Z, biết:
a) x – 2 = -6 + 17
b) x + 2 = -9 - 11
c) 2x + 5 = x – 1
d) |x – 4| = | -81 |
a) x – 2 = -6 + 17
x – 2 = 11
x = 11 + 2 = 13
b) x + 2 = -9 – 11
x + 2 = -20
x = -20 – 2 = -22
c) 2x + 5 = x – 1
2x – x = -1 – 5
x = -6
d) | x – 4 | = | -81 |
x – 4 = 81 hoặc x – 4 = -81
x = 81 + 4 hoặc x = -81 + 4
x = 85 hoặc x = -77
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1:Tìm số nguyên x, biết:
Bỏ ngoặc rồi tìm x.
a) x-8-(12-2x)= -20
b) -27+(x+8)-(+11)=2
c) -2x-16=2-(3x+9)
a) x - 8 - (12 - 2x) = -20
=> x - 8 - 12 + 2x = -20
=> (x + 2x) + (-8 - 12) = -20
=> 3x - 20 = -20
=> 3x = 0 => x = 0
b) -27 + (x + 8) - ( +11) = 2
=> -27 + x + 8 - 11 = 2
=> -27 + x = 2 + 11 - 8
=> -27 + x = 5
=> x = 5 - (-27) = 32
c) -2x - 16 = -2 - (3x + 9)
=> -2x - 16 = -2 - 3x - 9
=> -2x - 16 + 2 + 3x + 9 = 0
=> (-2x + 3x) + (-16 + 2 + 9) = 0
=> x - 5 = 0
=> x = 5
\(a,x-8-\left(12-2x\right)=-20\)
\(x-8-12+2x=-20\)
\(x+2x-8-12=-20\)
\(3x-20=-20\)
\(3x=-20+20\)
\(3x=0\)
\(x=0\)
\(b,-27+\left(x+8\right)-\left(+11\right)=2\)
\(-27+x+8-11=2\)
\(x-27+8-11=2\)
\(x-30=2\)
\(x=2+30\)
\(x=32\)
\(c,-2x-16=2-\left(3x+9\right)\)
\(-2x-16=2-3x-9\)
\(-2x+3x=2-9+16\)
\(x=9\)
Học tốt
a) x - 8 - ( 12 - 2x ) = -20
x - 8 - 12 + 2x = -20
x + 2x = -20 + 8 + 12
3x = 0
x = 0 \(\left(x\in Z,tm\right)\)
Vậy x=0
b) -27 + ( x + 8 ) - ( +11 ) = 2
-27 + x + 8 - 11 = 2
x = 2 + 27 - 8 + 11
x = 32 \(\left(x\in Z,tm\right)\)
Vậy x = 32
c) -2x - 16 = 2 - ( 3x + 9 )
-2x - 16 = 2 - 3x - 9
-2x + 3x = 2 - 9 +16
x = 9 \(\left(x\in Z,tm\right)\)
Vậy x = 9
Xem thêm câu trả lời


















