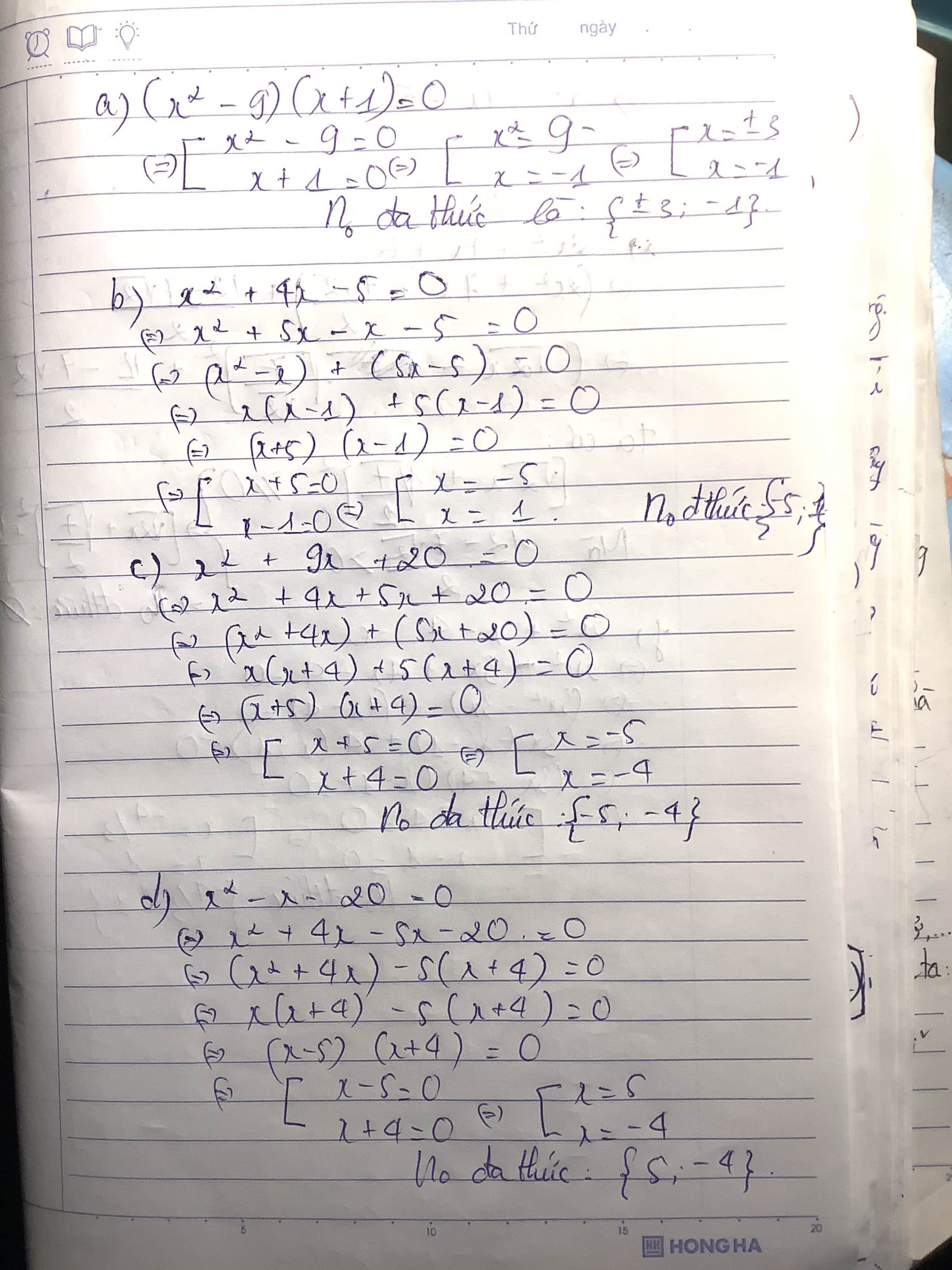Tìm nghiệm K(x) = x2 - 7x + 12

Những câu hỏi liên quan
giúp mình
1 ) giải và biện luận pt sau :
A (m-1)x2+7x-12=0
B x2−2(m−1)x−(2m+1)=0
2) tìm m để pt x2-2(m+1)x+m2-1=0 có 2 nghiệm phân biệt
\(1,\\ a,ĐK:m\ne1\\ \Delta=49+48\left(m-1\right)=48m+1\\ \text{PT vô nghiệm }\Leftrightarrow48m+1< 0\Leftrightarrow m< -\dfrac{1}{48}\\ \text{PT có nghiệm kép }\Leftrightarrow48m+1=0\Leftrightarrow m=-\dfrac{1}{48}\\ \text{PT có 2 nghiệm phân biệt }\Leftrightarrow48m+1>0\Leftrightarrow m>-\dfrac{1}{48};m\ne1\)
\(b,\Delta=4\left(m-1\right)^2+4\left(2m+1\right)=4m^2+8>0,\forall m\\ \text{Vậy PT có 2 nghiệm phân biệt với mọi m}\\ 2,\\ \text{PT có 2 nghiệm phân biệt }\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\Delta=4\left(m+1\right)^2-4\left(m^2-1\right)>0\\ \Leftrightarrow4m^2+8m+4-4m^2+4>0\\ \Leftrightarrow8m+8>0\\ \Leftrightarrow m>-1\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm nghiệm x của đa thức sau:
k(x) = \(x^2\)- 7x + 12
\(K\left(x\right)=x^2-7x+12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x-4x+12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-3\right)-4\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x-4\right)=0\)
Đến đây đơn giản rồi nhá
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cách 2: hơi dài nhưng là cách khác !
\(k\left(x\right)=x^2-7x+12\)
\(=\left(x-3,5\right)^2-0,25\)
\(=\left(x-3\right)\left(x-4\right)\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Dùng hệ thức Vi-et để tính nhẩm các nghiệm của phương trình.
a
)
x
2
−
7
x
+
12
0
b
)
x
2
+
7
x...
Đọc tiếp
Dùng hệ thức Vi-et để tính nhẩm các nghiệm của phương trình.
a ) x 2 − 7 x + 12 = 0 b ) x 2 + 7 x + 12 = 0
a) x 2 – 7 x + 12 = 0
Có a = 1; b = -7; c = 12
⇒ Δ = b 2 – 4 a c = ( - 7 ) 2 – 4 . 1 . 12 = 1 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt x 1 ; x 2 thỏa mãn:
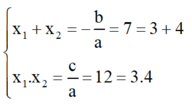
Vậy dễ dàng nhận thấy phương trình có hai nghiệm là 3 và 4.
b) x2 + 7x + 12 = 0
Có a = 1; b = 7; c = 12
⇒ Δ = b2 – 4ac = 72 – 4.1.12 = 1 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt x1; x2 thỏa mãn:
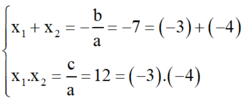
Vậy dễ dàng nhận thấy phương trình có hai nghiệm là -3 và -4.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Biết rằng x^3-7x+5=0 có nghiệm duy nhất x1,x2 .Gía trị của biểu thức x1x2 -(x1+x2) bằng :
A,-12
B,-2
C,2
D,12
Tìm nghiệm của đa thức f(x) = x2 - 7x + 6
\(f\left(x\right)=x2-7x+6\)
ta có f(x)=0
hay\(x2-7x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x2-7x=-6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(-5\right)=-6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{6}{5}\)
vậy nghiệm của đa thức f(x) là 6/5
\(f\left(x\right)=x^2-7x+6\)
\(f\left(x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x^2-7x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x-6x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x.\left(x-1\right)-6.\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right).\left(x-6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-1=0\\x-6=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow}\orbr{\begin{cases}z=1\\x=6\end{cases}}\)
Vậy phương trình có 2 nghiệm \(x=\left\{1,6\right\}\)
Để \(f\left(x\right)=x^2-7x+6\) có nghiệm
=> \(f\left(x\right)=x^2-7x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f\left(x\right)=\left(x-1\right)\left(x-6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-1=0\\x-6=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=6\end{cases}}}\)
vậy x=1;x=6
Xem thêm câu trả lời
1. Cho f(x)= x3 - 2x2 + 3x + 1; g(x)+ x3 + x - 1; h(x)= 2x2 -1
a) Tính f(x) - g(x) + h(x)
b) Tìm x sao cho f(x) - g(x) + h(x) = 0
2. Tìm nghiệm của
a) 5x + 3 (3x + 7) - 35
b) x2 + 8x - (x2 + 7x + 8) - 9
3. Tìm f(x) = x3 + 4x2 - 3x + 2; g(x) = x2 (x+4) + x - 5
Tìm x sao cho f(x) = g(x)
4. Tìm m sao cho k(x)= mx2 - 2x + 4 có nghiệm là -2
tìm nghiệm của các đa thức:
h(x)=x2+5x+6
g(x)=2x2+7x-9
Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử thôi bạn :
Ta có :
\(h\left(x\right)=x^2+5x+6\)
\(h\left(x\right)=x\left(x+2\right)+3\left(x+2\right)\)
\(h\left(x\right)=\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow N_oh\left(x\right)=-2;-3\)
\(g\left(x\right)=2x^2+7x-9\)
\(g\left(x\right)=2x^2+9x-2x-9\)
\(g\left(x\right)=2x\left(x-1\right)+9\left(x-1\right)\)
\(g\left(x\right)=\left(x-1\right)\left(2x+9\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow N_og\left(x\right)=1;-4,5\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Bài 2 Tìm nghiệm của các đa thức sau:
a) (x2 – 9)(x + l); b) x2 + 4x – 5;
c) x2+ 9x + 20; d) x2 – x – 20;
e) 2x2 +7x + 6; f) 3x2 + x – 4.
tìm nghiệm của đa thức f(x)= x^2+7x-8
Tìm nghiệm của đa thức k(x)= 5x^2+9x+4
a) \(f\left(x\right)=x^2+7x-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f\left(x\right)=x^2-x+8x-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f\left(x\right)=\left(x^2-x\right)+\left(8x-8\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f\left(x\right)=x\left(x-1\right)+8\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f\left(x\right)=\left(x-1\right)\left(x+8\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x-1=0\) hoặc \(x+8=0\)
Nếu \(x-1=0\Rightarrow x=1\)
Nếu \(x+8=0\Rightarrow x=-8\)
Vậy đa thức f(x) có nghiệm là 1 và -8
b) \(k\left(x\right)=5x^2+9x+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow k\left(x\right)=5x^2+5x+4x+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow k\left(x\right)=\left(5x^2+5x\right)+\left(4x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow k\left(x\right)=5x\left(x+1\right)+4\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow k\left(x\right)=\left(x+1\right)\left(5x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x+1=0\) hoặc \(5x+4=0\)
Nếu \(x+1=0\Rightarrow x=-1\)
Nếu \(5x+4=0\Rightarrow x=-\frac{4}{5}\)
Vậy đa thức k(x) có nghiệm là -1 và -4/5
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)