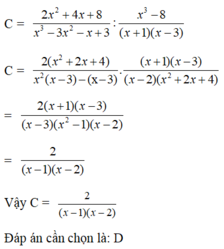PTĐTTNT: 3x5 - 10x4 - 8x3 - 3x2 +10x + 8

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Cho hai đa thức
P
(
x
)
-
5
x
3
-
2
x
+
4
x
4
+
3
+
3
x
2
-
4
x
4
+
10
x
3
-
8
,
...
Đọc tiếp
Cho hai đa thức
P ( x ) = - 5 x 3 - 2 x + 4 x 4 + 3 + 3 x 2 - 4 x 4 + 10 x 3 - 8 , Q ( x ) = 6 x 2 + 5 x 3 - 3 x 5 + 4 + 8 x - 4 x 2 + 3 x 5 - 10 x
b. Tính M ( x ) = P ( x ) + Q ( x ) ; N ( x ) = P ( x ) - Q ( x )
b. M(x) = P(x) + Q(x) = 10x3 + 5x2 - 4x - 1 (0.5 điểm)
N(x) = P(x) - Q(x) = x2 - 9 (0.5 điểm)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho hai đa thức
P
(
x
)
-
5
x
3
-
2
x
+
4
x
4
+
3
+
3
x
2
-
4
x
4
+
10
x
3
-
8
,
...
Đọc tiếp
Cho hai đa thức
P ( x ) = - 5 x 3 - 2 x + 4 x 4 + 3 + 3 x 2 - 4 x 4 + 10 x 3 - 8 , Q ( x ) = 6 x 2 + 5 x 3 - 3 x 5 + 4 + 8 x - 4 x 2 + 3 x 5 - 10 x
c. x = 3, x = -3 có là nghiệm của đa thức N(x) không ? Vì sao ?
c. x = 3, x = -3 có là nghiệm của N(x) vì N(3) = N(-3) = 0 (0.5 điểm)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho hai đa thức
P
(
x
)
-
5
x
3
-
2
x
+
4
x
4
+
3
+
3
x
2
-
4
x
4
+
10
x
3
-
8
,
...
Đọc tiếp
Cho hai đa thức
P ( x ) = - 5 x 3 - 2 x + 4 x 4 + 3 + 3 x 2 - 4 x 4 + 10 x 3 - 8 , Q ( x ) = 6 x 2 + 5 x 3 - 3 x 5 + 4 + 8 x - 4 x 2 + 3 x 5 - 10 x
d. Tính giá trị của đa thức A ( x ) = M ( x ) + 2 N ( x ) khi x = 1
d. A(x) = M(x) + 2N(x)
= 10x3 + 5x2 - 4x - 1 + 2(x2 - 9)
= 10x3 + 7x2 - 4x - 19 (0.5 điểm)
Thay x = 1 vào biểu thức ta có: A(1) = -6 (0.5 điểm)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho hai đa thức
P
(
x
)
-
5
x
3
-
2
x
+
4
x
4
+
3
+
3
x
2
-
4
x
4
+
10
x
3
-
8
,
...
Đọc tiếp
Cho hai đa thức
P ( x ) = - 5 x 3 - 2 x + 4 x 4 + 3 + 3 x 2 - 4 x 4 + 10 x 3 - 8 , Q ( x ) = 6 x 2 + 5 x 3 - 3 x 5 + 4 + 8 x - 4 x 2 + 3 x 5 - 10 x
a. Rút gọn và sắp xếp các đa thức trên theo lũy thừa giảm dần của biến .
a. Rút gọn và sắp xếp
P(x) = -5x3 - 2x + 4x4 + 3 + 3x2 - 4x4 + 10x3 - 8
= 5x3 + 3x2-2x-5 (0.75 điểm)
Q(x) = 6x2 + 5x3 - 3x5 + 4 + 8x - 4x2 + 3x5 - 10x
= 5x3 + 2x2 - 2x + 4 (0.75 điểm)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a) x2 - 4x + 4
b) x2 - 2
c) 1 - 8x3
d) x3 + 3x2 + 3x + 1
e) (x + y)2 - 9x
f)x2+6x+9
g)10x-25-x2
h)8x3-\(\dfrac{1}{8}\)
giúp em vs mn thx mn ạ
\(a,=\left(x-2\right)^2\\ b,=\left(x-\sqrt{2}\right)\left(x+\sqrt{2}\right)\\ c,=\left(1-2x\right)\left(1+2x+4x^2\right)\\ d,=\left(x+1\right)^3\\ e,Sửa:\left(x+y\right)^2-9x^2=\left(x+y-3x\right)\left(x+y+3x\right)\\ =\left(y-2x\right)\left(4x+y\right)\\ f,=\left(x+3\right)^2\\ g,=-\left(x^2-10x+25\right)=-\left(x-5\right)^2\\ h,=8\left(x^3-\dfrac{1}{64}\right)=8\left(x-\dfrac{1}{4}\right)\left(x^2+\dfrac{1}{4}x+\dfrac{1}{16}\right)\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (1)
a) \(\left(x-2\right)^2\)
b) \(\left(x-\sqrt{2}\right)\left(x+\sqrt{2}\right)\)
c) \(\left(1-2x\right)\left(1+2x+4x^2\right)\)
d) \(\left(x+1\right)^3\)
e) \(\left(x+y-3\sqrt{x}\right)\left(x+y+3\sqrt{x}\right)\)
f) \(\left(x+3\right)^2\)
g) \(-\left(x-5\right)^2\)
h) \(\left(2x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\left(4x^2+x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
Kết quả của phép nhân 5x3.(3x2 – 2x + 1) là: A. 15x5 – 10x4 – 5x3 B. 15x5 – 10x4 + 5x3 C. 15x5 + 10x4 + 5x3 D. 15x6 – 10x4 + 5x3
a,x3+3x2+3x+1
b,x2+6x+9
c,-x3+9x2-27x+27
d,x2+4x+4
k,10x-25-x2
f,(x+y)2-9x2
g,8x3+42x2y+16xy2+6xy+y3
a) \(x^3+3x^2+3x+1=x^2+3\cdot x^2\cdot1+3\cdot x\cdot1^2+1^3=\left(x-1\right)^3\)
b) \(x^2+6x+9=x^2+2\cdot3\cdot x+3^2=\left(x+3\right)^2\)
c) \(-x^3+9x^2-27x+27\)
\(=-\left(x^3-9x^2+27x-27\right)\)
\(=-\left(x^3-3\cdot3\cdot x^2+3\cdot3^2\cdot x-3^3\right)=-\left(x-3\right)^3\)
d) \(x^2+4x+4=x^2+2\cdot2\cdot x+2^2=\left(x+2\right)^2\)
k) \(10x-25-x^2=-x^2+10x-25=-\left(x^2-10x+25\right)\)
\(=-\left(x^2-2\cdot5\cdot x+5^2\right)=-\left(x-5\right)^2\)
f) \(\left(x+y\right)^2-9x^2=\left(x-y\right)^2-\left(3x\right)^2=\left[\left(x-y\right)-3x\right]\left[\left(x-y\right)+3x\right]\)
\(=\left(x-y-3x\right)\left(x-y+3x\right)=\left(-2x-y\right)\left(4x-y\right)\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (1)
Tìm đạo hàm của các hàm số sau y = 3 x 5 8 - 3 x 2
Cách 1 : y = 3x5 (8 - 3x2)
= 3x5.8 – 3x5.3x2 = 24x5 – 9x7
⇒ y’ = (24x5 – 9x7)’
= (24x5)' – (9x7)’
= 24.5x4 – 9.7x6
= 120x4 – 63x6.
Cách 2 : Áp dụng công thức tính đạo hàm của tích :
⇒ y’ = [(3x5)’].(8 – 3x2) + 3x5.[(8 – 3x2)’]
= 3.5x4(8 – 3x2) + 3x5.[(8)’ – (3x2)’]
= 15x4(8 – 3x2) + 3x5.(0 – 3.2x)
= 15x4.8 – 15x4.3x2 + 3x5.(-6x)
= 120x4 – 45x6 – 18x6
= 120x4 – 63x6.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Thực hiện phép tính C
2
x
2
+
4
x
+
8
x
3
−
3
x
2
−
x
+
3
:...
Đọc tiếp
Thực hiện phép tính C = 2 x 2 + 4 x + 8 x 3 − 3 x 2 − x + 3 : x 3 − 8 ( x + 1 ) ( x − 3 )
A. C = ( x − 1 ) ( x − 2 ) 2
B. C = 1 ( x − 1 ) ( x − 2 )
C. C = − 2 ( x − 1 ) ( x − 2 )
D. C = 2 ( x − 1 ) ( x − 2 )