Tích phân ∫ 0 1 1 2 x + 5 d x bằng:
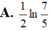



1) phân tích thành phân tử:
a) x^3y^3 + 1/125
b) (x+5)^3-(x-5)^3
c) (6-x)^3+(6+x)^3
d) 27x^3 -135x^2+225x-125
2) tìm x:
a)4x^2-25x^4=0
b) x^2-8x+16=0
c)x^3-3x^2+3x-1=0
1.
a) = (xy + \(\frac{1}{5}\)) (x2y2 - \(\frac{xy}{5}\)+ \(\frac{1}{25}\))
b) = (x + 5 - x + 5) [(x+5)2 + (x+5)(x-5) + (x-5)2] = 10 (x2 + 10x + 25 + x2 - 25 + x2 - 10x + 25) = 10 (3x2 +25)
c) = (6 - x + 6 + x) [(6-x)2 - (6-x)(6+x) + (6+x)2] = 12 (36 - 12x + x2 - 26 + x2 + 36 + 12x + x2) = 12 (3x2 + 36) = 12. 3(x2 + 12) = 36(x2 +12)
d) = (3x - 5)3
2.
a) => (2x - 5x2)(2x + 5x2) = 0 ............. giải ra
b) => (x-4)2 = 0 => x - 4 = 0 => x= 4
c) => (x - 1)3 = 0 => x - 1 = 0 => x = 1
Phân tích thành nhân tử
(x-3)^2-5(x-2)+5=0
(2x-1)^2-3(x-2)(x+2)-25=0
\(\left(x-3\right)^2-5\left(x-2\right)+5=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-6x+9-5x+10+5=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-11x+24=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-8\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=8\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left(2x-1\right)^2-3\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)-25=0\\ \Leftrightarrow4x^2-4x+1-3\left(x^2-4\right)-25=0\\ \Leftrightarrow4x^2-4x-24-3x^2+12=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-4x-12=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-6\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
a: Ta có: \(\left(x-3\right)^2-5\left(x-2\right)+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-6x+9-5x+10+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-11x+24=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-8\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=8\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: Ta có: \(\left(2x-1\right)^2-3\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)-25=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-4x+1-3x^2+12-25=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x-12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-6\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
1. Rút gọn phân thức \(\dfrac{15-5x}{5x^2-15x}\)
A. \(\dfrac{-1}{x}\) B. x C. \(\dfrac{1}{x}\) D. -x
2. Phân thức \(\dfrac{x\left(x-5\right)}{x^2+25}\) có giá trị bằng 0 khi x bằng
A. -5 B. 0 C. 0 hoặc 5 D. 5
3. Phân thức nào dưới đây có kết quả rút gọn là một hằng số
A. \(\dfrac{3x-3}{x\left(x-1\right)}\) B. \(\dfrac{x^2y}{xy}\) C. \(\dfrac{x-1}{x^2-1}\) D. \(\dfrac{2x-5}{5-2x}\)
1) \(\dfrac{15-5x}{5x^2-15x}=\dfrac{5\left(3-x\right)}{5x\left(x-3\right)}=-\dfrac{5\left(x-3\right)}{5x\left(x-3\right)}=-\dfrac{1}{x}\)
Chọn A
2) \(\dfrac{x\left(x-5\right)}{x^2+25}=\dfrac{x\left(x-5\right)}{\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)}=\dfrac{x}{x+5}\)
\(A=0\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x}{x+5}=0\Leftrightarrow x=0\)
Chọn B
3) \(\dfrac{2x-5}{5-2x}=-\dfrac{5-2x}{5-2x}=-1\)
Chọn D
bài 1: Tìm x
a)5(x-1)=x-1
b)x(x-2)+(x-2)=0
c)5x(x-3)-x+3=0
d)x(2x-7)-4x+17=0
bai2:phân tích thành nhân tử
a)2x^2+2y-x^2z+z-y^2z-2
a) 5(x-1)=x-1
5x-5=x-1
5x-x=5-1
4x=4=>x=1
b)x(x-2)+(x-2)=0
(x-2)(x+1)=0
=>x=2 hay x=-1
c)5x(x-3)-x+3=0
5x(x-3)-(x-3)=0
(5x-1)(x-3)=0
=>x=\(\frac{1}{5}\)hay x=3
d)x(2x-7)-4x+17=0
x(2x-7-4)+17=0
x(2x-11)+17=0
=> đa thức này không có nghiệm
I) THỰC HIỆN PHÉP TÍNH a) 2x(x^2-4y) b)3x^2(x+3y) c) -1/2x^2(x-3) d) (x+6)(2x-7)+x e) (x-5)(2x+3)+x II phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử a) 6x^2+3xy b) 8x^2-10xy c) 3x(x-1)-y(1-x) d) x^2-2xy+y^2-64 e) 2x^2+3x-5 f) 16x-5x^2-3 g) x^2-5x-6 IIITÌM X BIẾT a)2x+1=0 b) -3x-5=0 c) -6x+7=0 d)(x+6)(2x+1)=0 e)2x^2+7x+3=0 f) (2x-3)(2x+1)=0 g) 2x(x-5)-x(3+2x)=26 h) 5x(x-1)=x-1 IV TÌM GTNN,GTLN. a) tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất x^2-6x+10 2x^2-6x b) tìm giá trị lớn nhất 4x-x^2-5 4x-x^2+3
Giải như sau.
(1)+(2)⇔x2−2x+1+√x2−2x+5=y2+√y2+4⇔(x2−2x+5)+√x2−2x+5=y2+4+√y2+4⇔√y2+4=√x2−2x+5⇒x=3y(1)+(2)⇔x2−2x+1+x2−2x+5=y2+y2+4⇔(x2−2x+5)+x2−2x+5=y2+4+y2+4⇔y2+4=x2−2x+5⇒x=3y
⇔√y2+4=√x2−2x+5⇔y2+4=x2−2x+5, chỗ này do hàm số f(x)=t2+tf(x)=t2+t đồng biến ∀t≥0∀t≥0
Công việc còn lại là của bạn !
\(\left(x+6\right)\left(2x+1\right)=0\)
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x+6=0\\2x+1=0\end{cases}}\)
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-6\\x=-\frac{1}{2}\end{cases}}\)
Vậy....
hk tốt
^^
1. Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử: a) (x+4)^2+8x(x+4)^3+15x^2
2. Tìm x: a) 3x(x-2020)-x+2020=0
b)(2x-3).(3x+2)-6x^2=1
c)(3x-1)^2-(x+5)^2=0
d)4x^2-4x-35=0
Phân tích thành nhân tử
a. x2 - 7
b.4x2 - 5
c.3x2 - 1
d. x - 1 với x>= 0
e. x-4 với x>=0
f. 9x-4 với x>=0
Bài làm:
a) \(x^2-7=\left(x-\sqrt{7}\right)\left(x+\sqrt{7}\right)\)
b) \(4x^2-5=\left(2x-\sqrt{5}\right)\left(2x+\sqrt{5}\right)\)
c) \(3x^2-1=\left(x\sqrt{3}-1\right)\left(x\sqrt{3}+1\right)\)
d) \(x-1=\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)\)
e) \(x-4=\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)\)
f) \(9x-4=\left(3\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(3\sqrt{x}+2\right)\)
Bai 1: Tìm x ( Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử)
a, x.(8x-2)-8x2+12=0
b,x.(4x-5)-(2x+1)2=0
c,(5-2x).(2x+7)=(2x-5).(2x+5)
d,64x2-49=0
e,(x2+6x+9).(x2+8x+7)=0
g,(x2+1).(x2-8x+7)=0
Bai 2: Rút gọn (Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử)
a,(x-1)2-(x-2).(x+2)
c,(3x+5)2+(26x+10).(2-3x)+(2-3x)2
d,(x+y)2-(x+y-2)2
Bài 3 Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất
A=3x2+18x+33
B=x2-6x+10+y2
C=(2x-1)2+(x+2)2
D=-2 / 7x2-8x+7
Giúp mik với mik đg cần gấp!!!
Bài 1.
a) x( 8x - 2 ) - 8x2 + 12 = 0
<=> 8x2 - 2x - 8x2 + 12 = 0
<=> 12 - 2x = 0
<=> 2x = 12
<=> x = 6
b) x( 4x - 5 ) - ( 2x + 1 )2 = 0
<=> 4x2 - 5x - ( 4x2 + 4x + 1 ) = 0
<=> 4x2 - 5x - 4x2 - 4x - 1 = 0
<=> -9x - 1 = 0
<=> -9x = 1
<=> x = -1/9
c) ( 5 - 2x )( 2x + 7 ) = ( 2x - 5 )( 2x + 5 )
<=> -4x2 - 4x + 35 = 4x2 - 25
<=> -4x2 - 4x + 35 - 4x2 + 25 = 0
<=> -8x2 - 4x + 60 = 0
<=> -8x2 + 20x - 24x + 60 = 0
<=> -4x( 2x - 5 ) - 12( 2x - 5 ) = 0
<=> ( 2x - 5 )( -4x - 12 ) = 0
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}2x-5=0\\-4x-12=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{5}{2}\\x=-3\end{cases}}\)
d) 64x2 - 49 = 0
<=> ( 8x )2 - 72 = 0
<=> ( 8x - 7 )( 8x + 7 ) = 0
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}8x-7=0\\8x+7=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{7}{8}\\x=-\frac{7}{8}\end{cases}}\)
e) ( x2 + 6x + 9 )( x2 + 8x + 7 ) = 0
<=> ( x + 3 )2( x2 + x + 7x + 7 ) = 0
<=> ( x + 3 )2 [ x( x + 1 ) + 7( x + 1 ) ] = 0
<=> ( x + 3 )2( x + 1 )( x + 7 ) = 0
<=> x = -3 hoặc x = -1 hoặc x = -7
g) ( x2 + 1 )( x2 - 8x + 7 ) = 0
Vì x2 + 1 ≥ 1 > 0 với mọi x
=> x2 - 8x + 7 = 0
=> x2 - x - 7x + 7 = 0
=> x( x - 1 ) - 7( x - 1 ) = 0
=> ( x - 1 )( x - 7 ) = 0
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x-1=0\\x-7=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=7\end{cases}}\)
Bài 2.
a) ( x - 1 )2 - ( x - 2 )( x + 2 )
= x2 - 2x + 1 - ( x2 - 4 )
= x2 - 2x + 1 - x2 + 4
= -2x + 5
b) ( 3x + 5 )2 + ( 26x + 10 )( 2 - 3x ) + ( 2 - 3x )2
= 9x2 + 30x + 25 - 78x2 + 22x + 20 + 9x2 - 12x + 4
= ( 9x2 - 78x2 + 9x2 ) + ( 30x + 22x - 12x ) + ( 25 + 20 + 4 )
= -60x2 + 40x2 + 49
d) ( x + y )2 - ( x + y - 2 )2
= [ x + y - ( x + y - 2 ) ][ x + y + ( x + y - 2 ) ]
= ( x + y - x - y + 2 )( x + y + x + y - 2 )
= 2( 2x + 2y - 2 )
= 4x + 4y - 4
Bài 3.
A = 3x2 + 18x + 33
= 3( x2 + 6x + 9 ) + 6
= 3( x + 3 )2 + 6 ≥ 6 ∀ x
Đẳng thức xảy ra <=> x + 3 = 0 => x = -3
=> MinA = 6 <=> x = -3
B = x2 - 6x + 10 + y2
= ( x2 - 6x + 9 ) + y2 + 1
= ( x - 3 )2 + y2 + 1 ≥ 1 ∀ x,y
Đẳng thức xảy ra <=> \(\hept{\begin{cases}x-3=0\\y^2=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=3\\y=0\end{cases}}\)
=> MinB = 1 <=> x = 3 ; y = 0
C = ( 2x - 1 )2 + ( x + 2 )2
= 4x2 - 4x + 1 + x2 + 4x + 4
= 5x2 + 5 ≥ 5 ∀ x
Đẳng thức xảy ra <=> 5x2 = 0 => x = 0
=> MinC = 5 <=> x = 0
D = -2/7x2 - 8x + 7 ( sửa thành tìm Max )
Để D đạt GTLN => 7x2 - 8x + 7 đạt GTNN
7x2 - 8x + 7
= 7( x2 - 8/7x + 16/49 ) + 33/7
= 7( x - 4/7 )2 + 33/7 ≥ 33/7 ∀ x
Đẳng thức xảy ra <=> x - 4/7 = 0 => x = 4/7
=> MaxC = \(\frac{-2}{\frac{33}{7}}=-\frac{14}{33}\)<=> x = 4/7
Câu 1: Phân tích đa thức x^2 - 16 thành nhân tử
Câu 2: Tìm x biết 3x(x-5)+2(x-5)=0
câu 1:
x2-16=x2-42=(x+4)(x-4)
câu 2:
3x(x-5)+2(x-5)=0
(3x+2)(x-5)=0
TH1: 3x+2=0 TH2: x-5=0
3x=-2 x=5
x=-2/3
vậy x\(\in\)\(\left\{\dfrac{-2}{3};5\right\}\)
Bài 3: Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử:
a) x2 + 10x + 25. b) 8x - 16 - x2
c) x3 + 3x2 + 3x + 1 d) (x + y)2 - 9x2
e) (x + 5)2 – (2x -1)2
Bài 4: Tìm x biết
a) x2 – 9 = 0 b) (x – 4)2 – 36 = 0
c) x2 – 10x = -25 d) x2 + 5x + 6 = 0
Bài 3
a) x² + 10x + 25
= x² + 2.x.5 + 5²
= (x + 5)²
b) 8x - 16 - x²
= -(x² - 8x + 16)
= -(x² - 2.x.4 + 4²)
= -(x - 4)²
c) x³ + 3x² + 3x + 1
= x³ + 3.x².1 + 3.x.1² + 1³
= (x + 1)³
d) (x + y)² - 9x²
= (x + y)² - (3x)²
= (x + y - 3x)(x + y + 3x)
= (y - 2x)(4x + y)
e) (x + 5)² - (2x - 1)²
= (x + 5 - 2x + 1)(x + 5 + 2x - 1)
= (6 - x)(3x + 4)
Bài 4
a) x² - 9 = 0
x² = 9
x = 3 hoặc x = -3
b) (x - 4)² - 36 = 0
(x - 4 - 6)(x - 4 + 6) = 0
(x - 10)(x + 2) = 0
x - 10 = 0 hoặc x + 2 = 0
*) x - 10 = 0
x = 10
*) x + 2 = 0
x = -2
Vậy x = -2; x = 10
c) x² - 10x = -25
x² - 10x + 25 = 0
(x - 5)² = 0
x - 5 = 0
x = 5
d) x² + 5x + 6 = 0
x² + 2x + 3x + 6 = 0
(x² + 2x) + (3x + 6) = 0
x(x + 2) + 3(x + 2) = 0
(x + 2)(x + 3) = 0
x + 2 = 0 hoặc x + 3 = 0
*) x + 2 = 0
x = -2
*) x + 3 = 0
x = -3
Vậy x = -3; x = -2