Giải phương trình sau: 1 + sin 2 x + cos 2 x 1 + cot 2 x = 2 sinx . sin 2 x
A. x = - π 4 + k2π
B. x = - π 4 + k π 2
C. x = π 2 + kπ; π 4 + k2π
D. x = π 2 + kπ
Giải các phương trình sau:
1. tan2x+3= (1+√2 sin x)(tan x+ √2 cos x)
2. (1- cos x. cos2x )/ sin2x - 1/ cos x= 4 sin2x - sin x-1
3. sin3x + 2 cos3x+ cos2x - 2sin2x - 2sinx-1=0
Giải phương trình
(2sinx + 1) (\(\sqrt{3}\sin x\) + \(2\cos^2x\) - 1) = Sin2x + cosx
làm giúp mình với huhu
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2\sin x+1\right)\left(\sqrt{3}\sin x+2\cos^2x-1\right)-\sin2x-\cos x=0\Leftrightarrow\left(2\sin x+1\right)\left(\sqrt{3}\sin x+2\cos^2x-1-2\cos^2x+1-\cos x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(2\sin x+1\right)\left(\sqrt{3}\sin x-\cos x\right)=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2\sin x+1=0\\\sqrt{3}\sin x-\cos x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Giải phương trình:
(sin^2(2x+pi)+cos2x)/(cotx)=1/2.sin2x
1) Giải phương trình : \(\sqrt{x^2+1}+\sqrt{x^2+2}=2\)
2) Rút gọn biểu thức
C= \(\sqrt{m-n-2\sqrt{m-n-1}}\)
\(B=\tan^2x.\left(2\cos^2x+\sin^2x-1\right)\)
Trong các phương trình sau: cos x = 5 - 3 (1); sin x = 1 - 2 (2); sin x + cos x = 2 (3), phương trình nào vô nghiệm?
A. (2)
B. (1)
C. (3)
D. (1) và (2)
Trong các phương trình sau: cos x = 5 - 3 (1); sin x = 1 - 2 (2); sin x + cos x = 2 (3), phương trình nào vô nghiệm?
A. (2).
B. (1).
C. (3).
D. (1) và (2).
Chọn C
Ta có: ![]() nên (1) và (2) có nghiệm.
nên (1) và (2) có nghiệm.
Cách 1:
Xét: ![]()
![]() nên (3) vô nghiệm.
nên (3) vô nghiệm.
Cách 2:
Điều kiện có nghiệm của phương trình: sin x + cos x = 2 là: 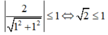
(vô lý) nên (3) vô nghiệm.
Cách 3:
Vì 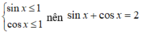
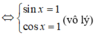
nên (3) vô nghiệm.
Giải phương trình sau: |x-2|(x-1)(x+1)(x+2)=4.
Nếu x lớn hơn hoặc bằng 2, có:
|x - 2|(x - 1)(x + 1)(x + 2) = 4
(x - 2)(x + 2)(x - 1)(x + 1) = 4
(x2 - 4)(x2 - 1) = 4
x4 - 4x2 + 4 = 4
(x2 - 2)2 = 4 => x2 - 2 = 2 => x2 = 4 => x = 2
Nếu x nhỏ hơn 2, có:
|x - 2|(x - 1)(x + 1)(x + 2) = 4
(2 - x)(2 + x)(x - 1)(x + 1) = 4
(4 - x2)(x2 - 1) = 4
5x2 - x4 - 4 = 4
x2 - (x4 - 4x2 + 4) = 4
x2 - 4 - (x2 - 2)2 = 0
(x - 2)(x + 2) - (x2 - 2)2 = 0
Giải các phương trình sau :
a) \(\cos^2x+2\sin x\cos x+5\sin^2x=2\)
b) \(3\cos^2x-2\sin2x+\sin^2x=1\)
c) \(4\cos^2x-3\sin x\cos x+3\sin^2x=1\)
Đưa về tích rồi giải các phương trình sau:
a) \(\sin 2x -2.\sin x +\cos x -1=0\)
b) \(\sqrt{2} . (\sin x - 2.\cos x) = 2-\sin 2x\)
c) \(\frac{1}{\cos x} - \frac{1}{\sin x}=2\sqrt 2 .\cos(x + \frac{\pi}{4}) \)
\(a,sin2x-2sinx+cosx-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2sinxcosx-2sinx+cosx-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2sinx\left(cosx-1\right)+cosx-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(cosx-1\right)\left(2sinx+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}cosx=1\\sinx=-\frac{1}{2}\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2k\pi\\x=\frac{-\pi}{6}+2k\pi\end{cases}}}\)
\(b,\sqrt{2}\left(sinx-2cosx\right)=2-sin2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2}sinx-2\sqrt{2}cosx-2+2sinxcosx=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2}sinx\left(1+\sqrt{2}cosx\right)-2.\left(\sqrt{2}cosx+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{2}cosx+1\right)\left(\sqrt{2}sinx-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}cosx=\frac{-\sqrt{2}}{2}\\sinx=\frac{2\sqrt{2}}{2}\left(l\right)\end{cases}}\)(vì \(-1\le sinx\le1\))
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{3\pi}{4}+2k\pi\\x=\frac{5\pi}{4}+2k\pi\end{cases}}\)
\(c,\frac{1}{cosx}-\frac{1}{sinx}=2\sqrt{2}cos\left(x+\frac{\pi}{4}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{sinx-cosx}{sinx.cosx}=2\sqrt{2}cos\left(x+\frac{\pi}{4}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{-\sqrt{2}cos\left(x+\frac{\pi}{4}\right)}{sinx.cosx}=2\sqrt{2}cos\left(x+\frac{\pi}{4}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin2x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin2x=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=\frac{3\pi}{2}+2k\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{3\pi}{4}+k\pi\)
@Bùi Nhật Vy, Bạn nhớ kĩ cái này nha
\(asinx+bcosx=\sqrt{a^2+b^2}sin\left(x+\alpha\right)=-\sqrt{a^2+b^2}cos\left(x-\alpha\right)\)
trong đó \(\cos\alpha=\frac{a}{\sqrt{a^2+b^2}},sin\alpha=\frac{b}{\sqrt{a^2+b^2}}\)
giải các phương trình sau :
1. sin( x+\(\pi\)/4)=2/3
2.cos2x-5sinx-3=0
3.cos3x=sin2x
4.cos3x=-\(\sqrt{ }\)3 với -\(\pi\)/2<x<0
5.4sin\(^4\)x + 12cos\(^2\)x=7
6.cot(x-1)=(cos2x)/(1+tanx) + sin\(^2\)x - 1/2sin2x
7.sin\(^2\)3x-cos\(^2\)4x=sin\(^2\)5x-cos\(^2\)6x